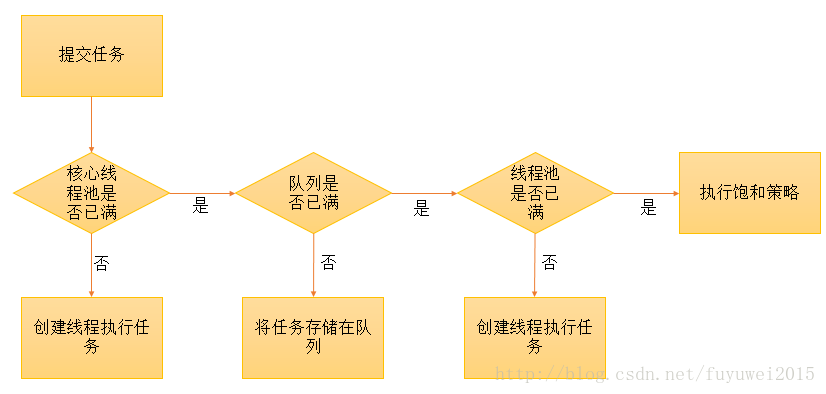
一.线程池核心参数
public ThreadPoolExecutor(
int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler) {
this(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue,
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), handler);
corePoolSize:池中的线程数,即使其处于IDLE状态
maximumPoolSize:池中允许的最大线程数
keepAliveTime:当线程数大于核心时,空闲线程在终止之前等待新任务的最长时间
unit:keepAliveTime的时间单位
workQueue:队列,用于在执行task之前保存task
handler:当达到了线程边界和队列容量,无法及时处理时,reject task使用的处理程序
/**
* @param corePoolSize 线程池基本大小,核心线程池大小,活动线程小于corePoolSize则直接创建,大于等于则先加到workQueue中,
* 队列满了才创建新的线程。当提交一个任务到线程池时,线程池会创建一个线程来执行任务,即使其他空闲的基本线程能够执行新任务也会创建线程,
* 等到需要执行的任务数大于线程池基本大小时就不再创建。如果调用了线程池的prestartAllCoreThreads()方法,
* 线程池会提前创建并启动所有基本线程。
* @param maximumPoolSize 最大线程数,超过就reject;线程池允许创建的最大线程数。如果队列满了,
* 并且已创建的线程数小于最大线程数,则线程池会再创建新的线程执行任务
* @param keepAliveTime
* 线程池的工作线程空闲后,保持存活的时间。所以,如果任务很多,并且每个任务执行的时间比较短,可以调大时间,提高线程的利用率
* @param unit 线程活动保持时间的单位):可选的单位有天(DAYS)、小时(HOURS)、分钟(MINUTES)、
* 毫秒(MILLISECONDS)、微秒(MICROSECONDS,千分之一毫秒)和纳秒(NANOSECONDS,千分之一微秒)
* @param workQueue 工作队列,线程池中的工作线程都是从这个工作队列源源不断的获取任务进行执行
*/
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue) {
// threadFactory用于设置创建线程的工厂,可以通过线程工厂给每个创建出来的线程设置更有意义的名字
this(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue,
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), defaultHandler);
}
二.向线程池提交任务
可以使用两个方法向线程池提交任务,分别为execute()和submit()方法。execute()方法用于提交不需要返回值的任务,所以无法判断任务是否被线程池执行成功。通过以下代码可知execute()方法输入的任务是一个Runnable类的实例。
threadsPool.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
}
});
submit()方法用于提交需要返回值的任务。线程池会返回一个future类型的对象,通过这个future对象可以判断任务是否执行成功,并且可以通过future的get()方法来获取返回值,get()方法会阻塞当前线程直到任务完成,而使用get(long timeout,TimeUnit unit)方法则会阻塞当前线程一段时间后立即返回,这时候有可能任务没有执行完。
Future<Object> future = executor.submit(harReturnValuetask); try { Object s = future.get(); }catch( InterruptedException e) { // 处理中断异常 }catch( ExecutionException e) { // 处理无法执行任务异常 }finally { // 关闭线程池 executor.shutdown(); }
三.关闭线程池
可以通过调用线程池的shutdown或shutdownNow方法来关闭线程池。它们的原理是遍历线程池中的工作线程,然后逐个调用线程的interrupt方法来中断线程,所以无法响应中断的任务可能永远无法终止。但是它们存在一定的区别,shutdownNow首先将线程池的状态设置成STOP,然后尝试停止所有的正在执行或暂停任务的线程,并返回等待执行任务的列表,而shutdown只是将线程池的状态设置成SHUTDOWN状态,然后中断所有没有正在执行任务的线程。
只要调用了这两个关闭方法中的任意一个,isShutdown方法就会返回true。当所有的任务都已关闭后,才表示线程池关闭成功,这时调用isTerminaed方法会返回true。至于应该调用哪一种方法来关闭线程池,应该由提交到线程池的任务特性决定,通常调用shutdown方法来关闭线程池,如果任务不一定要执行完,则可以调用shutdownNow方法。
import java.util.concurrent.*; import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger; /** * @Author:Zach * @Description: 定制属于自己的非阻塞线程池 * @Date:Created in 15:26 2018/8/14 * @Modified By: */ public class CustomThreadPoolExecutor { private ThreadPoolExecutor pool = null; /** * 线程池初始化方法 * * corePoolSize 核心线程池大小----10 * maximumPoolSize 最大线程池大小----30 * keepAliveTime 线程池中超过corePoolSize数目的空闲线程最大存活时间----30+单位TimeUnit * TimeUnit keepAliveTime时间单位----TimeUnit.MINUTES * workQueue 阻塞队列----new ArrayBlockingQueue<Runnable>(10)====10容量的阻塞队列 * threadFactory 新建线程工厂----new CustomThreadFactory()====定制的线程工厂 * rejectedExecutionHandler 当提交任务数超过maxmumPoolSize+workQueue之和时, * 即当提交第41个任务时(前面线程都没有执行完,此测试方法中用sleep(100)), * 任务会交给RejectedExecutionHandler来处理 */ public void init() { pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(10,30,30, TimeUnit.MINUTES,new ArrayBlockingQueue<Runnable>(10),new CustomThreadFactory(), new CustomRejectedExecutionHandler()); } public void destory() { if(pool !=null) { pool.shutdownNow(); } } public ExecutorService getCustomThreadPoolExecutor() { return this.pool; } private class CustomRejectedExecutionHandler implements RejectedExecutionHandler { @Override public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor executor) { //记录异常 System.out.println("error..................."); } } private class CustomThreadFactory implements ThreadFactory { private AtomicInteger count = new AtomicInteger(0); @Override public Thread newThread(Runnable r) { Thread t = new Thread(r); String threadName = CustomThreadPoolExecutor.class.getSimpleName()+count.addAndGet(1); System.out.println(threadName); t.setName(threadName); return t; } } public static void main(String[] args){ CustomThreadPoolExecutor exec = new CustomThreadPoolExecutor(); //1. 初始化 exec.init(); ExecutorService pool = exec.getCustomThreadPoolExecutor(); for(int i=1;i<100;i++) { System.out.println("提交第"+i+"个任务"); pool.execute(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { try { System.out.println(">>>task is running========"); Thread.sleep(3000); }catch (InterruptedException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } }); } //2. 销毁----此处不能销毁,因为任务没有提交执行完,如果销毁线程池,任务也就无法执行 //exec.destory(); try { Thread.sleep(10000); }catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } /** * 方法中建立一个核心线程数为30个,缓冲队列有10个的线程池。每个线程任务,执行时会先睡眠3秒,保证提交10任务时,线程数目被占用完,再提交30任务时,阻塞队列被占用完,,这样提交第41个任务是,会交给CustomRejectedExecutionHandler 异常处理类来处理。 提交任务的代码如下: /* * Proceed in 3 steps: * * 1. If fewer than corePoolSize threads are running, try to * start a new thread with the given command as its first * task. The call to addWorker atomically checks runState and * workerCount, and so prevents false alarms that would add * threads when it shouldn't, by returning false. * * 2. If a task can be successfully queued, then we still need * to double-check whether we should have added a thread * (because existing ones died since last checking) or that * the pool shut down since entry into this method. So we * recheck state and if necessary roll back the enqueuing if * stopped, or start a new thread if there are none. * * 3. If we cannot queue task, then we try to add a new * thread. If it fails, we know we are shut down or saturated * and so reject the task. */ /** public void execute(Runnable command) { if (command == null) throw new NullPointerException(); int c = ctl.get(); if (workerCountOf(c) < corePoolSize) { if (addWorker(command, true)) return; c = ctl.get(); } if (isRunning(c) && workQueue.offer(command)) { int recheck = ctl.get(); if (! isRunning(recheck) && remove(command)) reject(command); else if (workerCountOf(recheck) == 0) addWorker(null, false); } else if (!addWorker(command, false)) reject(command); } 注意:41以后提交的任务就不能正常处理了,因为,execute中提交到任务队列是用的offer方法,如上面代码, 这个方法是非阻塞的,所以就会交给CustomRejectedExecutionHandler 来处理, 所以对于大数据量的任务来说,这种线程池,如果不设置队列长度会OOM,设置队列长度,会有任务得不到处理,接下来我们构建一个阻塞的自定义线程池 */ }