一、递归方式遍历
递归方法完成二叉树的遍历,每一个节点都能回去3次(虽然某一次回去的时候什么也没干)
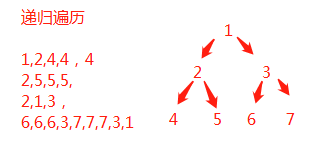
在递归序的基础上,选择打印的时机不同可演变出前序、中序、后续三种遍历方式
前序-打印递归遍历时第1次出现的数字(头左右):1,2,4,5,3,6,7
中序-打印递归遍历时第2次出现的数字(左头右):4,2,5,1,6,3,7
后续-打印递归遍历时第3次出现的数字(左右头):4,5,2,6,7,3,1

public static void preOrderRecur(Node head) { if (head == null) { return; } System.out.print(head.value + " "); //此位置为前序递归 preOrderRecur(head.left); //System.out.print(head.value + " "); //此位置为中序递归 preOrderRecur(head.right); //System.out.print(head.value + " "); //此位置为后序递归 }
二、非递归方式遍历
1、前序遍历
先把头节点放入栈中
1)每次在栈中弹出一个节点,记为cur
2)打印(处理)cur
3)如有cur有左右孩子(没有孩子就不操作,继续步骤1),先把cur右孩子压栈,再把cur左孩子压栈
4)循环以上三步操作
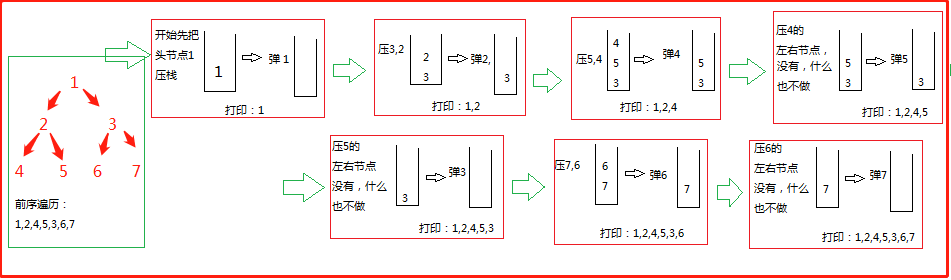

//前序非递归 public static void preOrderUnRecur(Node head) { System.out.print("pre-order: "); if (head != null) { Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>(); stack.add(head); //先把头节点压入栈中 while (!stack.isEmpty()) { //只要栈不是空的,循环3个步骤 head = stack.pop(); System.out.print(head.value + " "); if (head.right != null) { stack.push(head.right); } if (head.left != null) { stack.push(head.left); } } } System.out.println(); }
2、后续遍历
由前序遍历进行改进而来:
准备两栈(多一个收集栈),先把头节点放入正常栈中
1)每次在正常栈中弹出一个节点,记为cur
2)把cur放入一个收集栈中
3)如有cur有左右孩子(没有孩子就不操作,继续步骤1),先把cur左孩子压入正常栈,再把cur右孩子压正常栈
循环以上三步操作
4)再把收集栈中的元素依次弹出就是后续遍历结果

//后序非递归 public static void posOrderUnRecur1(Node head) { System.out.print("pos-order: "); if (head != null) { Stack<Node> s1 = new Stack<Node>(); //正常栈 Stack<Node> s2 = new Stack<Node>(); //收集栈 s1.push(head); //先压入头节点 while (!s1.isEmpty()) { //循环1/2/3 head = s1.pop(); //1、每次弹出一个元素 s2.push(head); //2、弹出之后不打印,而是放入收集栈中 if (head.left != null) { s1.push(head.left); //3、先压左节点 } if (head.right != null) { s1.push(head.right); //3、再压右节点 } } while (!s2.isEmpty()) { System.out.print(s2.pop().value + " "); //4、最后把收集栈中的元素弹出进行打印 } } }
3、中序遍历
1)把当前节点的所有左节点压栈
2)依次弹出节点的过程中,打印
3)每弹出一个节点,把目标移到弹出节点的右节点上面
循环以上三个操作
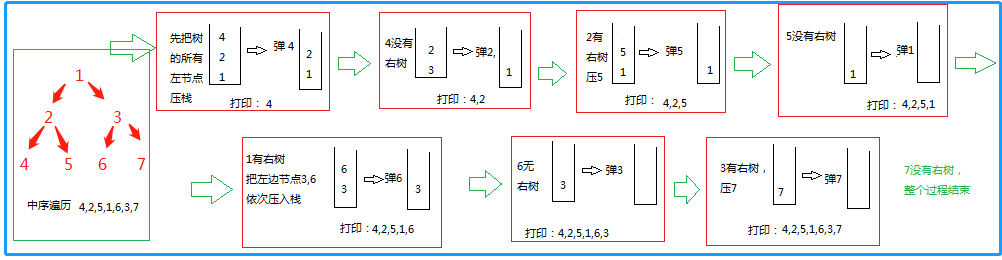

//中序非递归 public static void inOrderUnRecur(Node head) { System.out.print("in-order: "); if (head != null) { Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>(); while (!stack.isEmpty() || head != null) { if (head != null) { //1、把当前节点所有的左节点压栈 stack.push(head); head = head.left; } else { //所有左节点压栈之后 head = stack.pop(); //2、弹出一个节点,打印 System.out.print(head.value + " "); head = head.right; //3、然后移动到弹出节点的右节点上面,循环以上步骤 } } } }
为什么进行以上三步操作就能实现前中后的中序遍历?
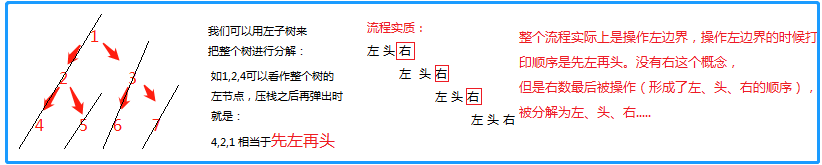
整体代码
package Algorithms; /** * @author : zhang * @version : 1.0 * @date : Create in 2021/8/11 * @description : */ import java.util.Stack; public class PreInPosTraversal { public static class Node { public int value; public Node left; public Node right; public Node(int data) { this.value = data; } } //前序递归 public static void preOrderRecur(Node head) { if (head == null) { return; } System.out.print(head.value + " "); preOrderRecur(head.left); preOrderRecur(head.right); } //中序递归 public static void inOrderRecur(Node head) { if (head == null) { return; } inOrderRecur(head.left); System.out.print(head.value + " "); inOrderRecur(head.right); } //后序递归 public static void posOrderRecur(Node head) { if (head == null) { return; } posOrderRecur(head.left); posOrderRecur(head.right); System.out.print(head.value + " "); } //前序非递归 public static void preOrderUnRecur(Node head) { System.out.print("pre-order: "); if (head != null) { Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>(); stack.add(head); //先把头节点压入栈中 while (!stack.isEmpty()) { //只要栈不是空的,循环3个步骤 head = stack.pop(); System.out.print(head.value + " "); if (head.right != null) { stack.push(head.right); } if (head.left != null) { stack.push(head.left); } } } System.out.println(); } //中序非递归 public static void inOrderUnRecur(Node head) { System.out.print("in-order: "); if (head != null) { Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>(); while (!stack.isEmpty() || head != null) { if (head != null) { //1、把当前节点所有的左节点压栈 stack.push(head); head = head.left; } else { //所有左节点压栈之后 head = stack.pop(); //2、弹出一个节点,打印 System.out.print(head.value + " "); head = head.right; //3、然后移动到弹出节点的右节点上面,循环以上步骤 } } } } //后序非递归 public static void posOrderUnRecur1(Node head) { System.out.print("pos-order: "); if (head != null) { Stack<Node> s1 = new Stack<Node>(); //正常栈 Stack<Node> s2 = new Stack<Node>(); //收集栈 s1.push(head); //先压入头节点 while (!s1.isEmpty()) { //循环1/2/3 head = s1.pop(); //1、每次弹出一个元素 s2.push(head); //2、弹出之后不打印,而是放入收集栈中 if (head.left != null) { s1.push(head.left); //3、先压左节点 } if (head.right != null) { s1.push(head.right); //3、再压右节点 } } while (!s2.isEmpty()) { System.out.print(s2.pop().value + " "); //4、最后把收集栈中的元素弹出进行打印 } } System.out.println(); } public static void posOrderUnRecur2(Node h) { System.out.print("pos-order: "); if (h != null) { Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>(); stack.push(h); Node c = null; while (!stack.isEmpty()) { c = stack.peek(); if (c.left != null && h != c.left && h != c.right) { stack.push(c.left); } else if (c.right != null && h != c.right) { stack.push(c.right); } else { System.out.print(stack.pop().value + " "); h = c; } } } System.out.println(); } public static void main(String[] args) { Node head = new Node(1); head.left = new Node(2); head.right = new Node(3); head.left.left = new Node(4); head.left.right = new Node(5); head.right.left = new Node(6); head.right.right = new Node(7); // recursive System.out.println("==============recursive=============="); System.out.print("pre-order: "); preOrderRecur(head); System.out.println(); System.out.print("in-order: "); inOrderRecur(head); System.out.println(); System.out.print("pos-order: "); posOrderRecur(head); System.out.println(); // unrecursive System.out.println("============unrecursive============="); preOrderUnRecur(head); inOrderUnRecur(head); posOrderUnRecur1(head); posOrderUnRecur2(head); } } /** * ==============recursive============== * pre-order: 1 2 4 5 3 6 7 * in-order: 4 2 5 1 6 3 7 * pos-order: 4 5 2 6 7 3 1 * ============unrecursive============= * pre-order: 1 2 4 5 3 6 7 * in-order: 4 2 5 1 6 3 7 * pos-order: 4 5 2 6 7 3 1 * pos-order: 4 5 2 6 7 3 1 */
