Spring的jdbc与Hibernate,Mybatis相比较,功能不是特别强大,但是在小型项目中,也到还是比较灵活简单。
首先可以看看一下传统的jdbc是如何操作的呢
传统JDBC
首先呢先要创建一个bean实例,例如Student.java
1 public class Student { 2 3 private Integer id; 4 private String name; 5 private String password; 6 7 public Integer getId() { 8 return id; 9 } 10 11 public void setId(Integer id) { 12 this.id = id; 13 } 14 15 public String getName() { 16 return name; 17 } 18 19 public void setName(String name) { 20 this.name = name; 21 } 22 23 public String getPassword() { 24 return password; 25 } 26 27 public void setPassword(String password) { 28 this.password = password; 29 } 30 31 }
为了方便简单,直接在main里面创建数据源的连接了
1 import org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource; 2 import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate; 3 4 public class TestJdbc { 5 6 public static void main(String[] args) { 7 8 //创建数据源连接池 9 BasicDataSource dataSource = new BasicDataSource(); 10 11 dataSource.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"); 12 dataSource.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/stu?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC&rewriteBatchedStatements=true"); 13 dataSource.setUsername("root"); 14 dataSource.setPassword("123456"); 15 16 //创建jdbc模板 17 JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = new JdbcTemplate(); 18 jdbcTemplate.setDataSource(dataSource); 19 20 //通过api操作执行sql 21 jdbcTemplate.update("insert into student(stu_name,stu_pwd) values(?,?);", "jack","46asd4634"); 22 23 } 24 25 }
因为我这里使用的是mysql8.0,所以驱动名和url有所不一样,可以参考https://www.cnblogs.com/zhangyuanbo/p/11248334.html
以上就是传统的JDBC操作数据库,然后我们用Spring的xml来配置一下,现在用的是DBCP连接池来测试的:
步骤类似,先创建实体类Student.java,然后需要一个StudentDao.java,简单一点,什么接口类实现类Service的,通通不要了,这些做起来应该也不是什么难事吧。
要操作数据库,当然要有CRUD什么的啦,那就整一个update()方法吧
public void update(Student stu) { String sql = "update student set stu_name=? where stu_id=?"; Object[] pro = {stu.getName(),stu.getId()}; jdbcTemplate.update(sql, pro); }
我这里是根据Id来执行修改操作的,jdbc模板的方法有很多
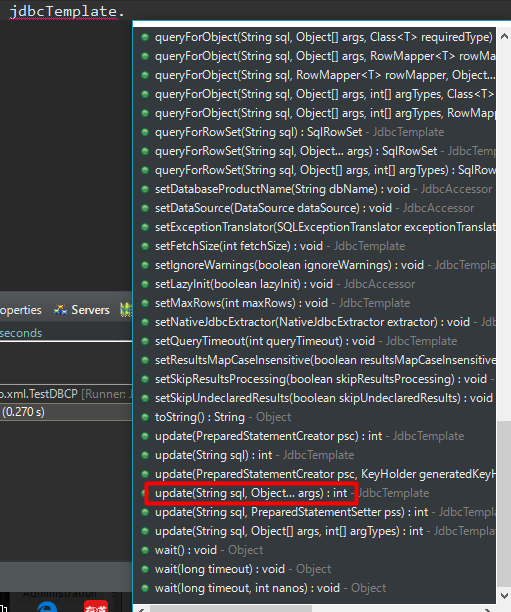
我用的是这里红框框的方法,第一个参数很显然啦,意思就是你操作数据库执行的sql语句,第二个就是sql中要传的参数,比如我这里的sql“update student set stu_name=? where stu_id=?”,参数就是stu_name和stu_id。
哦,对了,有一件很重要的事情,可不要忘了JdbcTemplate了,不创建一下,给个setter()方法的话,就会报错的——“jdbcTemplate is not writable or has an anvalid setter method..............”,很明显告诉我们需要一个jdbcTemplate的setter()方法呀,所以完整的StudentDao.java就写成这样:
1 import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate; 2 3 public class StudentDao { 4 5 private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate; 6 7 public void setJdbcTemplate(JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate) { 8 this.jdbcTemplate = jdbcTemplate; 9 } 10 11 public void update(Student stu) { 12 String sql = "update student set stu_name=? where stu_id=?"; 13 Object[] pro = {stu.getName(),stu.getId()}; 14 15 jdbcTemplate.update(sql, pro); 16 } 17 18 }
再整一个bean.xml呗,当然了,实际项目中可不这样命名,一般是“applicationContext.xml”,这里就随意了,怎么简单方便怎么来
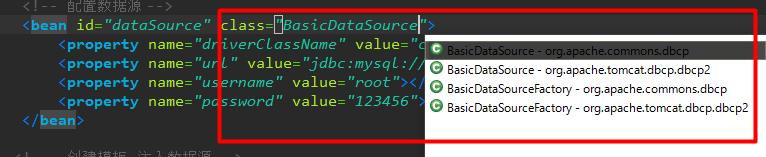
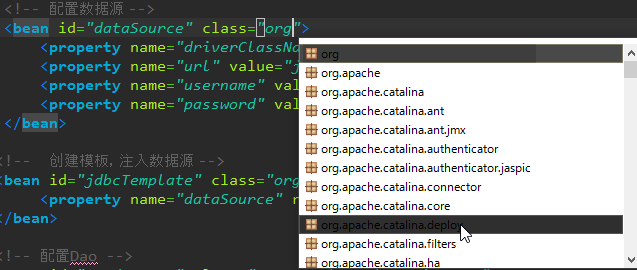
在写xml的时候,比如“<bean id="dataSource" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource"></bean>”,在class=""这里面按alt+/没有代码提示很烦,像我这样不喜欢敲这么长一串的人来说,特别记忆力又不好,一不小心敲错了,最后报错了呀,找起来也烦。于是,还可以这样来解决:
Windows→Preferences

