Linux C语言编程基础(必做)
任务详情
- 基于Ubuntu或OpenEuler完成下面的任务(OpenEuler有加分)
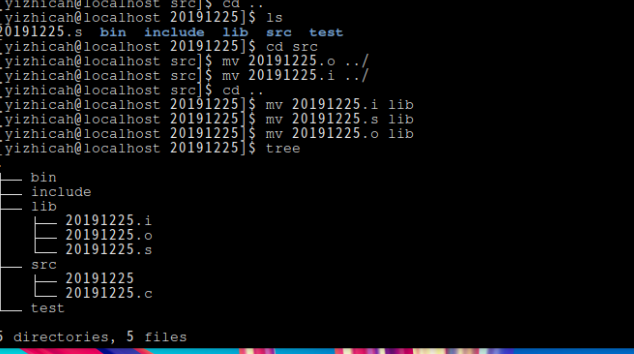
选择教材第二章的一节进行编程基础练习(2.10,2.11,2.12,2.13,2.14任选一个) - 建立自己的项目目录,包含自己学号信息(如20190100linkedlist),构建项目结构(src, include, bin, lib, docs, test...),然后把相应代码和文档放置到正确位置,用tree命令查看项目结构,提交截图(5分)
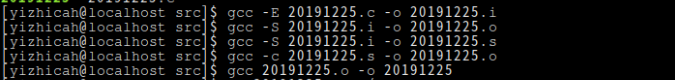
- 进行gcc相关练习(ESc, iso, -I等)提交相关截图(5分)
- 进行静态库,动态库制作和调用练习,提交相关截图(5分)
- 进行gdb相关练习,至少包含四种断点的设置,提交相关截图(10分)
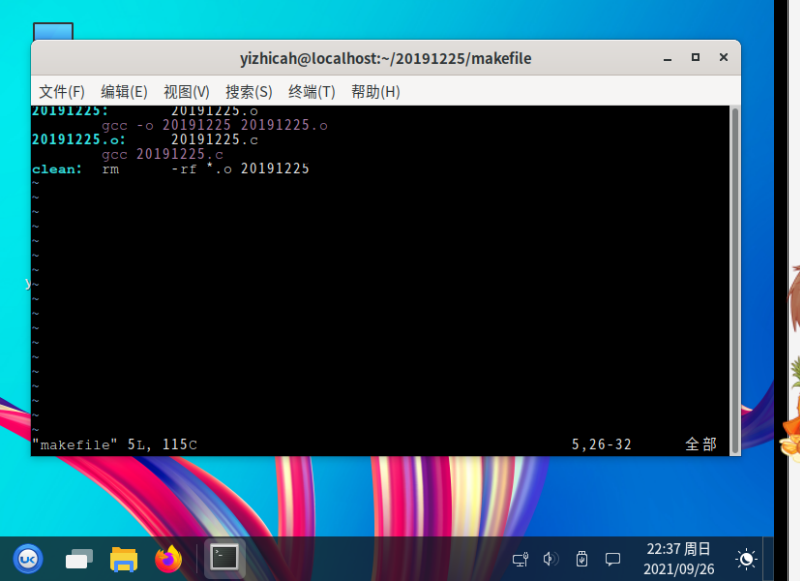
- 编写makefile(5分)
1.打印链表:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
/* 定义一个表示链表的结构体指针 */
struct list {
int id;
char data[20];
struct list *next;
};
/* 定义一个链表头部 */
static struct list *list_head = NULL;
/* 为了保证每一个链表元素的id不同,特意把id定义成一个全局静态变量 */
static int list_id = 0;
static void list_add(struct list **head, struct list *list)
{
struct list *temp;
/* 判断链表是否为空 */
if(NULL == *head)
{
/* 为空 */
*head = list;
(*head)->next = NULL;
}
else
{
/* 不为空 */
temp = *head;
while(temp)
{
if(NULL == temp->next)
{
temp->next = list;
list->next = NULL;
}
temp = temp->next;
}
}
}
/** 遍历一个链表,打印链表中每个元素所包含的数据
* head : 表示要遍历的链表的头部的指针
*/
static void list_print(struct list **head)
{
struct list *temp;
temp = *head;
printf("list information :
");
while(temp)
{
printf(" list %d : %s
", temp->id, temp->data);
temp = temp->next;
}
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int i = 0;
struct list *lists = NULL;
/* 分配10个元素 */
lists = malloc(sizeof(struct list) * 10);
if(NULL == lists)
{
printf("malloc error!
");
return -1;
}
/* 将分配的10个元素依次填充数据并加入到链表当中 */
for(i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
lists[i].id = list_id++;
sprintf(lists[i].data, "TECH-PRO - %d", i);
list_add(&list_head, &lists[i]);
}
/* 遍历链表,把链表中每个元素的信息都打印出来 */
list_print(&list_head);
return 0;
}
- 运行结果:
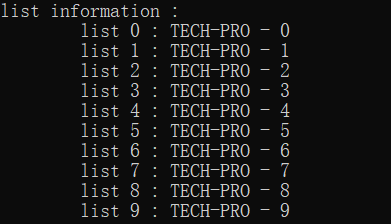
2.tree目录:
3.gcc相关练习:
4.静态库,动态库制作和调用:
- 静态库
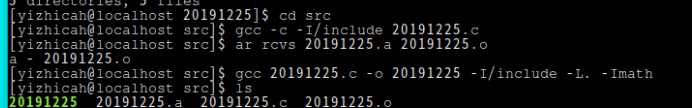
- 动态库

5.gdb相关练习

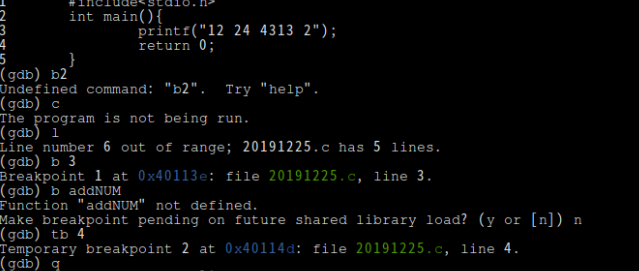
6.编写makefile: