题目链接:
Ryouko is an extremely forgetful girl, she could even forget something that has just happened. So in order to remember, she takes a notebook with her, called Ryouko's Memory Note. She writes what she sees and what she hears on the notebook, and the notebook became her memory.
Though Ryouko is forgetful, she is also born with superb analyzing abilities. However, analyzing depends greatly on gathered information, in other words, memory. So she has to shuffle through her notebook whenever she needs to analyze, which is tough work.
Ryouko's notebook consists of n pages, numbered from 1 to n. To make life (and this problem) easier, we consider that to turn from page x to page y, |x - y| pages should be turned. During analyzing, Ryouko needs m pieces of information, the i-th piece of information is on page ai. Information must be read from the notebook in order, so the total number of pages that Ryouko needs to turn is 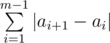 .
.
Ryouko wants to decrease the number of pages that need to be turned. In order to achieve this, she can merge two pages of her notebook. If Ryouko merges page x to page y, she would copy all the information on page x to y (1 ≤ x, y ≤ n), and consequently, all elements in sequence a that was x would become y. Note that x can be equal to y, in which case no changes take place.
Please tell Ryouko the minimum number of pages that she needs to turn. Note she can apply the described operation at most once before the reading. Note that the answer can exceed 32-bit integers.
The first line of input contains two integers n and m (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 105).
The next line contains m integers separated by spaces: a1, a2, ..., am (1 ≤ ai ≤ n).
Print a single integer — the minimum number of pages Ryouko needs to turn.
4 6
1 2 3 4 3 2
3
10 5
9 4 3 8 8
6
题意:
a[i]表示a[i]页,按顺序翻页,现在可以把其中一页的内容全部复制到另一页,问最少翻的页数;
思路:
假设把第x页的内容复制走,|a[i]-x|+|a[j]-x|+...+|a[k]-x|,排序后去掉绝对值得x-a[i]+x-a[j]+...+a[k]-x;把x变成a[i],a[j],...a[k]的中位数就可以得到最小值;
其中a[i],a[j]...a[k]这些数是与x相邻的的页数,有个wa点就是要把一开始相邻的相同的页数合并,因为这个wa了好多发;
AC代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h> /*#include <vector> #include <iostream> #include <queue> #include <cmath> #include <map> #include <cstring> #include <algorithm> #include <cstdio> */ using namespace std; #define Riep(n) for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) #define Riop(n) for(int i=0;i<n;i++) #define Rjep(n) for(int j=1;j<=n;j++) #define Rjop(n) for(int j=0;j<n;j++) #define mst(ss,b) memset(ss,b,sizeof(ss)); typedef long long LL; template<class T> void read(T&num) { char CH; bool F=false; for(CH=getchar();CH<'0'||CH>'9';F= CH=='-',CH=getchar()); for(num=0;CH>='0'&&CH<='9';num=num*10+CH-'0',CH=getchar()); F && (num=-num); } int stk[70], tp; template<class T> inline void print(T p) { if(!p) { puts("0"); return; } while(p) stk[++ tp] = p%10, p/=10; while(tp) putchar(stk[tp--] + '0'); putchar(' '); } const LL mod=1e9+7; const double PI=acos(-1.0); const LL inf=1e14; const int N=1e5+15; int n,m; int a[N],vis[N],c[N]; LL b[N],sum=0; vector<int>ve[N]; int main() { read(n);read(m); int cnt=0; Riep(m) { read(c[i]); if(c[i]!=c[i-1])a[++cnt]=c[i],vis[c[i]]++; } m=cnt; for(int i=2;i<=m;i++)sum=sum+abs(a[i]-a[i-1]); Riep(m) { if(i==1)ve[a[i]].push_back(a[2]),b[a[i]]=b[a[i]]+abs(a[2]-a[1]); else if(i==m)ve[a[i]].push_back(a[m-1]),b[a[i]]=b[a[i]]+abs(a[m]-a[m-1]); else ve[a[i]].push_back(a[i-1]),ve[a[i]].push_back(a[i+1]),b[a[i]]=b[a[i]]+abs(a[i]-a[i-1])+abs(a[i]-a[i+1]); } LL ans=sum; if(m>1) for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { if(vis[i]) { sort(ve[i].begin(),ve[i].end()); int len=ve[i].size(); LL s=0; for(int j=0;j<len;j++) { s=s+abs(ve[i][j]-ve[i][len/2]); } ans=min(ans,sum-b[i]+s); } } cout<<ans<<" "; return 0; }