一、首先说一下分支限界法的思想:
(1)比较:分支限界法和回朔法有相似之处,但是回朔法是搜索问题的所有解,采用深度优先搜索;而分支限界法是搜索问题的最优解,采用的是广度优先搜索;
(2)核心思想:分支限界法中,每一个活节点都只有一次机会成为扩展节点。活节点一旦成为扩展节点,就一次性产生所有的儿子节点。在这些儿子节点中,导致不可行解或者导致非最优解的儿子节点被舍弃,其余儿子节点被加入活节点表中。此后,从活节点表中取下一节点成为当前扩展节点,并重复上述节点的扩展过程。这个过程一直在持续到找到所需要的最优解或者活节点表为空时为止;其中:选择扩展节点的方式可以分为:队列式分支限界法 和 优先队列式分支限界法。后者相对于前者的改进是对活节点加入了优先级,优先级最高的成为扩展节点(通常通过最大堆最小堆实现);
二、布线问题描述:
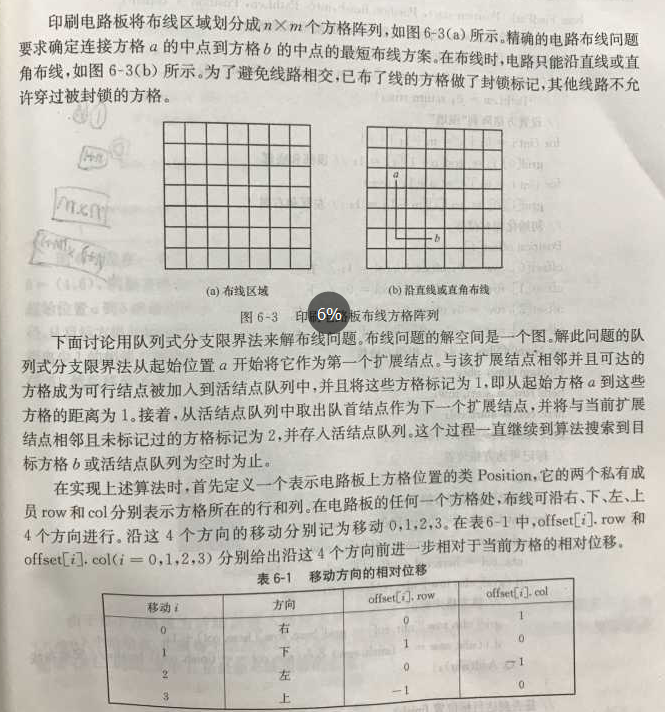

代码如下:
//队列类 : LinkedQueue.h
#ifndef LINKEDQUEUE_H
#define LINKEDQUEUE_H
template <class Type>
class LinkedQueue{
public:
LinkedQueue(){};
explicit LinkedQueue(int Capacity); //创建队列
bool IsEmpty(); //判断是否空
bool IsFull(); //判断是否满
bool Add(Type &cell); //向队列中加入元素
bool Delete(Type &cell); //删除队列中的元素
~LinkedQueue();
private:
Type cell;
Type *ptr; //队列中的元素指针
int QueueLen; //队列元素个数
int QueueCapacity; //队列容量
int Head;
int Tail;
};
template <class Type>
LinkedQueue<Type>::~LinkedQueue()
{
delete[]ptr;
ptr = nullptr;
}
template <class Type>
LinkedQueue<Type>::LinkedQueue(int Capacity)
{
QueueCapacity = Capacity;
Head = 0;
Tail = 0;
QueueLen = 0;
ptr = new Type[QueueCapacity];
}
template <class Type>
bool LinkedQueue<Type>::IsEmpty()
{
if (QueueLen == 0)
return true;
else
return false;
}
template <class Type>
bool LinkedQueue<Type>::IsFull()
{
if (QueueLen == QueueCapacity)
return true;
else
return false;
}
template <class Type>
bool LinkedQueue<Type>::Add(Type &cell)
{
if (IsFull())
return false;
else
{
ptr[Tail] = cell;
Tail++;
QueueLen++;
return true;
}
}
template <class Type>
bool LinkedQueue<Type>::Delete(Type &cell)
{
if (IsEmpty())
return false;
else
{
cell = ptr[Head];
Head++;
QueueLen--;
return true;
}
}
#endif
//使用分支限界法解决布线问题main.cpp
//====================================================
#include <iostream>
#include "LinkedQueue.h"
//#include <queue>
using namespace std;
int n, m; //布线盘是n * m大小
class Position{
public:
int row;
int col;
};
bool FindPath(int ** grid , Position start, Position finish, int &PathLen, Position * &path)
{
//计算从起始位置start到目标位置finish的最短布线路径
//找到最短布线路径则返回true,否则返回flase
if ((start.row == finish.row) && (start.col == finish.col))
{
PathLen = 0;
return true;
}
//设置方格阵列“围墙”
for (int i = 0; i < m + 1; i++)
{
grid[0][i] = grid[n + 1][i] = 1; //顶部和底部
}
for (int i = 0; i < n + 1; i++)
{
grid[i][0] = grid[i][m + 1] = 1; //左翼和右翼
}
//初始化相对位移
Position offset[4];
offset[0].row = 0; offset[0].col = 1; //右
offset[1].row = 1; offset[1].col = 0; //下
offset[2].row = 0; offset[2].col = -1; //左
offset[3].row = -1; offset[3].col = 0; //上
int neigh_num = 4; //相邻方格数
Position here, nbr;
here.row = start.row;
here.col = start.col;
grid[start.row][start.col] = 2;
//标记所有可以到达的方格位置
LinkedQueue<Position> Q(n * m + 1); //队列
//queue<Position> Q(); //队列
//标记可到达的相邻方格
do {
for (int i = 0; i < neigh_num; i++)
{
nbr.row = here.row + offset[i].row;
nbr.col = here.col + offset[i].col;
if (grid[nbr.row][nbr.col] == 0) //该方格未被锁定
{
grid[nbr.row][nbr.col] = grid[here.row][here.col] + 1;
if ((nbr.row == finish.row) && (nbr.col == finish.col)) //完成布线
break;
Q.Add(nbr); //压入队列称为活节点
}
}
//是否到达目标位置finish?
if ((nbr.row == finish.row) && (nbr.col == finish.col)) //完成布线,是否要加这一步?
break;
//活节点队列是否非空
if (Q.IsEmpty()) //无解
return false;
Q.Delete(here); //取下一个扩展节点
} while (true);
//构造最短布线路径
PathLen = grid[finish.row][finish.col] - 2;
path = new Position[PathLen];
//从目标位置finish开始向起始位置回溯
here = finish;
for (int j = PathLen - 1; j >= 0; j--)
{
path[j] = here;
//找前驱位置
for (int i = 0; i < neigh_num; i++)
{
nbr.row = here.row + offset[i].row;
nbr.col = here.col + offset[i].col;
if (grid[nbr.row][nbr.col] == j + 2)
break;
}
here = nbr; //向前移动
}
return true;
}
int main(void)
{
Position start, finish; //开始位置和目标位置
int PathLen; //最短路径的长度
Position *path; //记录的最短路径
cout << "请输入布线盘的大小,n * m 规格: " << endl;
cin >> n >> m;
cout << "请输入开始位置(x , y) :" << endl;
cin >> start.col >> start.row;
cout << "请输入结束位置(x , y) :" << endl;
cin >> finish.col >> finish.row;
int ** grid = new int*[n + 2];
for (int i = 0; i < n + 2; i++)
{
grid[i] = new int[m + 2];
}
for (int i = 0; i < n + 2; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < m + 2; j++)
{
grid[i][j] = 0;
}
}
FindPath(grid, start, finish, PathLen, path);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
{
cout << grid[i][j] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
cout << "最短路径是: " << endl;
cout << PathLen << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
效果图类似:
