A way to make a new task is to make it nondeterministic or probabilistic. For example, the hard task of Topcoder SRM 595, Constellation, is the probabilistic version of a convex hull.
Let's try to make a new task. Firstly we will use the following task. There are n people, sort them by their name. It is just an ordinary sorting problem, but we can make it more interesting by adding nondeterministic element. There are n people, each person will use either his/her first name or last name as a handle. Can the lexicographical order of the handles be exactly equal to the given permutation p?
More formally, if we denote the handle of the i-th person as hi, then the following condition must hold: 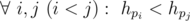 .
.
The first line contains an integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 105) — the number of people.
The next n lines each contains two strings. The i-th line contains strings fi and si (1 ≤ |fi|, |si| ≤ 50) — the first name and last name of thei-th person. Each string consists only of lowercase English letters. All of the given 2n strings will be distinct.
The next line contains n distinct integers: p1, p2, ..., pn (1 ≤ pi ≤ n).
If it is possible, output "YES", otherwise output "NO".
3 gennady korotkevich petr mitrichev gaoyuan chen 1 2 3
NO
3 gennady korotkevich petr mitrichev gaoyuan chen 3 1 2
YES
2 galileo galilei nicolaus copernicus 2 1
YES
10 rean schwarzer fei claussell alisa reinford eliot craig laura arseid jusis albarea machias regnitz sara valestin emma millstein gaius worzel 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
NO
10 rean schwarzer fei claussell alisa reinford eliot craig laura arseid jusis albarea machias regnitz sara valestin emma millstein gaius worzel 2 4 9 6 5 7 1 3 8 10
YES
In example 1 and 2, we have 3 people: tourist, Petr and me (cgy4ever). You can see that whatever handle is chosen, I must be the first, then tourist and Petr must be the last.
In example 3, if Copernicus uses "copernicus" as his handle, everything will be alright.
给出n个人,每个人有两个字符串的人名可以用,再给出一个顺序,要求按照这个顺序取人名,每人取一个,使得字符串排列严格递增
就是sb题!但是我看不懂英文蛋疼了好久……唉文化课不行伤不起
我的代码好长……在可行的情况下一定是取字符串小的好,每次比较两个字符串和当前的解的大小,然后取一个小的。如果两个都不行,直接打‘NO’
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
#include<queue>
#include<deque>
#include<set>
#include<map>
#include<ctime>
#define LL long long
#define inf 0x7ffffff
#define pa pair<int,int>
using namespace std;
struct people{
char ch1[51],ch2[51];
}a[100010];
LL n;
LL s[100010];
char now[51];
inline LL read()
{
LL x=0,f=1;char ch=getchar();
while(ch<'0'||ch>'9'){if(ch=='-')f=-1;ch=getchar();}
while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9'){x=x*10+ch-'0';ch=getchar();}
return x*f;
}
inline int cmp(char a[51],char b[51])
{
int l1=strlen(a+1);
int l2=strlen(b+1);
for (int i=1;i<=min(l1,l2);i++)
{
if (a[i]<b[i])return 1;
if (a[i]>b[i])return -1;
}
if (l1<l2)return 1;
if (l1>l2)return -1;
return 0;
}
int main()
{
n=read();
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++)scanf("%s%s",a[i].ch1+1,a[i].ch2+1);
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++)s[i]=read();
now[1]='A';
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
int aaa=s[i];
char work1[51],work2[51];
memset(work1,0,sizeof(work1));
memset(work2,0,sizeof(work2));
if (cmp(a[aaa].ch1,a[aaa].ch2)==1)
{
for(int j=1;j<=strlen(a[aaa].ch1+1);j++)work1[j]=a[aaa].ch1[j];
for(int j=1;j<=strlen(a[aaa].ch2+1);j++)work2[j]=a[aaa].ch2[j];
}else
{
for(int j=1;j<=strlen(a[aaa].ch2+1);j++)work1[j]=a[aaa].ch2[j];
for(int j=1;j<=strlen(a[aaa].ch1+1);j++)work2[j]=a[aaa].ch1[j];
}
int l1=strlen(work1+1);
int l2=strlen(work2+1);
if (cmp(now,work2)==-1)
{
printf("NO");
return 0;
}else
{
if (cmp(now,work1)==-1)
{
memset(now,0,sizeof(now));
for (int j=1;j<=l2;j++)now[j]=work2[j];
}else
{
memset(now,0,sizeof(now));
for (int j=1;j<=l1;j++)now[j]=work1[j];
}
}
}
printf("YES");
}