里面那个红××请忽略,网络代理问题,与这个项目无关。再点“Add”:

注意:外部引用的是你要使用的炸包(jar)对应的“.xsd”格式文件,最后点确定就可以了。效果如下:
有意思吧,方便吧,懒癌患者的福音啊!!!!
咳咳咳,说正事,回到我们的bean.xml的写法
为了好理解,我们就倒着来写吧,以后就顺着写咯
首先肯定要配置Dao的bean
<bean id="studentDao" class="com.yuanbo.xml.StudentDao"> <property name="jdbcTemplate" ref="jdbcTemplate"></property> </bean>
怎么ide里的格式好好地,复制过来就这样了,算了,懒得改了,继续一顿操作
我们把jdbcTemplate注入到这个Dao的bean中,那么,必须要有一个jdbcTemplate的bean撒,
也可以从最开始的传统IDBC可以看到,我们不是new了一个jdbcTemplate嘛,一看到new,那
么,改成xml配置文件形式,得整一个相对应的bean出来撒,于是,吧啦啦啦,整出来了:
1 <!-- 创建模板,注入数据源 --> 2 <bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate"> 3 <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property> 4 </bean>
你看吧,现在格式又好好的了,,,,,,emmmm,想起来了,好像是复制的时候没有从定
格复制,少复制了一个“Tab”,算求了,无关紧要,没得啥子强迫症
模板里面必须要注入jdbcTemplate哦,从传统JDBC这里“jdbcTemplate.setDataSource(dataSource);”
有了set方法,就要想到,那得注入了呀不是,注入就等同于set
既然注入了,那不是还缺少一个dataSource呀,这还不洒洒水啊,明显需要再整一个数据源的bean撒,吧啦啦啦啦,小魔仙,全身变!出来吧
<!-- 配置数据源 --> <bean id="dataSource" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource"> <property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver "></property> <property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/stu?serverTimezone=GMT%2B8"></property> <property name="username" value="root"></property> <property name="password" value="123456"></property>
</bean>
哦,对了,有一个块选中的快捷键,shift+alt+a,就可以了,其实我还是喜欢代码对齐的,可读性必须高,
写代码的基本准则。再按一下组合键就可以退出当前模式了
这里的url不要在意,mysql8.0的url写法又好几种,这是比较随意的写法
最后看看bean.xml的完整代码:
1 <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" 2 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" 3 xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" 4 xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans 5 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd 6 http://www.springframework.org/schema/context 7 http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> 8 9 <!-- <context:property-placeholder location="classpath:com/yuanbo/xml/jdbc.properties"/> --> 10 11 <!-- 配置数据源 --> 12 <bean id="dataSource" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource"> 13 <property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver "></property> 14 <property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/stu?serverTimezone=GMT%2B8"></property> 15 <property name="username" value="root"></property> 16 <property name="password" value="123456"></property> 17 </bean> 18 19 <!-- 创建模板,注入数据源 --> 20 <bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate"> 21 <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property> 22 </bean> 23 24 <!-- 配置Dao --> 25 <bean id="studentDao" class="com.yuanbo.xml.StudentDao"> 26 <property name="jdbcTemplate" ref="jdbcTemplate"></property> 27 </bean> 28 </beans>
注释的别管,我把数据源里面属性提出来放到.properties文件里,注释掉的这句话就有用了。
最后,来个测试类吧
1 import org.junit.Test; 2 import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; 3 import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext; 4 import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; 5 6 public class TestDBCP { 7 8 @Test 9 public void demo01() { 10 Student stu = new Student(); 11 12 String xmlPath = "com/yuanbo/xml/beans.xml"; 13 ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(xmlPath); 14 StudentDao dao = (StudentDao) applicationContext.getBean("studentDao"); 15 16 stu.setName("ali"); 17 stu.setId(2); 18 dao.update(stu); 19 20 ((ConfigurableApplicationContext)applicationContext).close(); 21 } 22 23 }
好像还忘记了啥东西,哦,是了,贴上数据库的吧

还有炸包