A. Diagonal Walking
Mikhail walks on a 2D plane. He can go either up or right. You are given a sequence of Mikhail's moves. He thinks that this sequence is too long and he wants to make it as short as possible.
In the given sequence moving up is described by character U and moving right is described by character R. Mikhail can replace any pair of consecutive moves RU or UR with a diagonal move (described as character D). After that, he can go on and do some other replacements, until there is no pair of consecutive moves RU or UR left.
Your problem is to print the minimum possible length of the sequence of moves after the replacements.
The first line of the input contains one integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 100) — the length of the sequence. The second line contains the sequence consisting of n characters U and R.
Print the minimum possible length of the sequence of moves after all replacements are done.
5
RUURU
3
17
UUURRRRRUUURURUUU
13
In the first test the shortened sequence of moves may be DUD (its length is 3).
In the second test the shortened sequence of moves can be UUDRRRDUDDUUU (its length is 13).
题解:以R为点优先消去左边的U。
1 #pragma warning(disable:4996) 2 #include<map> 3 #include<queue> 4 #include<string> 5 #include<cstdio> 6 #include<bitset> 7 #include<cstring> 8 #include<iostream> 9 #include<algorithm> 10 using namespace std; 11 typedef long long ll; 12 13 const int INF = 1e9 + 7; 14 const int maxn = 1005; 15 16 int main() 17 { 18 int n; 19 string s; 20 while (cin >> n >> s) { 21 int t = 0; 22 bool use[105]; 23 memset(use, 0, sizeof(use)); 24 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { 25 if (s[i] == 'R') { 26 if (i == 0) { 27 if (s[i + 1] == 'U') { use[i + 1] = 1; t++; } 28 continue; 29 } 30 if (s[i - 1] == 'U' && !use[i - 1]) { use[i - 1] = 1; t++; } 31 else if (s[i + 1] == 'U' && !use[i + 1]) { use[i + 1] = 1; t++; } 32 } 33 } 34 cout << n - t << endl; 35 } 36 return 0; 37 }
B. String Typing
You are given a string s consisting of n lowercase Latin letters. You have to type this string using your keyboard.
Initially, you have an empty string. Until you type the whole string, you may perform the following operation:
- add a character to the end of the string.
Besides, at most once you may perform one additional operation: copy the string and append it to itself.
For example, if you have to type string abcabca, you can type it in 7 operations if you type all the characters one by one. However, you can type it in 5 operations if you type the string abc first and then copy it and type the last character.
If you have to type string aaaaaaaaa, the best option is to type 4 characters one by one, then copy the string, and then type the remaining character.
Print the minimum number of operations you need to type the given string.
The first line of the input containing only one integer number n (1 ≤ n ≤ 100) — the length of the string you have to type. The second line containing the string s consisting of n lowercase Latin letters.
Print one integer number — the minimum number of operations you need to type the given string.
7
abcabca
5
8
abcdefgh
8
The first test described in the problem statement.
In the second test you can only type all the characters one by one
题解:读懂题意,copy操作只能用一次,且是复制前面的所有字符。脑部了n重题意,花了一个多小时。
1 #pragma warning(disable:4996) 2 #include<map> 3 #include<queue> 4 #include<string> 5 #include<cstdio> 6 #include<bitset> 7 #include<cstring> 8 #include<iostream> 9 #include<algorithm> 10 using namespace std; 11 typedef long long ll; 12 13 const int INF = 1e9 + 7; 14 const int maxn = 1005; 15 16 string s; 17 int n; 18 19 int Find(int x) { 20 string a; 21 for (int i = 0; i < x; i++) a += s[i]; 22 23 24 bool flag = true; 25 int t = 0; 26 for (int i = x; i < n; i++) { 27 if (s[i] != a[t++]) flag = false; 28 if (t == a.size() || !flag) break; 29 } 30 31 if (t != a.size() || !flag) return 0; 32 else return x; 33 } 34 35 int main() 36 { 37 while (cin >> n >> s) { 38 int ans = 0; 39 for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) ans = max(ans, Find(i)); 40 if (!ans) cout << n << endl; 41 else cout << n - ans + 1 << endl; 42 } 43 return 0; 44 }
C. Matrix Walk
There is a matrix A of size x × y filled with integers. For every 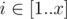 ,
, 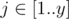 Ai, j = y(i - 1) + j. Obviously, every integer from [1..xy] occurs exactly once in this matrix.
