语句执行过程中,由于各种原因使得语句不能正常执行,可能会造成更大错误或整个系统的崩溃,所以PS/SQL提供了异常(exception)着一处理的方法来防止此类情况的发生。在代码运行的过程中无论何时发生错误,PL/SQL都能控制程序自动地转向执行异常部分。
1.预定义异常
预定义异常是由于系统产生的。例如出现0除,PL/SQL就会产生一个预定义的ZERO_DIVIDE异常。
--ZERO_DIVIDE异常。使用系统预定义的异常处理,使用该处理后,程序运行时系统就不会提示出现错误。 declare v_number1 number(3):=10; v_number2 number(3):=0; v_number3 number(3); begin v_number3:=v_number1/v_number2; DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE(v_number3); EXCEPTION when ZERO_DIVIDE then DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('除数不能为0'); end;
输出结果:DIVIDE ZERO
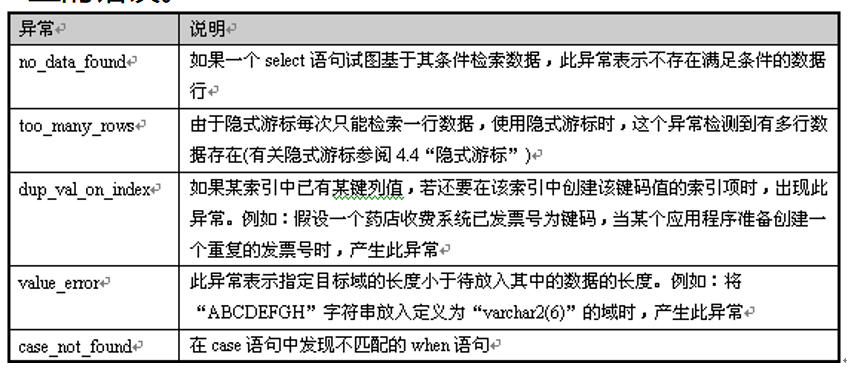
2.PL/SQL中常见的异常:
3.转换的错误处理
declare v_number1 number(3); v_char char(5):='123c'; begin v_number1:=to_number(v_char); //将字符转换成数字 DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('转换成功'); EXCEPTION when value_error then DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('转换没成功'); end;
4.联合的错误处理
declare v_name school_students.stu_name%type; begin select stu_name into v_name from school_students where stu_id='2016322180021'; dbms_output.put_line(v_name); EXCEPTION when no_data_found then dbms_output.put_line('没有数据'); when too_many_rows then dbms_output.put_line('数据太多'); when ZERO_DIVIDE then dbms_output.put_line('列出错列'); end;
5.用户定义异常
--用户可以通过自定义异常来处理发生的错误,语法格式为: exception when 异常名 then 语句块 1; when then 语句块2; [when others then 语句块3;] end;
注意:每个异常处理部分都是由when子句和相应的执行语句组成
6.自定义异常
declare e_name exception; v_num number(8); begin select count(*) into v_num from school_students; if v_num>10 then RAISE e_name; end if ; exception when e_name then dbms_output.put_line('最大值不能超过10'); end;
注意:同一个异常不允许多个when子句来处理,一个异常对应一个when子句。
7.使用others异常
declare v_name school_students.stu_name%type; begin select stu_name into v_name from school_students where stu_id='2016322180021'; dbms_output.put_line(v_name); EXCEPTION when OTHERS then dbms_output.put_line('出错了'); end;
对于一个异常有两个处理方式,分别位于不同的when子句,因此系统会认为是不合法的。可以使用others来处理那些不能由其他when子句处理的异常,others异常处理总是位于exception语句的最后。
其实,others异常处理可以借助两个函数来说明捕捉到的异常的类型,这两个函数是PL/SQL和SQLERRM,其中SQLLOCODE是用来说明当前错误的代码,如果是用户自定义异常。则返回1.SQLERRM返回的是当前错误的信息。
8.空操作和空值
declare n number(3):=-1; begin if n<0 then null; else DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('正常'); end if; end;