513、找树左下角的值
基本思想:
树的最后一行找到最左边的值
树的最后一行:深度最大的叶子节点---前序遍历
最左边:优先左边搜索---前序遍历
具体实现:
1、确定递归参数和返回值
参数:根节点和int型变量记录深度
返回值:不需要
如果要遍历整棵树,递归函数不能有返回值
如果要遍历某一条固定路线,递归函数就一定要返回值
本题要遍历整个树找到最深的叶子节点,需要遍历整棵树,所以没有返回值
2、终止条件
遇到叶子节点,统计一下最大的深度了,所以需要遇到叶子节点来更新最大深度maxLen。
if (root.left == null && root.right == null){ if (leftLen > maxLen) { maxLen = leftLen; maxLeftValue = root.val; } return; }
3、单层递归逻辑
回溯
代码:
class Solution { private int maxLen = -1; private int maxLeftValue = 0; public int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode root) { findLeftValue(root,0); return maxLeftValue; } private void findLeftValue (TreeNode root, int leftLen){ if (root == null) return; if (root.left == null && root.right == null){ if (leftLen > maxLen) { maxLen = leftLen; maxLeftValue = root.val; } return; } if (root.left != null){ leftLen++; findLeftValue(root.left,leftLen); leftLen--; } if(root.right != null){ leftLen++; findLeftValue(root.right,leftLen); leftLen--; } return; } }
迭代法
class Solution { public int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode root) { Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>(); queue.offer(root); int res = 0; while (!queue.isEmpty()) { int size = queue.size(); for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { TreeNode poll = queue.poll(); if (i == 0) { res = poll.val; } if (poll.left != null) { queue.offer(poll.left); } if (poll.right != null) { queue.offer(poll.right); } } } return res; } }
112、路径总和
基本思想:
前中后序遍历都可以
具体实现:
1、确定递归参数以及返回值
递归参数:根节点,计数器(用于计算二叉树的一条边是否正好是目标和)
返回值:搜索其中一条符合条件的路径,需要返回值
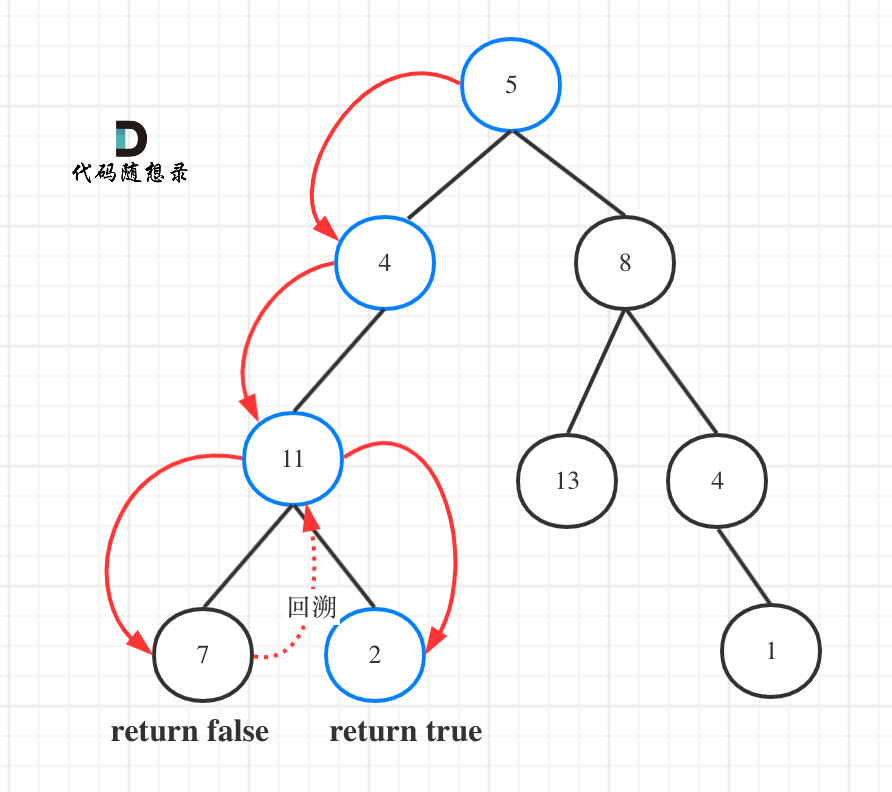
从遍历的路线看出,不需要遍历整棵树,所以递归函数需要返回值,用布尔类型
2、确定终止条件
计数器count初始化为目标和
然后每次减去遍历路径节点上的数值
如果count==0,同时到了叶子节点,说明找到了目标节点
如果到了叶子节点,count不为0,说明没找到
3、单层递归逻辑
回溯
代码:
class Solution { public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) { if (root == null) { return false; } return traversal(root, targetSum - (root.val)); } private boolean traversal(TreeNode root, int count){ if (root.left == null && root.right == null && count == 0) return true; if (root.left == null && root.right == null) return false; if (root.left != null) { count -= root.left.val; if (traversal(root.left, count)) return true; count += root.left.val; } if (root.right != null) { count -= root.right.val; if (traversal(root.right, count)) return true; count += root.right.val; } return false; } }
迭代法
class Solution { public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) { if (root == null) { return false; } Stack<TreeNode> stack1 = new Stack<>(); Stack<Integer> stack2 = new Stack<>(); stack1.push(root); stack2.push(root.val); while (!stack1.isEmpty()){ int size = stack1.size(); for (int i = 0; i < size; i++){ TreeNode node = stack1.pop(); int sum = stack2.pop(); // 如果该节点是叶子节点了,同时该节点的路径数值等于sum,那么就返回true if (node.left == null && node.right == null && sum == targetSum) return true; // 右节点,压进去一个节点的时候,将该节点的路径数值也记录下来 if (node.right != null) { stack1.push(node.right); stack2.push(sum+node.right.val); } // 左节点,压进去一个节点的时候,将该节点的路径数值也记录下来 if (node.left != null) { stack1.push(node.left); stack2.push(sum+node.left.val); } } } return false; } }
113、路径总和ii
基本思想:
具体实现:
返回值:不需要,因为要遍历整个树

代码:
class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) { List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>(); if (root == null) return res; List<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>(); preorderdfs(root, targetSum, res, path); return res; } public void preorderdfs(TreeNode root, int targetSum, List<List<Integer>> res, List<Integer> path){ path.add(root.val); if (root.left == null && root.right == null){ if (root.left == null && root.right == null){ if(targetSum - root.val == 0){ res.add(new ArrayList<>(path)); } } return; } if (root.left != null){ preorderdfs(root.left, targetSum - root.val, res, path); path.remove(path.size() - 1); } if (root.right != null){ preorderdfs(root.right, targetSum - root.val, res, path); path.remove(path.size() - 1); } } }