Ai, j = y(i - 1) + j. Obviously, every integer from [1..xy] occurs exactly once in this matrix.
You have traversed some path in this matrix. Your path can be described as a sequence of visited cells a1, a2, ..., an denoting that you started in the cell containing the number a1, then moved to the cell with the number a2, and so on.
From the cell located in i-th line and j-th column (we denote this cell as (i, j)) you can move into one of the following cells:
- (i + 1, j) — only if i < x;
- (i, j + 1) — only if j < y;
- (i - 1, j) — only if i > 1;
- (i, j - 1) — only if j > 1.
Notice that making a move requires you to go to an adjacent cell. It is not allowed to stay in the same cell. You don't know x and y exactly, but you have to find any possible values for these numbers such that you could start in the cell containing the integer a1, then move to the cell containing a2 (in one step), then move to the cell containing a3 (also in one step) and so on. Can you choose x and y so that they don't contradict with your sequence of moves?
The first line contains one integer number n (1 ≤ n ≤ 200000) — the number of cells you visited on your path (if some cell is visited twice, then it's listed twice).
The second line contains n integers a1, a2, ..., an (1 ≤ ai ≤ 109) — the integers in the cells on your path.
If all possible values of x and y such that 1 ≤ x, y ≤ 109 contradict with the information about your path, print NO.
Otherwise, print YES in the first line, and in the second line print the values x and y such that your path was possible with such number of lines and columns in the matrix. Remember that they must be positive integers not exceeding 109.
8
1 2 3 6 9 8 5 2
Note
The matrix and the path on it in the first test looks like this:
3 3
6
1 2 1 2 5 3
NO
1 #pragma warning(disable:4996) 2 #include<map> 3 #include<queue> 4 #include<string> 5 #include<cstdio> 6 #include<bitset> 7 #include<cstring> 8 #include<iostream> 9 #include<algorithm> 10 using namespace std; 11 typedef long long ll; 12 13 const int INF = 1e4 + 7; 14 const int maxn = 200005; 15 16 int n; 17 int a[maxn]; 18 19 int main() 20 { 21 while (cin >> n) { 22 int y = -1, mam = 0; 23 for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { 24 cin >> a[i]; mam = max(mam, a[i]); 25 } 26 /*判断否只在一行上移动*/ 27 bool flag = true; 28 for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) { 29 int k = abs(a[i] - a[i - 1]); 30 if (k == 1) continue; 31 if (k == 0) { flag = false; break; } 32 y = k; 33 } 34 if (flag && y == -1) { printf("YES %d %d ", maxn, mam); continue; } 35 /*判断是否有多个y值*/ 36 for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) { 37 int k = abs(a[i] - a[i - 1]); 38 if (k != 1 && k != y) { flag = false; break; } 39 } 40 /*判断越界*/ 41 for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) { 42 if (a[i] % y == 1) { 43 if (a[i + 1] - a[i] != 1 && a[i + 1] - a[i] != y && a[i] - a[i + 1] != y) { 44 flag = false; 45 break; 46 } 47 } 48 if (a[i] % y == 0) { 49 if (a[i] - a[i + 1] != 1 && a[i + 1] - a[i] != y && a[i] - a[i + 1] != y) { 50 flag = false; 51 break; 52 } 53 } 54 } 55 56 if (!flag) printf("NO "); 57 else printf("YES %d %d ", mam, y); 58 } 59 return 0; 60 }
D. Fight Against Traffic
Little town Nsk consists of n junctions connected by m bidirectional roads. Each road connects two distinct junctions and no two roads connect the same pair of junctions. It is possible to get from any junction to any other junction by these roads. The distance between two junctions is equal to the minimum possible number of roads on a path between them.
In order to improve the transportation system, the city council asks mayor to build one new road. The problem is that the mayor has just bought a wonderful new car and he really enjoys a ride from his home, located near junction s to work located near junction t. Thus, he wants to build a new road in such a way that the distance between these two junctions won't decrease.
