此处处理非结构化数据(即自然语言)。
1.item_description(描述)
计算描述的字符长度
def wordCount(text): # convert to lower case and strip regex try: # convert to lower case and strip regex text = text.lower() regex = re.compile('[' +re.escape(string.punctuation) + '0-9\r\t\n]') txt = regex.sub(" ", text) # tokenize # words = nltk.word_tokenize(clean_txt) # remove words in stop words words = [w for w in txt.split(" ") if not w in stop_words.ENGLISH_STOP_WORDS and len(w)>3] return len(words) except: return 0 # add a column of word counts to both the training and test set train['desc_len'] = train['item_description'].apply(lambda x: wordCount(x)) test['desc_len'] = test['item_description'].apply(lambda x: wordCount(x)) train.head()

分析价格和字符长度之间的关系
df = train.groupby('desc_len')['price'].mean().reset_index() trace1 = go.Scatter( x = df['desc_len'], y = np.log(df['price']+1), mode = 'lines+markers', name = 'lines+markers' ) layout = dict(title= 'Average Log(Price) by Description Length', yaxis = dict(title='Average Log(Price)'), xaxis = dict(title='Description Length')) fig=dict(data=[trace1], layout=layout) py.iplot(fig)
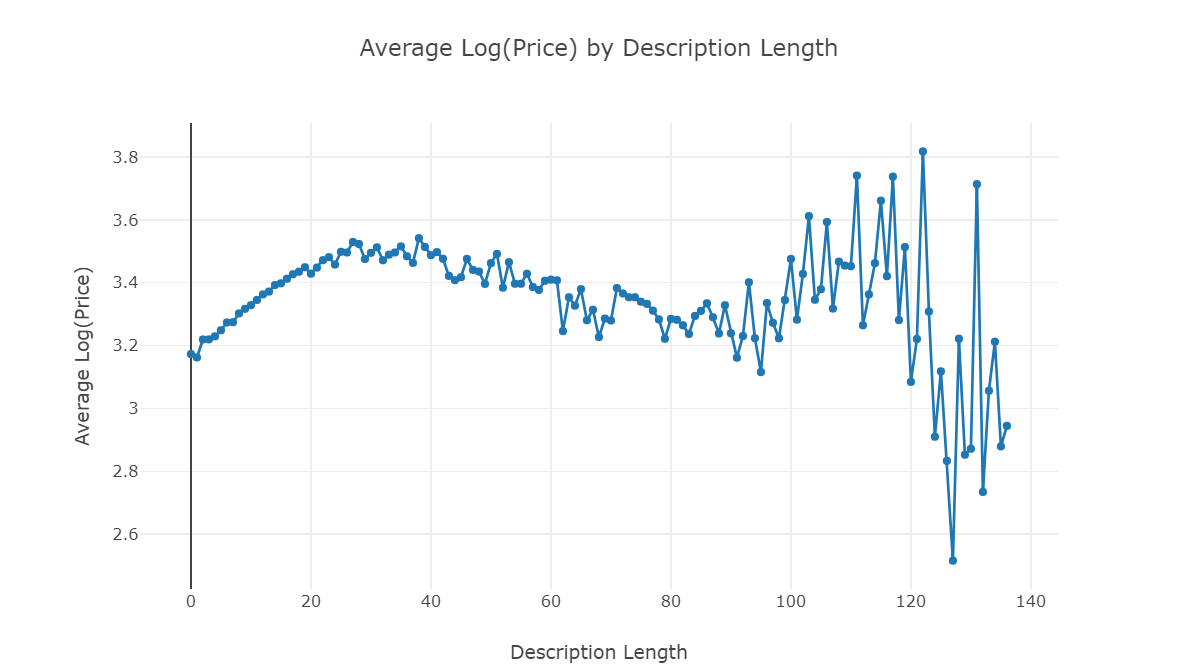
移除异常值(即没有描述的行)
预处理:分词
1.先把描述拆分成句子,然后再把句子拆分成单词
2.移除标点和停词
3.单词小写
4.考虑单词长度等于或者大于3
stop = set(stopwords.words('english')) def tokenize(text): """ sent_tokenize(): segment text into sentences word_tokenize(): break sentences into words """ try: regex = re.compile('[' +re.escape(string.punctuation) + '0-9\r\t\n]') text = regex.sub(" ", text) # remove punctuation tokens_ = [word_tokenize(s) for s in sent_tokenize(text)] tokens = [] for token_by_sent in tokens_: tokens += token_by_sent tokens = list(filter(lambda t: t.lower() not in stop, tokens)) filtered_tokens = [w for w in tokens if re.search('[a-zA-Z]', w)] filtered_tokens = [w.lower() for w in filtered_tokens if len(w)>=3] return filtered_tokens except TypeError as e: print(text,e)
# apply the tokenizer into the item descriptipn column train['tokens'] = train['item_description'].map(tokenize) test['tokens'] = test['item_description'].map(tokenize)
查看分词效果
for description, tokens in zip(train['item_description'].head(), train['tokens'].head()): print('description:', description) print('tokens:', tokens) print()

使用词云查看描述的词汇在每个标签中出现的频率
# build dictionary with key=category and values as all the descriptions related. cat_desc = dict() for cat in general_cats: text = " ".join(train.loc[train['general_cat']==cat, 'item_description'].values) cat_desc[cat] = tokenize(text) # find the most common words for the top 4 categories women100 = Counter(cat_desc['Women']).most_common(100) beauty100 = Counter(cat_desc['Beauty']).most_common(100) kids100 = Counter(cat_desc['Kids']).most_common(100) electronics100 = Counter(cat_desc['Electronics']).most_common(100)
def generate_wordcloud(tup): wordcloud = WordCloud(background_color='white', max_words=50, max_font_size=40, random_state=42 ).generate(str(tup)) return wordcloud
fig,axes = plt.subplots(2, 2, figsize=(30, 15)) ax = axes[0, 0] ax.imshow(generate_wordcloud(women100), interpolation="bilinear") ax.axis('off') ax.set_title("Women Top 100", fontsize=30) ax = axes[0, 1] ax.imshow(generate_wordcloud(beauty100)) ax.axis('off') ax.set_title("Beauty Top 100", fontsize=30) ax = axes[1, 0] ax.imshow(generate_wordcloud(kids100)) ax.axis('off') ax.set_title("Kids Top 100", fontsize=30) ax = axes[1, 1] ax.imshow(generate_wordcloud(electronics100)) ax.axis('off') ax.set_title("Electronic Top 100", fontsize=30)

预处理:tf-idf
使用tf-idf计算每个词的在文本中的重要性
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer vectorizer = TfidfVectorizer(min_df=10, max_features=180000, tokenizer=tokenize, ngram_range=(1, 2))
all_desc = np.append(train['item_description'].values, test['item_description'].values) vz = vectorizer.fit_transform(list(all_desc))
vz是一个tfidf矩阵:
·行数是描述的总书
·列数是相应描述在词上的个数
计算tfidf值
# create a dictionary mapping the tokens to their tfidf values tfidf = dict(zip(vectorizer.get_feature_names(), vectorizer.idf_)) tfidf = pd.DataFrame(columns=['tfidf']).from_dict( dict(tfidf), orient='index') tfidf.columns = ['tfidf']
查看tfidf值最小的10个词
tfidf.sort_values(by=['tfidf'], ascending=True).head(10)

查看tfidf值最大的10个词
tfidf.sort_values(by=['tfidf'], ascending=False).head(10)

由于tfidf矩阵太大,我们需要对他进行降维
这里使用t-SNE算法进行降维,但是t-SNE算法的时间复杂度相对较高,tfidf矩阵维度
又太大,我们需要先使用SVD先把矩阵降到50维,然后再使用t-SNE
trn = train.copy() tst = test.copy() trn['is_train'] = 1 tst['is_train'] = 0 sample_sz = 15000 combined_df = pd.concat([trn, tst]) combined_sample = combined_df.sample(n=sample_sz) vz_sample = vectorizer.fit_transform(list(combined_sample['item_description']))
from sklearn.decomposition import TruncatedSVD n_comp=30 svd = TruncatedSVD(n_components=n_comp, random_state=42) svd_tfidf = svd.fit_transform(vz_sample)
使用t-SNE
from sklearn.manifold import TSNE tsne_model = TSNE(n_components=2, verbose=1, random_state=42, n_iter=500)
tsne_tfidf = tsne_model.fit_transform(svd_tfidf)

进行可视化数据
output_notebook() plot_tfidf = bp.figure(plot_width=700, plot_height=600, title="tf-idf clustering of the item description", tools="pan,wheel_zoom,box_zoom,reset,hover,previewsave", x_axis_type=None, y_axis_type=None, min_border=1)
combined_sample.reset_index(inplace=True, drop=True)
tfidf_df = pd.DataFrame(tsne_tfidf, columns=['x', 'y']) tfidf_df['description'] = combined_sample['item_description'] tfidf_df['tokens'] = combined_sample['tokens'] tfidf_df['category'] = combined_sample['general_cat']
plot_tfidf.scatter(x='x', y='y', source=tfidf_df, alpha=0.7) hover = plot_tfidf.select(dict(type=HoverTool)) hover.tooltips={"description": "@description", "tokens": "@tokens", "category":"@category"} show(plot_tfidf)

图中颜色深的圆点是因为数量多导致的
2.使用k-means进行聚类
from sklearn.cluster import MiniBatchKMeans num_clusters = 30 # need to be selected wisely kmeans_model = MiniBatchKMeans(n_clusters=num_clusters, init='k-means++', n_init=1, init_size=1000, batch_size=1000, verbose=0, max_iter=1000)
kmeans = kmeans_model.fit(vz) kmeans_clusters = kmeans.predict(vz) kmeans_distances = kmeans.transform(vz)
sorted_centroids = kmeans.cluster_centers_.argsort()[:, ::-1] terms = vectorizer.get_feature_names() for i in range(num_clusters): print("Cluster %d:" % i) aux = '' for j in sorted_centroids[i, :10]: aux += terms[j] + ' | ' print(aux) print()
聚类完成后 我们需要把他降到二维来展示
# repeat the same steps for the sample kmeans = kmeans_model.fit(vz_sample) kmeans_clusters = kmeans.predict(vz_sample) kmeans_distances = kmeans.transform(vz_sample) # reduce dimension to 2 using tsne tsne_kmeans = tsne_model.fit_transform(kmeans_distances)
#combined_sample.reset_index(drop=True, inplace=True) kmeans_df = pd.DataFrame(tsne_kmeans, columns=['x', 'y']) kmeans_df['cluster'] = kmeans_clusters kmeans_df['description'] = combined_sample['item_description'] kmeans_df['category'] = combined_sample['general_cat'] #kmeans_df['cluster']=kmeans_df.cluster.astype(str).astype('category')
plot_kmeans = bp.figure(plot_width=700, plot_height=600, title="KMeans clustering of the description", tools="pan,wheel_zoom,box_zoom,reset,hover,previewsave", x_axis_type=None, y_axis_type=None, min_border=1)
source = ColumnDataSource(data=dict(x=kmeans_df['x'], y=kmeans_df['y'], color=colormap[kmeans_clusters], description=kmeans_df['description'], category=kmeans_df['category'], cluster=kmeans_df['cluster'])) plot_kmeans.scatter(x='x', y='y', color='color', source=source) hover = plot_kmeans.select(dict(type=HoverTool)) hover.tooltips={"description": "@description", "category": "@category", "cluster":"@cluster" } show(plot_kmeans)

使用LDA进行文本主题提取
它的输入是一个词库,即每个文档表示为一行,每列包含语料库中单词的计数。
我们将使用一个称为pyLDAvis的强大工具,为我们提供LDA的交互式可视化。
cvectorizer = CountVectorizer(min_df=4, max_features=180000, tokenizer=tokenize, ngram_range=(1,2))
cvz = cvectorizer.fit_transform(combined_sample['item_description'])
lda_model = LatentDirichletAllocation(n_components=20, learning_method='online', max_iter=20, random_state=42)
X_topics = lda_model.fit_transform(cvz)
n_top_words = 10 topic_summaries = [] topic_word = lda_model.components_ # get the topic words vocab = cvectorizer.get_feature_names() for i, topic_dist in enumerate(topic_word): topic_words = np.array(vocab)[np.argsort(topic_dist)][:-(n_top_words+1):-1] topic_summaries.append(' '.join(topic_words)) print('Topic {}: {}'.format(i, ' | '.join(topic_words)))

降维
# reduce dimension to 2 using tsne tsne_lda = tsne_model.fit_transform(X_topics)

unnormalized = np.matrix(X_topics) doc_topic = unnormalized/unnormalized.sum(axis=1) lda_keys = [] for i, tweet in enumerate(combined_sample['item_description']): lda_keys += [doc_topic[i].argmax()] lda_df = pd.DataFrame(tsne_lda, columns=['x','y']) lda_df['description'] = combined_sample['item_description'] lda_df['category'] = combined_sample['general_cat'] lda_df['topic'] = lda_keys lda_df['topic'] = lda_df['topic'].map(int)
source = ColumnDataSource(data=dict(x=lda_df['x'], y=lda_df['y'], color=colormap[lda_keys], description=lda_df['description'], topic=lda_df['topic'], category=lda_df['category'])) plot_lda.scatter(source=source, x='x', y='y', color='color') hover = plot_kmeans.select(dict(type=HoverTool)) hover = plot_lda.select(dict(type=HoverTool)) hover.tooltips={"description":"@description", "topic":"@topic", "category":"@category"} show(plot_lda)

def prepareLDAData(): data = { 'vocab': vocab, 'doc_topic_dists': doc_topic, 'doc_lengths': list(lda_df['len_docs']), 'term_frequency':cvectorizer.vocabulary_, 'topic_term_dists': lda_model.components_ } return data

import pyLDAvis lda_df['len_docs'] = combined_sample['tokens'].map(len) ldadata = prepareLDAData() pyLDAvis.enable_notebook() prepared_data = pyLDAvis.prepare(**ldadata)
import IPython.display from IPython.core.display import display, HTML, Javascript #h = IPython.display.display(HTML(html_string)) #IPython.display.display_HTML(h)