Actuator其实是监控Spring Boot应用的一些信息,如依赖关系,路径处理器关系,线程信息,JVM信息等,但是这些信息都是以json格式返回,没有可视化的页面,需要自己去搜索想要了解的详细信息。
而这些信息可以通过三种方式获取:
1.Actuator端点方式,Rest请求获取(使用spring-boot-starter-actuator自启动,如果不是web工程,还需要加spring-webmvc的依赖)
2.远程shell,使用命令查看(使用spring-boot-starter-remote-shell自启动,监听端口为2000,用户名默认为user,密码会在启动日志可以查看到)
3.JMX方式
Actuator端点信息:
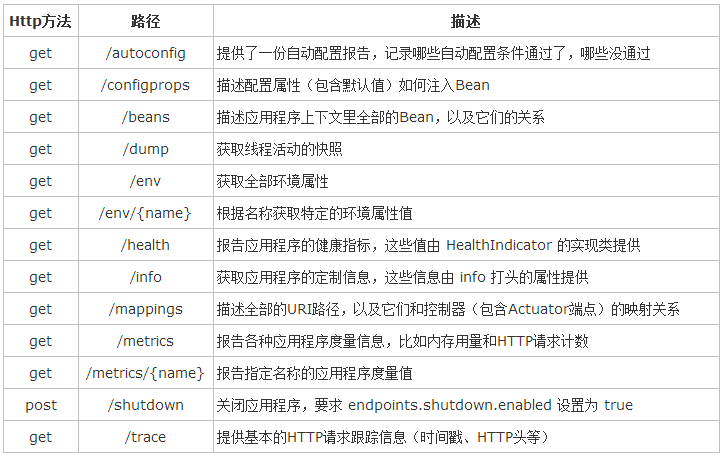
在使用Actuator端点查看信息时,有如下敏感信息会被隐藏,查看不了(页面出现错误信息的情况)

解决的方法是在application.properties加入如下配置:
management.security.enabled=false
如果我们需要对Actuator进行个性化设置,可在以下几方面进行定制:
1.端点重命名(避免请求路径冲突或者避免默认请求暴露,例如在application.properties中加上配置:endpoint.beans.id=beanlist)
2.端点禁用与启用(例如在application.properties中加上配置:endpoint.beans.enabled=false)
3.自定义度量信息,针对于metrics端点信息
3.1如果是统计的话,可使用CounterService接口跟GaugeService接口,无需实现,spring已经帮我们实现了,只要引用就好
@Controller @RequestMapping("/myworld") public class MyController { @Resource private CounterService counterService; @Resource private GaugeService gaugeService; @ResponseBody @RequestMapping("hello") public String hello(){ // 在metrics端点增加hello request属性(访问计数) counterService.increment("hello.request"); // 属性时间更新 gaugeService.submit( "hello.request.saved", System.currentTimeMillis()); return "hello"; } }
3.2如果需要自定义的一些信息,可实现PublicMetrics接口
@Component public class ApplicationContextMetrics implements PublicMetrics { @Resource private ApplicationContext context; @Override public Collection<Metric<?>> metrics() { List<Metric<?>> metrics = new ArrayList<Metric<?>>(); // 启动时间 metrics.add(new Metric<Long>("spring.context.startup-date", context.getStartupDate())); // bean的总数量 metrics.add(new Metric<Integer>("spring.beans", context.getBeanNamesForType(Object.class).length)); // Controller的数量 metrics.add(new Metric<Integer>("spring.controllers", context.getBeanNamesForAnnotation(Controller.class).length)); return metrics; } }
4.自定义跟踪数据的仓库(主要针对trace端点,默认保留100条跟踪信息,新来的会覆盖旧有的,我们可以加大容量设为1000或者10000,但还有一种方法就是自定义仓库,实现TraceRepository接口)
我使用的是redis作为跟踪数据的仓库,数据结构采用的set集合,也可以使用list列表,java实体转换json使用的是fastjson
引入redis自启动(如果引入不进来,可指定版本号,有可能spring-boot-starter-redis的版本号不及spring-boot版本的新,如redis自启动版本是1,
而spring-boot的版本是2,默认去找版本号为2的redis自启动是找不到的)
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
具体spring-boot的redis使用可参考网上例子,这里不做详细描述,以后可写一篇关于spring redis使用的博文。
在application.properties加入redis的配置:
# REDIS (RedisProperties) # Redis数据库索引(默认为0) spring.redis.database=0 # Redis服务器地址 spring.redis.host=127.0.0.1 # Redis服务器连接端口 spring.redis.port=6379 # Redis服务器连接密码(默认为空) spring.redis.password= # 连接池中的最大空闲连接 spring.redis.pool.max-idle=200 # 连接池中的最小空闲连接 spring.redis.pool.min-idle=100 spring.redis.pool.max-wait=-1 # 连接超时时间(毫秒) spring.redis.timeout=3000
代码如下:
@Component public class RedisTraceRepository implements TraceRepository { @Autowired private JedisService jedisService; @Override public List<Trace> findAll() { return jedisService.findObjectSet(Trace.class); } @Override public void add(Map<String, Object> map) { jedisService.objectSet((new Trace(new Date(), map))); } }
@Service public class JedisService { private static final Map<String, String> mapNames = new ConcurrentHashMap(); @Autowired private RedisTemplate redisTemplate; /** * 集合添加 * @param key * @param value */ public void add(String key,Object value){ SetOperations<String, Object> set = redisTemplate.opsForSet(); set.add(key,value); } /** * 集合获取 * @param key * @return */ public Set<Object> setMembers(String key){ SetOperations<String, Object> set = redisTemplate.opsForSet(); return set.members(key); } private static final boolean isUpperEnglishChar(char value) { return value >= 65 && value <= 90; } private static final <T> String getSimpleName(String simpleName) { char[] chars = simpleName.toCharArray(); StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(); for(int i = 0; i < chars.length; ++i) { char c = chars[i]; if(i > 0 && isUpperEnglishChar(c)) { sb.append("_").append(String.valueOf(c).toLowerCase()); } else { sb.append(String.valueOf(c).toLowerCase()); } } return new String(sb); } public static <T> String getMapName(Class<T> clazz) { String name = clazz.getName(); String mapName = (String)mapNames.get(name); if(StringUtils.isEmpty(mapName)) { mapName = getSimpleName(clazz.getSimpleName()); mapNames.put(name, mapName); } return mapName; } public <T> void objectSet(final T obj) { add(getMapName(obj.getClass()), JSON.toJSONString(obj)); } public <T> List<T> findObjectSet(Class<T> clazz) { String key =getMapName(clazz); Set<Object> set = setMembers(key); List<T> list = new ArrayList<T>(); String value; for(Object t :set){ value =t.toString(); if(value != null) { list.add(JSON.parseObject(value,clazz)); } } return list; } }
5.自定义健康指示器信息(主要针对于health端点,可实现HealthIndicator接口)
@Component public class BodyHealth implements HealthIndicator { @Override public Health health() { try { return Health.up().withDetail("reason", "吃饱了很健康").build(); } catch (Exception e) { return Health.down().withDetail("reason", "吃到一半拉肚子了").build(); } } }
actuator访问控制:
像rest直接请求端点信息,未免太不安全,所有人都可以看你工程的信息了,特别是/shutdown这请求,直接关了你的工程,那很嗨了。
所以接下来,这里结合spring security做端点访问的控制。
首先引入依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
在application.properties加入配置:
management.context-path=/admin management.security.enabled=true # 测试用户 security.user.name=admin security.user.password=admin security.basic.enabled=true # 测试用户角色 management.security.roles=ADMIN
在写一个自定义的WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter,用于实现自己的定制实现:
package com.zgz.security; import com.alibaba.druid.util.StringUtils; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.core.env.Environment; import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.authentication.builders.AuthenticationManagerBuilder; import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity; import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableWebSecurity; import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter; import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configurers.ExpressionUrlAuthorizationConfigurer; import org.springframework.security.core.GrantedAuthority; import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails; import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService; import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UsernameNotFoundException; import java.util.Collection; /** * Created by zgz on 2017/12/16. */ @Configuration @EnableWebSecurity public class WebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter { @Autowired Environment env; @Override protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { http.authorizeRequests() .antMatchers("/").access("hasRole('READER')") // 这里对/admin/**的请求都判断有没有ADMIN角色,还记得配置文件配了对actuator端点的访问基路径吗(/admin), // 没错,为了不影响其他请求,这里只对actuator端点进行鉴权 .antMatchers("/admin/**").access("hasRole('ADMIN')") .antMatchers("/**").permitAll().and().formLogin().and().httpBasic();; } /** 如果不想在配置文件添加测试用户,也可在这里添加用户 @Override protected void configure( AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception { auth.inMemoryAuthentication() .withUser("admin").password("admin") .roles("ADMIN"); } **/ }
以上这里只是为了举例实现对actuator的访问控制,其实spring security还有很多可说,这里就不做详述,以后可再写一篇关于spring security的博文。
以上纯属个人整理跟理解,如有错误,请帮忙纠正我,在此感谢!