You are assigned a task to compute the number of pairs of junctions that are not connected by the road, such that if the new road between these two junctions is built the distance between s and t won't decrease.
The firt line of the input contains integers n, m, s and t (2 ≤ n ≤ 1000, 1 ≤ m ≤ 1000, 1 ≤ s, t ≤ n, s ≠ t) — the number of junctions and the number of roads in Nsk, as well as the indices of junctions where mayors home and work are located respectively. The i-th of the following m lines contains two integers ui and vi (1 ≤ ui, vi ≤ n, ui ≠ vi), meaning that this road connects junctions ui and vi directly. It is guaranteed that there is a path between any two junctions and no two roads connect the same pair of junctions.
Print one integer — the number of pairs of junctions not connected by a direct road, such that building a road between these two junctions won't decrease the distance between junctions s and t.
5 4 1 5
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
0
5 4 3 5
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5
5 6 1 5
1 2
1 3
1 4
4 5
3 5
2 5
1 #pragma warning(disable:4996) 2 #include<map> 3 #include<queue> 4 #include<string> 5 #include<cstdio> 6 #include<bitset> 7 #include<cstring> 8 #include<iostream> 9 #include<algorithm> 10 using namespace std; 11 typedef long long ll; 12 13 const int INF = 1e9 + 7; 14 const int maxm = 1005; 15 16 struct node { 17 int to, next, va; 18 }e[4*maxm]; 19 20 int n, m, s, t, tot; 21 int head[maxm], d[maxm], use[maxm], mmp[maxm][maxm]; 22 23 void Inite() { 24 tot = 0; 25 memset(mmp, 0, sizeof(mmp)); 26 memset(head, -1, sizeof(head)); 27 } 28 29 void addedge(int u, int v) { 30 e[tot].to = v; 31 e[tot].va = 1; 32 e[tot].next = head[u]; 33 head[u] = tot++; 34 } 35 36 void DJS(int sta) { 37 memset(use, 0, sizeof(use)); 38 for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) d[i] = INF; 39 40 d[sta] = 0; 41 while (true) { 42 int v = -1; 43 for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) if (!use[i] && (v == -1 || d[i] < d[v])) v = i; 44 if (v == -1) break; 45 use[v] = 1; 46 for (int i = head[v]; i != -1; i = e[i].next) { 47 int u = e[i].to; 48 d[u] = min(d[u], d[v] + e[i].va); 49 } 50 } 51 } 52 53 int main() 54 { 55 while (scanf("%d%d%d%d", &n, &m, &s, &t) != EOF) { 56 Inite(); 57 for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) { 58 int u, v; 59 scanf("%d%d", &u, &v); 60 addedge(u, v); 61 addedge(v, u); 62 mmp[u][v] = 1; 63 mmp[v][u] = 1; 64 } 65 int a[maxm], b[maxm]; 66 67 DJS(s); 68 for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) a[i] = d[i]; 69 70 DJS(t); 71 for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) b[i] = d[i]; 72 73 74 int cnt = 0; 75 for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { 76 for (int j = i + 1; j <= n; j++) { 77 if (!mmp[i][j] && a[i] + 1 + b[j] >= a[t] && a[j] + 1 + b[i] >= a[t]) cnt++; 78 } 79 } 80 printf("%d ", cnt); 81 } 82 return 0; 83 }
E. Water Taps
Consider a system of n water taps all pouring water into the same container. The i-th water tap can be set to deliver any amount of water from 0 to ai ml per second (this amount may be a real number). The water delivered by i-th tap has temperature ti.
If for every 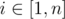 you set i-th tap to deliver exactly xi ml of water per second, then the resulting temperature of water will be
you set i-th tap to deliver exactly xi ml of water per second, then the resulting temperature of water will be 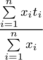 (if
(if 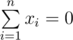 , then to avoid division by zero we state that the resulting water temperature is 0).
, then to avoid division by zero we state that the resulting water temperature is 0).
You have to set all the water taps in such a way that the resulting temperature is exactly T. What is the maximum amount of water you may get per second if its temperature has to be T?
The first line contains two integers n and T (1 ≤ n ≤ 200000, 1 ≤ T ≤ 106) — the number of water taps and the desired temperature of water, respectively.
The second line contains n integers a1, a2, ..., an (1 ≤ ai ≤ 106) where ai is the maximum amount of water i-th tap can deliver per second.
The third line contains n integers t1, t2, ..., tn (1 ≤ ti ≤ 106) — the temperature of water each tap delivers.
Print the maximum possible amount of water with temperature exactly T you can get per second (if it is impossible to obtain water with such temperature, then the answer is considered to be 0).
Your answer is considered correct if its absolute or relative error doesn't exceed 10 - 6.
题解:竟然是贪心。对式子化简得:
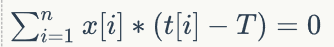
记所有正项的和为sum1,所有负项的和为sum2(代入的是 a[i])。sum1+sum2=0;如果sum1>sum2,说明负的可以全部加上,然后排序。sum1<sum2同理。
感受:少乘了个1LL,wa到怀疑人生,贪心体现在相同的项,t[i]越小x[i]越大,所以会用上排序。

1 #pragma warning(disable:4996) 2 #include<cstdio> 3 #include<cstring> 4 #include<iostream> 5 #include<algorithm> 6 using namespace std; 7 typedef long long ll; 8 9 const int maxn = 2e5 + 5; 10 11 struct node { int a, t; } p[maxn], q[maxn]; 12 13 bool cmp1(node a, node b) { return a.t < b.t; } 14 bool cmp2(node a, node b) { return a.t > b.t; } 15 16 int n, T; 17 int a[maxn], t[maxn]; 18 19 int main() 20 { 21 while (scanf("%d%d", &n, &T) != EOF) { 22 23 int cnt1 = 0, cnt2 = 0; 24 double sum1 = 0, sum2 = 0; 25 ll tot1 = 0, tot2 = 0; 26 double ans = 0; 27 28 for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) scanf("%d", a + i); 29 for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) scanf("%d", t + i); 30 31 for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { 32 if (t[i] >= T) { 33 tot1 += a[i]; 34 sum1 += 1LL*(t[i] - T)*a[i]; 35 p[cnt1].a = a[i]; 36 p[cnt1].t = t[i]; 37 cnt1++; 38 } 39 else { 40 tot2 += a[i]; 41 sum2 += 1LL*(T - t[i])*a[i]; 42 q[cnt2].a = a[i]; 43 q[cnt2].t = t[i]; 44 cnt2++; 45 } 46 } 47 48 sort(p, p + cnt1, cmp1); 49 sort(q, q + cnt2, cmp2); 50 51 if (sum1 >= sum2) { 52 ans = tot2; 53 double temp = 0; 54 for (int i = 0; i < cnt1; i++) { 55 double k = 1.0*p[i].a*(p[i].t - T); 56 if (temp + k <= sum2) { 57 temp += k; 58 ans += p[i].a; 59 } 60 else { 61 ans += (sum2 - temp) / (p[i].t - T); 62 break; 63 } 64 } 65 printf("%.8lf ", ans); 66 } 67 else { 68 ans = tot1; 69 double temp = 0; 70 for (int i = 0; i < cnt2; i++) { 71 double k = 1.0*q[i].a*(T - q[i].t); 72 if (temp + k <= sum1) { 73 temp += k; 74 ans += q[i].a; 75 } 76 else { 77 ans += (sum1 - temp) / (T - q[i].t); 78 break; 79 } 80 } 81 printf("%.8lf ", ans); 82 } 83 84 } 85 return 0; 86 }
F. Runner's Problem
You are running through a rectangular field. This field can be represented as a matrix with 3 rows and m columns. (i, j) denotes a cell belonging to i-th row and j-th column.
You start in (2, 1) and have to end your path in (2, m). From the cell (i, j) you may advance to:
- (i - 1, j + 1) — only if i > 1,
- (i, j + 1), or
- (i + 1, j + 1) — only if i < 3.
However, there are n obstacles blocking your path. k-th obstacle is denoted by three integers ak, lk and rk, and it forbids entering any cell (ak, j) such that lk ≤ j ≤ rk.
