比特币使用UTXO模型做为交易底层数据结构,UTXO 是 Unspent Transaction Output 的缩写,也就是未被使用的交易输出。本质上,就是只记录交易本身,而不记录交易的结果。比特币使用前后链接的区块(可以简单的理解为交易组成的集合)记录所有交易,每笔交易都有若干交易输入,也就是资金来源,也都有若干笔交易输出,也就是资金去向。一般来说,每一笔交易都要花费(spend)一笔输入,产生一笔输出,而其所产生的输出,就是“未花费过的交易输出”,也就是 UTXO。当之前的 UTXO 出现在后续交易的输入时,就表示这个 UTXO 已经花费掉了,不再是 UTXO 了。如果从第一个区块开始逐步计算所有比特币地址中的余额,就可以计算出不同时间的各个比特币账户的余额了。下面将结合比特币钱包源码0.1.0对比特币中的交易做详细说明。
1 数据结构及相关定义
1.1 区块
交易会被打包到区块中,打包成功的区块会被序列化到本地文件中,区块定义如下(只给出了主要类成员):

1 class CBlock 2 { 3 public: 4 // header 5 int nVersion; // 版本 6 uint256 hashPrevBlock; // 上一个块哈希值 7 uint256 hashMerkleRoot; // MerkleRoot哈希值 8 unsigned int nTime; // 时间戳 9 unsigned int nBits; // 块目标值 10 unsigned int nNonce; // nonce值 11 12 // network and disk 13 vector<CTransaction> vtx; // 交易 14 ... 15 }
1.2 交易
| 版本nVersion | vin0 | ... | vinn | vout0 | ... | voutm | 锁定时间nLockTime |
如表所示,单个交易由版本、若干输入、若干输出和锁定时间构成,其中当前版本值为1,输入和输出后续有更详细介绍,nLockTime定义了一个最早时间,只有过了这个最早时间,这个transaction可以被发送到比特币网络,当前版本用块高度来定义该时间,即只有交易中nLockTime小于当前比特币网络块高度,该交易才会被发送到比特币网络(其实后续版本的比特币引入了LOCKTIME_THRESHOLD=500000000,当nLock小于该值时为区块高度,否则为时间戳),nLockTime通常被设置为0,表示transaction一创建好就马上发送到比特币网络,交易源码定义如下:

1 class CTransaction 2 { 3 public: 4 int nVersion; 5 vector<CTxIn> vin; 6 vector<CTxOut> vout; 7 int nLockTime; 8 9 CTransaction() 10 { 11 SetNull(); 12 } 13 14 IMPLEMENT_SERIALIZE 15 ( 16 READWRITE(this->nVersion); 17 nVersion = this->nVersion; 18 READWRITE(vin); 19 READWRITE(vout); 20 READWRITE(nLockTime); 21 ) 22 23 void SetNull() 24 { 25 nVersion = 1; 26 vin.clear(); 27 vout.clear(); 28 nLockTime = 0; 29 } 30 31 bool IsNull() const 32 { 33 return (vin.empty() && vout.empty()); 34 } 35 36 uint256 GetHash() const 37 { 38 return SerializeHash(*this); 39 } 40 41 bool IsFinal() const 42 { 43 if (nLockTime == 0 || nLockTime < nBestHeight) 44 return true; 45 foreach(const CTxIn& txin, vin) 46 if (!txin.IsFinal()) 47 return false; 48 return true; 49 } 50 51 bool IsNewerThan(const CTransaction& old) const 52 { 53 if (vin.size() != old.vin.size()) 54 return false; 55 for (int i = 0; i < vin.size(); i++) 56 if (vin[i].prevout != old.vin[i].prevout) 57 return false; 58 59 bool fNewer = false; 60 unsigned int nLowest = UINT_MAX; 61 for (int i = 0; i < vin.size(); i++) 62 { 63 if (vin[i].nSequence != old.vin[i].nSequence) 64 { 65 if (vin[i].nSequence <= nLowest) 66 { 67 fNewer = false; 68 nLowest = vin[i].nSequence; 69 } 70 if (old.vin[i].nSequence < nLowest) 71 { 72 fNewer = true; 73 nLowest = old.vin[i].nSequence; 74 } 75 } 76 } 77 return fNewer; 78 } 79 80 bool IsCoinBase() const 81 { 82 return (vin.size() == 1 && vin[0].prevout.IsNull()); 83 } 84 85 bool CheckTransaction() const 86 { 87 // Basic checks that don't depend on any context 88 if (vin.empty() || vout.empty()) 89 return error("CTransaction::CheckTransaction() : vin or vout empty"); 90 91 // Check for negative values 92 foreach(const CTxOut& txout, vout) 93 if (txout.nValue < 0) 94 return error("CTransaction::CheckTransaction() : txout.nValue negative"); 95 96 if (IsCoinBase()) 97 { 98 if (vin[0].scriptSig.size() < 2 || vin[0].scriptSig.size() > 100) 99 return error("CTransaction::CheckTransaction() : coinbase script size"); 100 } 101 else 102 { 103 foreach(const CTxIn& txin, vin) 104 if (txin.prevout.IsNull()) 105 return error("CTransaction::CheckTransaction() : prevout is null"); 106 } 107 108 return true; 109 } 110 111 bool IsMine() const 112 { 113 foreach(const CTxOut& txout, vout) 114 if (txout.IsMine()) 115 return true; 116 return false; 117 } 118 119 int64 GetDebit() const 120 { 121 int64 nDebit = 0; 122 foreach(const CTxIn& txin, vin) 123 nDebit += txin.GetDebit(); 124 return nDebit; 125 } 126 127 int64 GetCredit() const 128 { 129 int64 nCredit = 0; 130 foreach(const CTxOut& txout, vout) 131 nCredit += txout.GetCredit(); 132 return nCredit; 133 } 134 135 int64 GetValueOut() const 136 { 137 int64 nValueOut = 0; 138 foreach(const CTxOut& txout, vout) 139 { 140 if (txout.nValue < 0) 141 throw runtime_error("CTransaction::GetValueOut() : negative value"); 142 nValueOut += txout.nValue; 143 } 144 return nValueOut; 145 } 146 147 int64 GetMinFee(bool fDiscount=false) const 148 { 149 unsigned int nBytes = ::GetSerializeSize(*this, SER_NETWORK); 150 if (fDiscount && nBytes < 10000) 151 return 0; 152 return (1 + (int64)nBytes / 1000) * CENT; 153 } 154 155 bool ReadFromDisk(CDiskTxPos pos, FILE** pfileRet=NULL) 156 { 157 CAutoFile filein = OpenBlockFile(pos.nFile, 0, pfileRet ? "rb+" : "rb"); 158 if (!filein) 159 return error("CTransaction::ReadFromDisk() : OpenBlockFile failed"); 160 161 // Read transaction 162 if (fseek(filein, pos.nTxPos, SEEK_SET) != 0) 163 return error("CTransaction::ReadFromDisk() : fseek failed"); 164 filein >> *this; 165 166 // Return file pointer 167 if (pfileRet) 168 { 169 if (fseek(filein, pos.nTxPos, SEEK_SET) != 0) 170 return error("CTransaction::ReadFromDisk() : second fseek failed"); 171 *pfileRet = filein.release(); 172 } 173 return true; 174 } 175 176 friend bool operator==(const CTransaction& a, const CTransaction& b) 177 { 178 return (a.nVersion == b.nVersion && 179 a.vin == b.vin && 180 a.vout == b.vout && 181 a.nLockTime == b.nLockTime); 182 } 183 184 friend bool operator!=(const CTransaction& a, const CTransaction& b) 185 { 186 return !(a == b); 187 } 188 189 string ToString() const 190 { 191 string str; 192 str += strprintf("CTransaction(hash=%s, ver=%d, vin.size=%d, vout.size=%d, nLockTime=%d) ", 193 GetHash().ToString().substr(0,6).c_str(), 194 nVersion, 195 vin.size(), 196 vout.size(), 197 nLockTime); 198 for (int i = 0; i < vin.size(); i++) 199 str += " " + vin[i].ToString() + " "; 200 for (int i = 0; i < vout.size(); i++) 201 str += " " + vout[i].ToString() + " "; 202 return str; 203 } 204 205 void print() const 206 { 207 printf("%s", ToString().c_str()); 208 } 209 210 bool DisconnectInputs(CTxDB& txdb); 211 bool ConnectInputs(CTxDB& txdb, map<uint256, CTxIndex>& mapTestPool, CDiskTxPos posThisTx, int nHeight, int64& nFees, bool fBlock, bool fMiner, int64 nMinFee=0); 212 bool ClientConnectInputs(); 213 214 bool AcceptTransaction(CTxDB& txdb, bool fCheckInputs=true, bool* pfMissingInputs=NULL); 215 216 bool AcceptTransaction(bool fCheckInputs=true, bool* pfMissingInputs=NULL) 217 { 218 CTxDB txdb("r"); 219 return AcceptTransaction(txdb, fCheckInputs, pfMissingInputs); 220 } 221 222 protected: 223 bool AddToMemoryPool(); 224 public: 225 bool RemoveFromMemoryPool(); 226 };
GetHash:获取交易哈希值
IsFinal:交易是否已确定,可以看到该函数中用到了nLockTime
CheckTransaction:交易的合法性检查
IsMine:交易是否和当前钱包相关
GetDebit:钱包进账
GetCredit:钱包出账
ReadFromDisk:从本地文件读取交易
1.3 交易输入
| 上个交易输出点prevout | 解锁脚本scriptSig | 序列号nSequence |
如表所示,交易输入由上个交易输出点、交易解锁脚本及序列号组成,其中上个交易输出点包含两个元素,一个是上一个交易的哈希值,另一个是上一个交易输出的索引号,由这两个元素便可确定唯一的UTXO,一个UTXO中包含一个锁定脚本,要想花费该UTXO必须提供有效的解锁脚本,解锁脚本由签名和公钥组成,nSequence字段默认填最大值0xffffffff,该字段在替换交易时有用,这里不做过多的解释。交易输入源码定义如下:

1 class CTxIn 2 { 3 public: 4 COutPoint prevout; 5 CScript scriptSig; 6 unsigned int nSequence; 7 8 CTxIn() 9 { 10 nSequence = UINT_MAX; 11 } 12 13 explicit CTxIn(COutPoint prevoutIn, CScript scriptSigIn=CScript(), unsigned int nSequenceIn=UINT_MAX) 14 { 15 prevout = prevoutIn; 16 scriptSig = scriptSigIn; 17 nSequence = nSequenceIn; 18 } 19 20 CTxIn(uint256 hashPrevTx, unsigned int nOut, CScript scriptSigIn=CScript(), unsigned int nSequenceIn=UINT_MAX) 21 { 22 prevout = COutPoint(hashPrevTx, nOut); 23 scriptSig = scriptSigIn; 24 nSequence = nSequenceIn; 25 } 26 27 IMPLEMENT_SERIALIZE 28 ( 29 READWRITE(prevout); 30 READWRITE(scriptSig); 31 READWRITE(nSequence); 32 ) 33 34 bool IsFinal() const 35 { 36 return (nSequence == UINT_MAX); 37 } 38 39 friend bool operator==(const CTxIn& a, const CTxIn& b) 40 { 41 return (a.prevout == b.prevout && 42 a.scriptSig == b.scriptSig && 43 a.nSequence == b.nSequence); 44 } 45 46 friend bool operator!=(const CTxIn& a, const CTxIn& b) 47 { 48 return !(a == b); 49 } 50 51 string ToString() const 52 { 53 string str; 54 str += strprintf("CTxIn("); 55 str += prevout.ToString(); 56 if (prevout.IsNull()) 57 str += strprintf(", coinbase %s", HexStr(scriptSig.begin(), scriptSig.end(), false).c_str()); 58 else 59 str += strprintf(", scriptSig=%s", scriptSig.ToString().substr(0,24).c_str()); 60 if (nSequence != UINT_MAX) 61 str += strprintf(", nSequence=%u", nSequence); 62 str += ")"; 63 return str; 64 } 65 66 void print() const 67 { 68 printf("%s ", ToString().c_str()); 69 } 70 71 bool IsMine() const; 72 int64 GetDebit() const; 73 };
1.4 交易输出
| 比特币数量nValue | 锁定脚本scriptPubKey |
如表所示,交易输出由比特币数量、锁定脚本组成,其中比特币数量表明了该输出包含的比特币数量,锁定脚本对UTXO上了“锁”,谁能提供有效的解锁脚本,谁就能花费该UTXO。交易输出源码定义如下:

1 // 2 // An output of a transaction. It contains the public key that the next input 3 // must be able to sign with to claim it. 4 // 5 class CTxOut 6 { 7 public: 8 int64 nValue; 9 CScript scriptPubKey; 10 11 public: 12 CTxOut() 13 { 14 SetNull(); 15 } 16 17 CTxOut(int64 nValueIn, CScript scriptPubKeyIn) 18 { 19 nValue = nValueIn; 20 scriptPubKey = scriptPubKeyIn; 21 } 22 23 IMPLEMENT_SERIALIZE 24 ( 25 READWRITE(nValue); 26 READWRITE(scriptPubKey); 27 ) 28 29 void SetNull() 30 { 31 nValue = -1; 32 scriptPubKey.clear(); 33 } 34 35 bool IsNull() 36 { 37 return (nValue == -1); 38 } 39 40 uint256 GetHash() const 41 { 42 return SerializeHash(*this); 43 } 44 45 bool IsMine() const 46 { 47 return ::IsMine(scriptPubKey); 48 } 49 50 int64 GetCredit() const 51 { 52 if (IsMine()) 53 return nValue; 54 return 0; 55 } 56 57 friend bool operator==(const CTxOut& a, const CTxOut& b) 58 { 59 return (a.nValue == b.nValue && 60 a.scriptPubKey == b.scriptPubKey); 61 } 62 63 friend bool operator!=(const CTxOut& a, const CTxOut& b) 64 { 65 return !(a == b); 66 } 67 68 string ToString() const 69 { 70 if (scriptPubKey.size() < 6) 71 return "CTxOut(error)"; 72 return strprintf("CTxOut(nValue=%I64d.%08I64d, scriptPubKey=%s)", nValue / COIN, nValue % COIN, scriptPubKey.ToString().substr(0,24).c_str()); 73 } 74 75 void print() const 76 { 77 printf("%s ", ToString().c_str()); 78 } 79 };
1.5 加密算法及签名验证
交易验证时会用到加密算法中的签名及签名验证,所以先对比特币系统的加解密算法进行说明。比特币系统加解密算法用的是椭圆曲线加密算法,该算法属于非对称加密算法,包含公钥和私钥,公钥对外公开,私钥秘密保存,比特币钱包的私钥保存于wallet.dat文件中,所以该文件一定要秘密保存。对于椭圆曲线加密算法来说,公钥和私钥是成对的,它们可以互相加解密,总得来说可以用“公钥加密,私钥签名”八个字总结两个密钥的作用。在应用到加密场景时,可以自己对本地文件用公钥进行加密,当该加密文件被其他人盗取时,由于其他人不知道私钥,所以他们看不了文件内容;另外,其他人可以用公钥对文件加密,并通过网络传输给你,即便文件被截获,截获者不知道私钥也无法获得文件内容,只有拥有私钥的你可以正确解密文件并获取正确内容。在应用到签名场景时,可以用私钥对文件A进行加密(签名)生成结果B,并把文件A和签名结果B发送给其他人或对外公布,由于公钥是公开的,其他人用公钥对签名结果解密发现和文件A一致,所以就可以确定是文件确实是你发布的(因为只有你拥有私钥),这个加密操作好比你给文件进行了“签名”,由于其他人没有私钥所以不能仿冒,进行签名时如果文件A比较大,一般不会直接对A进行签名,而是对A进行哈希操作获得所谓的摘要,再对摘要进行签名,签名验证时也是对相应的摘要进行验证。
比特币交易中的输入和输出可能有多个,对应有不同的签名类型,目前有三类:SIGHASH_ALL,SIGHASH_NONE,SIGHASH_SINGLE。
SIGHASH_ALL
该签名类型为默认类型,也是目前绝大部分交易采用的,顾名思义即签名整单交易。首先,组织所有输出、输入,就像上文分解Hex过程一样,每个输入都对应一个签名,暂时留空,其他包括sequence等字段均须填写,这样就形成了一个完整的交易Hex(只缺签名字段)。然后,每一个输入均需使用私钥对该段数据进行签名,签名完成后各自填入相应的位置,N个输入N个签名。简单理解就是:对于该笔单子,认可且只认可的这些输入、输出,并同意花费我的那笔输入。
SIGHASH_NONE
该签名类型是最自由松散的,仅对输入签名,不对输出签名,输出可以任意指定。某人对某笔币签名后交给你,你可以在任意时刻填入任意接受地址,广播出去令其生效。简单理解就是:我同意花费我的那笔钱,至于给谁,我不关心。
SIGHASH_SINGLE
该签名类型其次自由松散,仅对自己的输入、输出签名,并留空sequence字段。其输入的次序对应其输出的次序,比如输入是第3个,那么签名的输出也是第三个。简单理解就是:我同意花费我的那笔钱,且只能花费到我认可的输出,至于单子里的其他输入、输出,我不关心。
当我们拿到一笔交易时,如何验证这个交易输入是否有效,也就是如何校验该输入所引用的输出是否有效。首先,将当前输入的解锁脚本,和该输入所引用的上一笔交易输出的锁定脚本如图8一样组合在一起,并进行下的验证过程,最终若返回TRUE,说明交易有效。
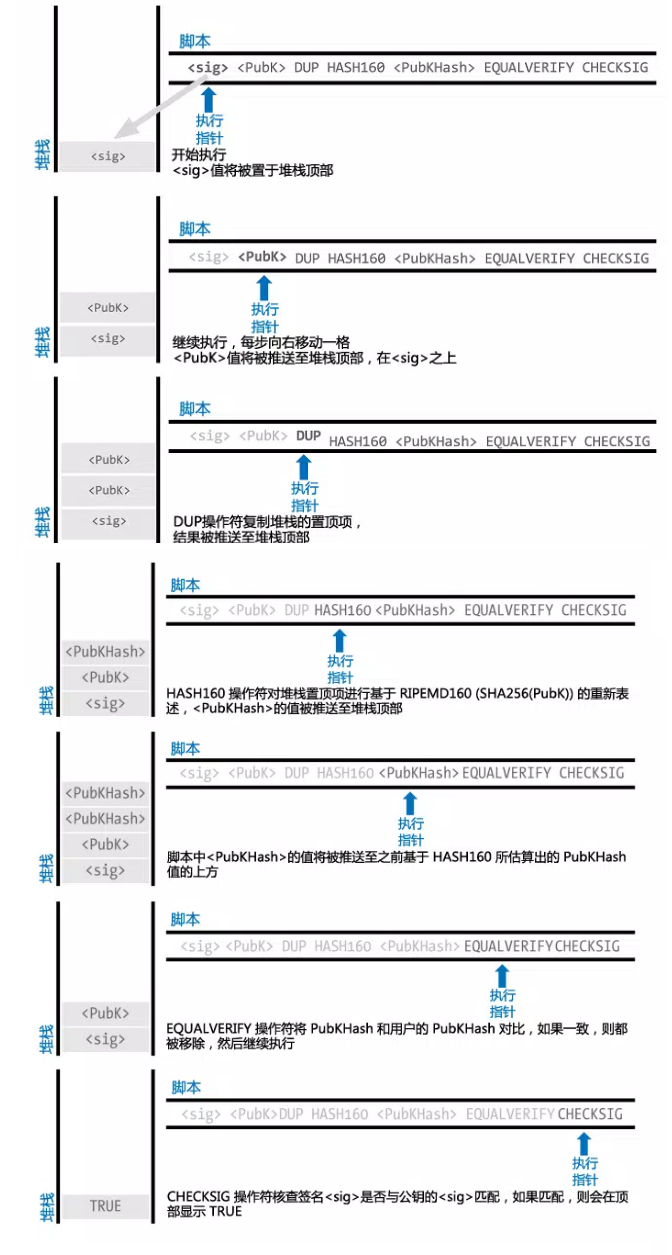
2 交易类型及实例
2.1 Coinbase交易
也称作产量交易(Generation TX),每个Block都对应一个产量交易,该类交易是没有输入交易的,产量交易产生的币是所有币的源头。以创世块包含的Coinbase交易为例来进行分析,打开比特区块文件blk00000.dat,内容如下:

F9BEB4D9 - 神奇数
0x0000011D - 区块大小285字节,不包含该长度字段
01000000 - version
0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 - prev block
3BA3EDFD7A7B12B27AC72C3E67768F617FC81BC3888A51323A9FB8AA4B1E5E4A - merkle root
29AB5F49 - timestamp
FFFF001D - bits
1DAC2B7C - nonce
01 - number of transactions
01000000 - version
01 - input
0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 - prev output
FFFFFFFF - index
4D04FFFF001D0104455468652054696D65732030332F4A616E2F32303039204368616E63656C6C6F72206F6E206272696E6B206F66207365636F6E64206261696C6F757420666F722062616E6B73 - scriptSig
FFFFFFFF - sequence
01 - outputs
00F2052A01000000 - 50 BTC
434104678AFDB0FE5548271967F1A67130B7105CD6A828E03909A67962E0EA1F61DEB649F6BC3F4CEF38C4F35504E51EC112DE5C384DF7BA0B8D578A4C702B6BF11D5FAC - scriptPubKey
00000000 - lock time
2.2 通用地址交易
该类交易是最常见的交易类型,由N个输入、M个输出构成。以交易cca7507897abc89628f450e8b1e0c6fca4ec3f7b34cccf55f3f531c659ff4d79为例进行说明,其Json格式内容如下:
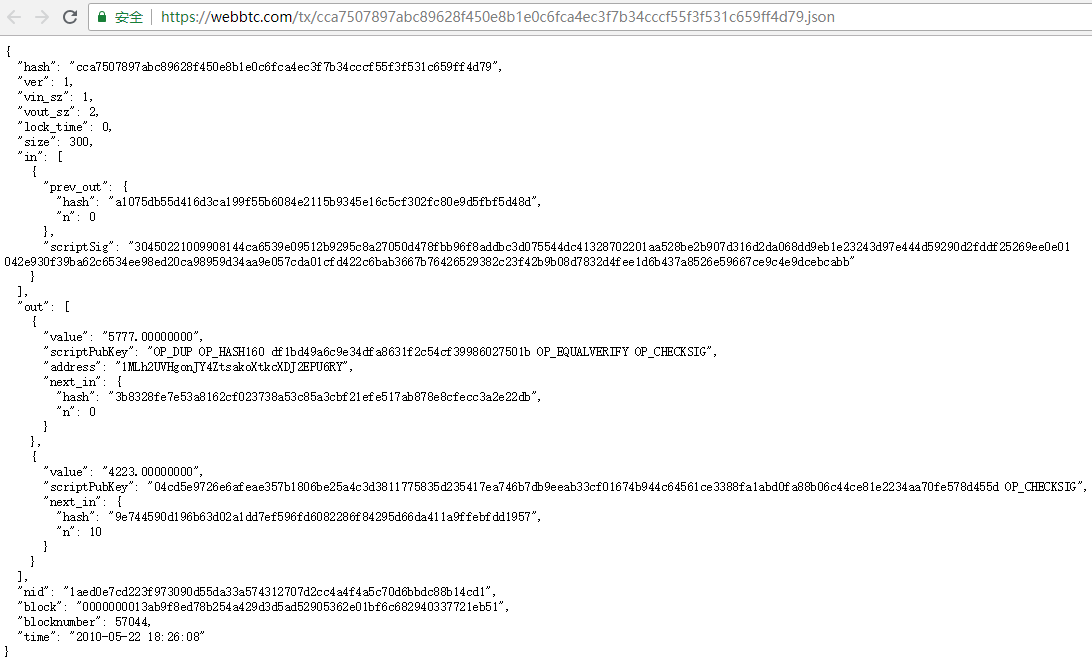
该交易包含1个输入2个输出,位于块0000000013ab9f8ed78b254a429d3d5ad52905362e01bf6c682940337721eb51中,该块包含两个交易,我们要分析的交易是第2个交易,块的二进制内容如下:

图中第1部分是块头信息,该部分的最后一个字节0x02说明该块中包含两个交易;第2部分是块中第一个交易,该交易是coinbase交易,不再详述;第3部分是第二个交易,开始4个字节0x00000001是交易版本号,之后该部分第1个红色字节0x01表示该交易有一个输入,再后面是上一个交易的哈希值0xa1075db55d416d3ca199f55b6084e2115b9345e16c5cf302fc80e9d5fbf5d48d及输出索引号0x00000000,之后粉色0x8B是交易输入解锁脚本的长度,后面蓝色部分是相应的解锁脚本,再之后红色字节0x02表示该交易有两个输出,黄色内容是第一个交易输出value值0x00000086819a7100(577700000000Satoshi=5777BTC),粉色0x19是第一个交易输出锁定脚本的长度,之后蓝色是相应锁定脚本,再后面是第二个交易输出value值0x00000062530A9F00(422300000000Satoshi=4223BTC),0x43是第二个交易输出锁定脚本的长度,之后蓝色是相应的锁定脚本,最后4个字节是交易的nLockTime,分析可知二进制内容和之前的Json格式的交易内容是能对应上的。下面看一下该交易对应的输出引用交易,由于引用交易的内容比较多,我们只列出引用交易的输出部分Json及二进制内容,如下图:

两个交易所在块的二进制文件可自行下载:https://files.cnblogs.com/files/zhaoweiwei/blockfiles.rar
3 相关源码分析
源码都是基于最初始比特币版本0.1.0,文章最后参考部分给出了源码的下载链接,读者可自行下载。
3.1 创建交易并广播
当单击发送按钮后,会获取目标地址及发送金额nValue,并调用如下代码
1 uint160 hash160; 2 bool fBitcoinAddress = AddressToHash160(strAddress, hash160); // 公钥SHA-256再执行RIPEMD-160后的值 3 4 if (fBitcoinAddress) 5 { 6 // Send to bitcoin address 7 CScript scriptPubKey; 8 scriptPubKey << OP_DUP << OP_HASH160 << hash160 << OP_EQUALVERIFY << OP_CHECKSIG; 9 10 if (!SendMoney(scriptPubKey, nValue, wtx)) 11 return; 12 13 wxMessageBox("Payment sent ", "Sending..."); 14 }
以上代码中第8行产生了锁定脚本scriptPubKey,并在第10行发送函数SendMoney中创建交易并进行了一些后续操作
1 bool SendMoney(CScript scriptPubKey, int64 nValue, CWalletTx& wtxNew) 2 { 3 CRITICAL_BLOCK(cs_main) 4 { 5 int64 nFeeRequired; 6 if (!CreateTransaction(scriptPubKey, nValue, wtxNew, nFeeRequired)) 7 { 8 string strError; 9 if (nValue + nFeeRequired > GetBalance()) 10 strError = strprintf("Error: This is an oversized transaction that requires a transaction fee of %s ", FormatMoney(nFeeRequired).c_str()); 11 else 12 strError = "Error: Transaction creation failed "; 13 wxMessageBox(strError, "Sending..."); 14 return error("SendMoney() : %s ", strError.c_str()); 15 } 16 if (!CommitTransactionSpent(wtxNew)) 17 { 18 wxMessageBox("Error finalizing transaction", "Sending..."); 19 return error("SendMoney() : Error finalizing transaction"); 20 } 21 22 printf("SendMoney: %s ", wtxNew.GetHash().ToString().substr(0,6).c_str()); 23 24 // Broadcast 25 if (!wtxNew.AcceptTransaction()) 26 { 27 // This must not fail. The transaction has already been signed and recorded. 28 throw runtime_error("SendMoney() : wtxNew.AcceptTransaction() failed "); 29 wxMessageBox("Error: Transaction not valid", "Sending..."); 30 return error("SendMoney() : Error: Transaction not valid"); 31 } 32 wtxNew.RelayWalletTransaction(); 33 } 34 MainFrameRepaint(); 35 return true; 36 }
3.1.1 新建交易
第6行代码处调用CreateTransaction函数创建新的交易,在该函数中又有以下主要关键点
(1)选取未花费的目标交易集(目标UTXO集)
从账户中选取目标UTXO集,选取主要遵循这样的原则:
1)如果存在某UTXO值正好等于发送金额nValue(已包含手续费nFee),则将该UTXO加入目标交易集并返回成功
2)找出账户中UTXO值小于发送金额nValue的UTXO集vValue,并将vValue中所有UTXO值求和为nTotalLower,并找出所有UTXO值大于nValue的最小值nLowestLarger,再分两种情况
2.1)nTotalLower小于nValue,如果nLowestLarger存在,则将该值对应的pcoinLowestLarger交易加入目标交易集并返回成功,如果nLowestLarger不存在,则说明“余额”不足,返回失败
2.2)nTotalLower大于nValue,则使用随进逼近法(最多1000次)找出UTXO值的和nBest最接近nValue的集合vfBest,看nBest和nLowestLarger(如果存在)谁更接近nValue,则选择谁为相应的目标UTXO集,并返回成功
以上总结为一句话就是,选择账户中最接近发送金额nValue的UTXO优先花费,该部分内容可参考:http://www.360bchain.com/article/123.html
1 // Choose coins to use 2 set<CWalletTx*> setCoins; 3 if (!SelectCoins(nValue, setCoins)) 4 return false; 5 int64 nValueIn = 0; 6 foreach(CWalletTx* pcoin, setCoins) 7 nValueIn += pcoin->GetCredit();
(2)填充输出和输入
1 // Fill vout[0] to the payee 2 wtxNew.vout.push_back(CTxOut(nValueOut, scriptPubKey)); 3 4 // Fill vout[1] back to self with any change 5 if (nValueIn > nValue) 6 { 7 // Use the same key as one of the coins 8 vector<unsigned char> vchPubKey; 9 CTransaction& txFirst = *(*setCoins.begin()); 10 foreach(const CTxOut& txout, txFirst.vout) 11 if (txout.IsMine()) 12 if (ExtractPubKey(txout.scriptPubKey, true, vchPubKey)) 13 break; 14 if (vchPubKey.empty()) 15 return false; 16 17 // Fill vout[1] to ourself 18 CScript scriptPubKey; 19 scriptPubKey << vchPubKey << OP_CHECKSIG; 20 wtxNew.vout.push_back(CTxOut(nValueIn - nValue, scriptPubKey)); 21 } 22 23 // Fill vin 24 foreach(CWalletTx* pcoin, setCoins) 25 for (int nOut = 0; nOut < pcoin->vout.size(); nOut++) 26 if (pcoin->vout[nOut].IsMine()) 27 wtxNew.vin.push_back(CTxIn(pcoin->GetHash(), nOut));
注意5~21行,如果目标UTXO集值的和大于发送目标则将剩余的再还给本账户。
(3)签名
1 // Sign 2 int nIn = 0; 3 foreach(CWalletTx* pcoin, setCoins) 4 for (int nOut = 0; nOut < pcoin->vout.size(); nOut++) 5 if (pcoin->vout[nOut].IsMine()) 6 SignSignature(*pcoin, wtxNew, nIn++);
在SignSignature函数中,调用SignatureHash来获取交易哈希值,调用Solver对交易哈希值进行签名。
(4)重新计算交易费
1 // Check that enough fee is included 2 if (nFee < wtxNew.GetMinFee(true)) 3 { 4 nFee = nFeeRequiredRet = wtxNew.GetMinFee(true); 5 continue; 6 }
如果默认的交易费小于当前计算的交易费用,则需要根据当前计算的交易费重新填充交易。
(5)后续处理
1 // Fill vtxPrev by copying from previous transactions vtxPrev 2 wtxNew.AddSupportingTransactions(txdb); 3 wtxNew.fTimeReceivedIsTxTime = true;
该函数作用还不太明白。
3.1.2 提交请求
本节开始部分源码中的CommitTransactionSpent函数用于“提交请求”,函数中会修改本地的一些存储信息(CommitTransactionSpent),在修改本地的存储信息中有一点很关键,就是标记该交易是已被花费过的。注意这里的标记是和CWalletTx相绑定的,并且标记的是当前的这个新产生的交易的TxIn所关联的交易。因为我们一般都认为在一个交易中一个参与者只应该提供一个地址,所以对于这个交易者来说,CWalletTx的fSpend标记可以代表这个交易对于该交易者的Out有没有有被花费(也就是说fSpend是针对该交易者的),之后在检索的时候可以节省很多。

1 // Call after CreateTransaction unless you want to abort 2 bool CommitTransactionSpent(const CWalletTx& wtxNew) 3 { 4 CRITICAL_BLOCK(cs_main) 5 CRITICAL_BLOCK(cs_mapWallet) 6 { 7 //// todo: make this transactional, never want to add a transaction 8 //// without marking spent transactions 9 10 // Add tx to wallet, because if it has change it's also ours, 11 // otherwise just for transaction history. 12 AddToWallet(wtxNew); 13 14 // Mark old coins as spent 15 set<CWalletTx*> setCoins; 16 foreach(const CTxIn& txin, wtxNew.vin) 17 setCoins.insert(&mapWallet[txin.prevout.hash]); 18 foreach(CWalletTx* pcoin, setCoins) 19 { 20 pcoin->fSpent = true; 21 pcoin->WriteToDisk(); 22 vWalletUpdated.push_back(make_pair(pcoin->GetHash(), false)); 23 } 24 } 25 MainFrameRepaint(); 26 return true; 27 }
3.1.3 接受交易
1 // Broadcast 2 if (!wtxNew.AcceptTransaction()) 3 { 4 // This must not fail. The transaction has already been signed and recorded. 5 throw runtime_error("SendMoney() : wtxNew.AcceptTransaction() failed "); 6 wxMessageBox("Error: Transaction not valid", "Sending..."); 7 return error("SendMoney() : Error: Transaction not valid"); 8 }
该函数最终会调用到CTransaction类的AcceptTransaction函数,在其中会进行一系列有效性检查,通过检查后会把交易放入到交易内存池。
(1)检查交易是否有效
1 // Coinbase is only valid in a block, not as a loose transaction 2 if (IsCoinBase()) 3 return error("AcceptTransaction() : coinbase as individual tx"); 4 5 if (!CheckTransaction()) 6 return error("AcceptTransaction() : CheckTransaction failed");
(2)检查交易是否已经存在
1 // Do we already have it? 2 uint256 hash = GetHash(); 3 CRITICAL_BLOCK(cs_mapTransactions) 4 if (mapTransactions.count(hash)) 5 return false; 6 if (fCheckInputs) 7 if (txdb.ContainsTx(hash)) 8 return false;
(3)检查交易是否冲突
1 // Check for conflicts with in-memory transactions 2 CTransaction* ptxOld = NULL; 3 for (int i = 0; i < vin.size(); i++) 4 { 5 COutPoint outpoint = vin[i].prevout; 6 if (mapNextTx.count(outpoint)) 7 { 8 // Allow replacing with a newer version of the same transaction 9 if (i != 0) 10 return false; 11 ptxOld = mapNextTx[outpoint].ptx; 12 if (!IsNewerThan(*ptxOld)) 13 return false; 14 for (int i = 0; i < vin.size(); i++) 15 { 16 COutPoint outpoint = vin[i].prevout; 17 if (!mapNextTx.count(outpoint) || mapNextTx[outpoint].ptx != ptxOld) 18 return false; 19 } 20 break; 21 } 22 }
(4)检查交易中的前置交易
1 // Check against previous transactions 2 map<uint256, CTxIndex> mapUnused; 3 int64 nFees = 0; 4 if (fCheckInputs && !ConnectInputs(txdb, mapUnused, CDiskTxPos(1,1,1), 0, nFees, false, false)) 5 { 6 if (pfMissingInputs) 7 *pfMissingInputs = true; 8 return error("AcceptTransaction() : ConnectInputs failed %s", hash.ToString().substr(0,6).c_str()); 9 }
(5)将交易提交到内存池
1 // Store transaction in memory 2 CRITICAL_BLOCK(cs_mapTransactions) 3 { 4 if (ptxOld) 5 { 6 printf("mapTransaction.erase(%s) replacing with new version ", ptxOld->GetHash().ToString().c_str()); 7 mapTransactions.erase(ptxOld->GetHash()); 8 } 9 AddToMemoryPool(); 10 }
(6)移除旧版本交易
1 ///// are we sure this is ok when loading transactions or restoring block txes 2 // If updated, erase old tx from wallet 3 if (ptxOld) 4 EraseFromWallet(ptxOld->GetHash());
3.1.4 广播交易
1 wtxNew.RelayWalletTransaction();
最终会调用如下函数把交易广播到所连接的每个节点
1 void CWalletTx::RelayWalletTransaction(CTxDB& txdb) 2 { 3 foreach(const CMerkleTx& tx, vtxPrev) 4 { 5 if (!tx.IsCoinBase()) 6 { 7 uint256 hash = tx.GetHash(); 8 if (!txdb.ContainsTx(hash)) 9 RelayMessage(CInv(MSG_TX, hash), (CTransaction)tx); 10 } 11 } 12 if (!IsCoinBase()) 13 { 14 uint256 hash = GetHash(); 15 if (!txdb.ContainsTx(hash)) 16 { 17 printf("Relaying wtx %s ", hash.ToString().substr(0,6).c_str()); 18 RelayMessage(CInv(MSG_TX, hash), (CTransaction)*this); 19 } 20 } 21 }
3.2 接收交易并处理
钱包作为节点会在函数循环ThreadMessageHandler2中会调用函数ProcessMessages不断接收来自其他节点的各种消息,在该函数中又会调用ProcessMessage来处理接收的各种消息,以下是对交易消息处理的代码段:
1 else if (strCommand == "tx") 2 { 3 vector<uint256> vWorkQueue; 4 CDataStream vMsg(vRecv); 5 CTransaction tx; 6 vRecv >> tx; 7 8 CInv inv(MSG_TX, tx.GetHash()); 9 pfrom->AddInventoryKnown(inv); 10 11 bool fMissingInputs = false; 12 if (tx.AcceptTransaction(true, &fMissingInputs)) 13 { 14 AddToWalletIfMine(tx, NULL); 15 RelayMessage(inv, vMsg); 16 mapAlreadyAskedFor.erase(inv); 17 vWorkQueue.push_back(inv.hash); 18 19 // Recursively process any orphan transactions that depended on this one 20 for (int i = 0; i < vWorkQueue.size(); i++) 21 { 22 uint256 hashPrev = vWorkQueue[i]; 23 for (multimap<uint256, CDataStream*>::iterator mi = mapOrphanTransactionsByPrev.lower_bound(hashPrev); 24 mi != mapOrphanTransactionsByPrev.upper_bound(hashPrev); 25 ++mi) 26 { 27 const CDataStream& vMsg = *((*mi).second); 28 CTransaction tx; 29 CDataStream(vMsg) >> tx; 30 CInv inv(MSG_TX, tx.GetHash()); 31 32 if (tx.AcceptTransaction(true)) 33 { 34 printf(" accepted orphan tx %s ", inv.hash.ToString().substr(0,6).c_str()); 35 AddToWalletIfMine(tx, NULL); 36 RelayMessage(inv, vMsg); 37 mapAlreadyAskedFor.erase(inv); 38 vWorkQueue.push_back(inv.hash); 39 } 40 } 41 } 42 43 foreach(uint256 hash, vWorkQueue) 44 EraseOrphanTx(hash); 45 } 46 else if (fMissingInputs) 47 { 48 printf("storing orphan tx %s ", inv.hash.ToString().substr(0,6).c_str()); 49 AddOrphanTx(vMsg); 50 } 51 }
可以看到源码12行调用了和交易生成时相同的函数AcceptTransaction,也会对接收到交易做一系列的合法性检查,如果通过检查,该交易会继续被进行广播。另外,如果交易中的前置交易缺失而导致无法通过检查,则认为该交易是OrphanTransaction,会暂时把它放到mapOrphanTransactionsByPrev队列中,每次有通过检查的新的交易,都会检查新的交易是否为mapOrphanTransactionsByPrev队列中OrphanTransaction的前置交易,如果是则继续检查OrphanTransaction合法性,如果合法则继续广播该OrphanTransaction交易,并把该OrphanTransaction从队列里移除。
参考
谈谈自己对比特币脚本的理解:https://blog.csdn.net/pony_maggie/article/details/73656597
比特币源码解读之交易发起:http://www.360bchain.com/article/89.html
比特币交易原理分析:https://blog.csdn.net/wen294299195/article/details/80220651
比特币0.1.0版本源码:https://files.cnblogs.com/files/zhaoweiwei/bitcoin-0.1.0.rar
