一、减少过拟合
奥卡姆剃刀原理:没必要的东西尽量少用。
因此过拟合有以下几种:
(1)更多数据
(2)限制网络复杂性:使用浅层网络、新数据集使用大网络后加惩罚。
(3)droupout
(4)数据增强
(5)用验证数据早停。

二、损失函数加惩罚
1、原始

2、加惩罚项以后
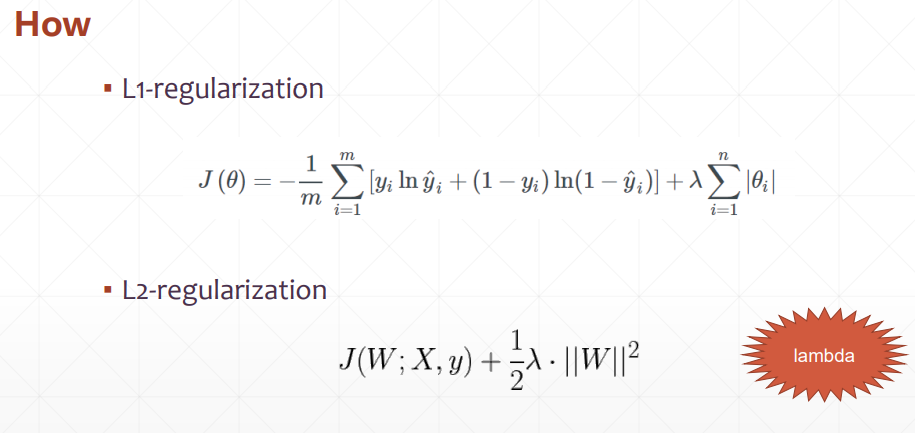
三、加惩罚项方法
1、keras方法

2、手动写

四、实战
import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.keras import datasets, layers, optimizers, Sequential, metrics def preprocess(x, y): x = tf.cast(x, dtype=tf.float32) / 255. y = tf.cast(y, dtype=tf.int32) return x,y batchsz = 128 (x, y), (x_val, y_val) = datasets.mnist.load_data() print('datasets:', x.shape, y.shape, x.min(), x.max()) db = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x,y)) db = db.map(preprocess).shuffle(60000).batch(batchsz).repeat(10) ds_val = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x_val, y_val)) ds_val = ds_val.map(preprocess).batch(batchsz) network = Sequential([layers.Dense(256, activation='relu'), layers.Dense(128, activation='relu'), layers.Dense(64, activation='relu'), layers.Dense(32, activation='relu'), layers.Dense(10)]) network.build(input_shape=(None, 28*28)) network.summary() optimizer = optimizers.Adam(lr=0.01) for step, (x,y) in enumerate(db): with tf.GradientTape() as tape: # [b, 28, 28] => [b, 784] x = tf.reshape(x, (-1, 28*28)) # [b, 784] => [b, 10] out = network(x) # [b] => [b, 10] y_onehot = tf.one_hot(y, depth=10) # [b] loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.losses.categorical_crossentropy(y_onehot, out, from_logits=True)) loss_regularization = [] for p in network.trainable_variables: loss_regularization.append(tf.nn.l2_loss(p)) loss_regularization = tf.reduce_sum(tf.stack(loss_regularization)) loss = loss + 0.0001 * loss_regularization grads = tape.gradient(loss, network.trainable_variables) optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(grads, network.trainable_variables)) if step % 100 == 0: print(step, 'loss:', float(loss), 'loss_regularization:', float(loss_regularization)) # evaluate if step % 500 == 0: total, total_correct = 0., 0 for step, (x, y) in enumerate(ds_val): # [b, 28, 28] => [b, 784] x = tf.reshape(x, (-1, 28*28)) # [b, 784] => [b, 10] out = network(x) # [b, 10] => [b] pred = tf.argmax(out, axis=1) pred = tf.cast(pred, dtype=tf.int32) # bool type correct = tf.equal(pred, y) # bool tensor => int tensor => numpy total_correct += tf.reduce_sum(tf.cast(correct, dtype=tf.int32)).numpy() total += x.shape[0] print(step, 'Evaluate Acc:', total_correct/total)