You have to calculate the number of different paths from (2, 1) to (2, m), and print it modulo 109 + 7.
感受:c++没学好啊。。。看大神的代码都很费力,还好明白了坐标离散和矩阵的快速幂,总算学到了一些知识和技巧。照着网上巨佬的代码手抄了一份。

1 #include<bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 typedef long long ll; 4 5 template <class T> 6 struct matrix { 7 vector< vector<T> > a; 8 int n, m; 9 matrix(int n = 1, int m = 1) :n(n), m(m) { 10 assert(n > 0 && m > 0); 11 a = vector< vector<T> >(n); 12 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) a[i] = vector<T>(m); 13 } 14 matrix& operator << (const string& s) { 15 stringstream ss(s); 16 T x; 17 for (int i = 0; i < n*m && ss >> x; i++) a[i / m][i%m] = x; 18 } 19 T& operator()(int x, int y) { return a[x][y]; } 20 matrix modmul(matrix &b, T mod)const { 21 assert(m == b.n); 22 matrix<T> res(n, b.m); 23 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { 24 for (int j = 0; j < b.m; j++) { 25 for (int k = 0; k < m; k++) { 26 T tmp = a[i][k] * b.a[k][j] % mod; 27 res.a[i][j] = (res.a[i][j] + tmp) % mod; 28 } 29 } 30 } 31 return res; 32 } 33 matrix modpow(T e, T mod)const { 34 assert(n == m); 35 matrix<T> a = *this, res(n, n); 36 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) res.a[i][i] = 1; 37 for (; e > 0; e >>= 1) { 38 if (e & 1) res = res.modmul(a, mod); 39 a = a.modmul(a, mod); 40 } 41 return res; 42 } 43 inline void set(int r, int c, string s, T x = 0) { 44 assert(!(r < 0 && c < 0) && !(r >= 0 && c >= 0)); 45 stringstream ss(s); 46 for (int i = 0; ((c < 0 && i < m) || (c >= 0 && i < n)) && ss >> x; i++) c < 0 ? a[r][i] = x : a[i][c] = x; 47 } 48 }; 49 50 const int maxn = 1e4 + 4; 51 const int mod = 1e9 + 7; 52 53 typedef matrix<ll> mat; 54 55 map<ll, int> mp; 56 57 int n, nn; 58 int a[maxn], s[4][4 * maxn]; 59 ll m, b[4*maxn], l[maxn], r[maxn]; 60 61 int main() 62 { 63 cin >> n >> m; 64 for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { 65 cin >> a[i] >> l[i] >> r[i]; 66 b[i] = l[i] - 1; 67 b[n + i] = l[i]; 68 b[2 * n + i] = r[i]; 69 b[3 * n + i] = r[i] + 1; 70 } 71 72 b[4 * n + 1] = 1; 73 b[4 * n + 2] = m; 74 75 sort(b + 1, b + 4 * n + 3); 76 nn = unique(b + 1, b + 4 * n + 3) - b - 1; 77 78 for (int i = 1; i <= nn; i++) mp[b[i]] = i; 79 for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { 80 int id = a[i]; 81 int lb = mp[l[i]]; 82 int rb = mp[r[i]]; 83 s[id][lb]++; 84 s[id][rb + 1]--; 85 } 86 for (int i = 1; i <= 3; i++) { 87 for (int j = 1; j <= nn; j++) s[i][j] += s[i][j - 1]; 88 } 89 90 mat A(3, 3), ans(3, 1); 91 A << "1 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 1"; 92 ans << "0 1 0"; 93 for (int i = 2; i <= nn; i++) { 94 mat B = A; 95 for (int j = 1; j <= 3; j++) { 96 if (s[j][i] > 0) B.set(j - 1, -1, "0 0 0"); 97 if (s[j][i - 1] > 0) B.set(-1, j - 1, "0 0 0"); 98 } 99 ans = B.modpow(b[i] - b[i - 1], mod).modmul(ans, mod); 100 } 101 cout << ans(1, 0) << endl; 102 103 return 0; 104 }
