实现mypwd
首先获取当前目录的i节点编号,切换到其的父目录,在里面寻找当前i节点编号对应的文件名即可。这样我们就很容易联想到使用递归来实现,终止条件是此判断是否发到达了根目录。
pwd以绝对路径打印当前的工作目录。因为整个系统的文件组织是树形的,可以从当前目录逐层向根目录进行查找,当找到根目录,即可得到完全路径。
pwd 代表的是打印当前目录Print Working Directory,它会打印出以根目录为起点的完整目录名即为绝对目录。这条命令是一条shell内建命令,并且在大多数shell中都可以使用,如bash 、 Bourne shell , ksh ,zsh等。
** pwd 通常不带选项运行,且没有任何参数**
代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <dirent.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define MAX_DIR_DEPTH (256) //限制最大的目录深度
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
ino_t get_ino_byname(char *filename)
{
struct stat file_stat;
if(0 != stat(filename, &file_stat)) //stat()
{
perror("stat");
exit(-1);
}
return file_stat.st_ino;
}
char *find_name_byino(ino_t ino)
{
DIR *dp = NULL;
struct dirent *dptr = NULL;
char *filename = NULL;
if(NULL == (dp = opendir("."))) //opendir()
{
fprintf(stderr, "Can not open Current Directory
");
exit(-1);
}
else
{
while(NULL != (dptr = readdir(dp))) //readdir()
{
if(dptr->d_ino == ino)
{
filename = strdup(dptr->d_name); //strdup()
break;
}
}
closedir(dp);
}
return filename;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
char *dir_stack[MAX_DIR_DEPTH];
unsigned current_depth = 0;
while(TRUE)
{
ino_t current_ino = get_ino_byname(".");
ino_t parent_ino = get_ino_byname("..");
if(current_ino == parent_ino)
break;
chdir("..");
dir_stack[current_depth++] = find_name_byino(current_ino);
if(current_depth >= MAX_DIR_DEPTH)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Directory tree is too deep.
");
exit(-1);
}
}
int i = current_depth - 1;
for(i = current_depth - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
fprintf(stdout, "/%s", dir_stack[i]);
}
fprintf(stdout, "%s
", current_depth == 0 ? "/" : "");
return 0;
}
dirent结构体:
struct dirent
{
long d_ino; //inode number
off_t d_off; //offset to this dirent
unsigned short d_reclen;// length of this d_name
unsigned char d_type; //the type of d_name
char d_name [NAME_MAX+1]; //file name (null-terminated)
};
DIR结构体:
struct __dirstream
{
void *__fd; // `struct hurd_fd' pointer for descriptor.
char *__data; // Directory block.
int __entry_data; // Entry number `__data' corresponds to.
char *__ptr; // Current pointer into the block.
int __entry_ptr; // Entry number `__ptr' corresponds to.
size_t __allocation;// Space allocated for the block.
size_t __size; // Total valid data in the block.
__libc_lock_define (, __lock) // Mutex lock for this structure.
};
typedef struct __dirstream DIR;
结构体stat:
struct stat {
dev_t st_dev; //文件的设备编号
ino_t st_ino; //节点
mode_t st_mode; //文件的类型和存取的权限
nlink_t st_nlink; //连到该文件的硬连接数目,刚建立的文件值为1
uid_t st_uid; //用户ID
gid_t st_gid; //组ID
dev_t st_rdev; //(设备类型)若此文件为设备文件,则为其设备编号
off_t st_size; //文件字节数(文件大小)
unsigned long st_blksize; //块大小(文件系统的I/O 缓冲区大小)
unsigned long st_blocks; //块数
time_t st_atime; //最后一次访问时间
time_t st_mtime; //最后一次修改时间
time_t st_ctime; //最后一次改变时间(指属性)
};
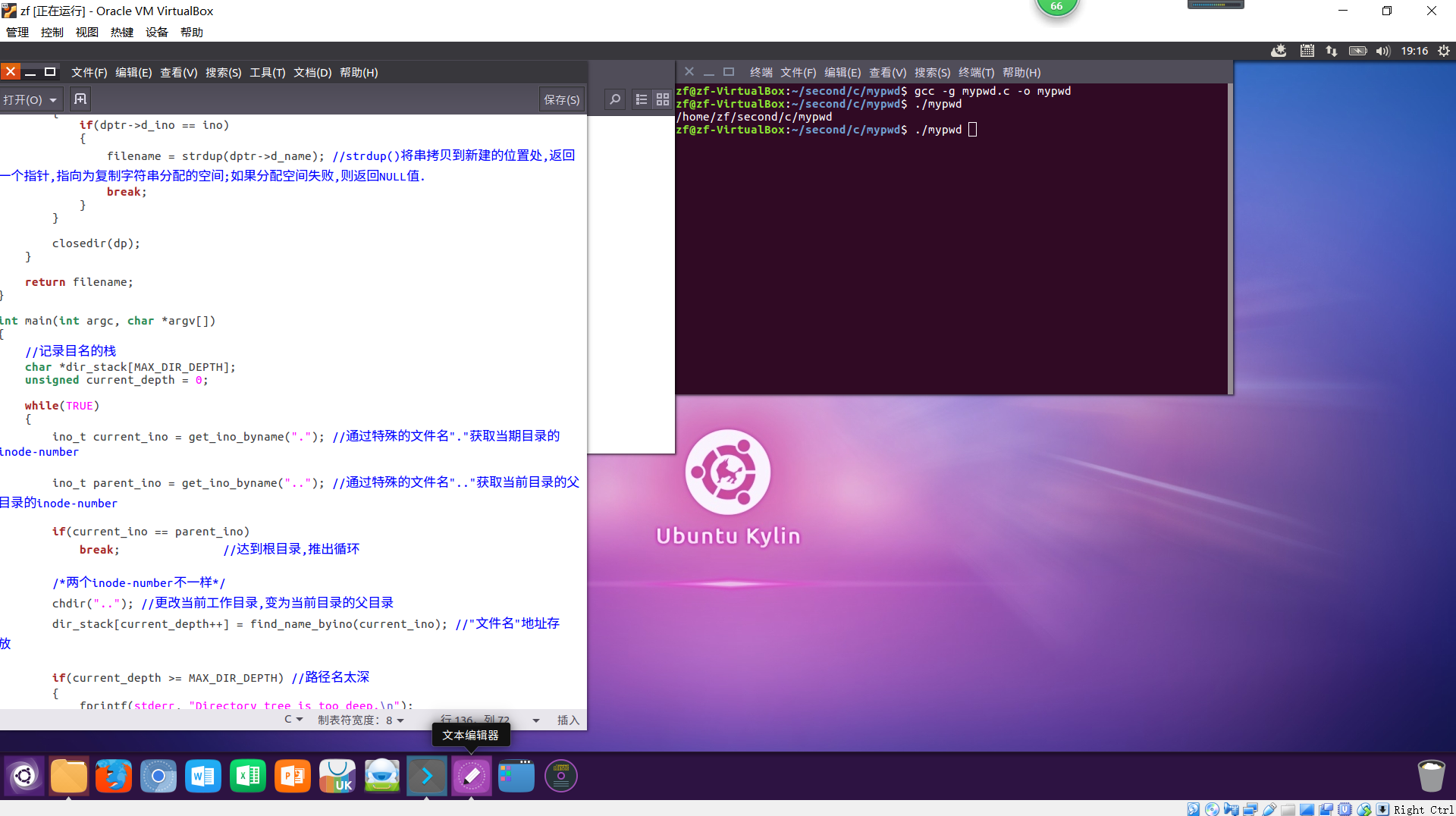
实现截图