一.概述
-
在日常开发中我们经常执行定时任务,此时我们可以使用守护线程或者是Timer类,此处我们避免守护线程使用的繁琐就使用Timer类
1.Timer类和TimerTask类
-
在java.util包下
-
Timer类:实现线程任务调度
-
void schedule(TimerTask task, long delay, long period) :在指定的延迟之后开始 ,重新执行固定延迟执行的指定任务。
-
void schedule(TimerTask task, long delay) :在指定的延迟之后安排指定的任务执行。
-
-
TimerTask类:实现定时处理任务的接口,我们需要实现此接口来完成定时任务
转载:https://www.cnblogs.com/xsjzhao/p/10651704.html
1 关于 (时间宝贵的请跳过)
- 什么是定时任务调度
基于给定的时间点,给定的时间间隔或者给定的执行次数自动执行的任务。
- 在Java中的定时调度工具
- Timer
- Quartz
- Timer
- 两者主要区别
- 出身上,Timer是Java提供的原生Scheduler(任务调度)工具类,不需要导入其他jar包;而Quartz是OpenSymphony开源组织在任务调度领域的一个开源项目,完全基于Java实现。
- 功能上,如需要实现在某个具体时间执行什么任务的话,Timer足以胜任;如需要实现每个星期六8点闹钟提醒之类的复杂任务,就需要用Quartz。因此,Quartz在时间控制上的功能远比Timer强大和完善。
- 底层上,Timer使用一个后台线程去执行定时任务,Quartz拥有后台线程执行池(类比JDBC连接池),能够使用多个执行线程去执行定时任务。
- 出身上,Timer是Java提供的原生Scheduler(任务调度)工具类,不需要导入其他jar包;而Quartz是OpenSymphony开源组织在任务调度领域的一个开源项目,完全基于Java实现。
简而言之,Quartz > Timer,Timer是被动地根据既定时间去调度任务的,Quartz则是自己主动定制时间规则去支持更加丰富地调度方法。
本文主要是讲解Timer工具类的,故而下文中不会过多讨论Quartz。
- 前导知识
| Timer, Quartz的使用 | Quartz, Spring的整合 |
|---|---|
| Java编程知识 | Spring基础知识 |
2 Timer简介和配套视频课程
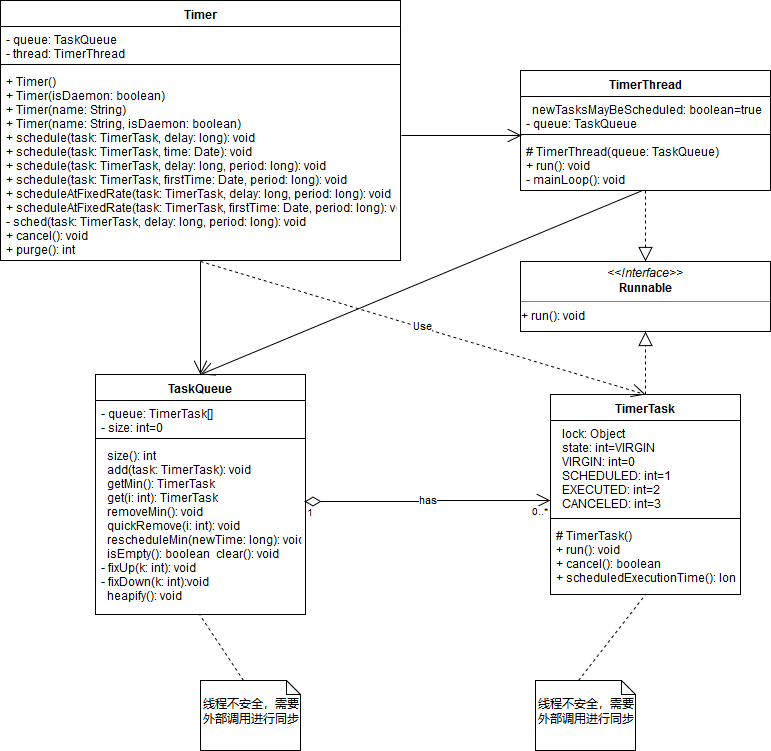
Timer类位于java.util包下,有关Timer类的详细描述信息请点击这里访问Oracle Java的官方api文档查阅。
Timer工具类图是Timer工具类及有关类的类图。
快速开始:
/*
* Foo.java -- JDK 1.8
*/
package timer;
import java.util.Timer;
import java.util.TimerTask;
/**
* Description:
* <p>
* <p>
* @author ascribed
* @date 2019-04-03 Wed PM 19:15:08
*/
public class Foo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Timer timer = new Timer(); // 1. 创建Timer实例,关联线程不能是daemon(守护/后台)线程
FooTimerTask fooTimerTask = new FooTimerTask(); // 2. 创建任务对象
timer.schedule(fooTimerTask, 3000L, 2000L); // 3. 通过Timer定时定频率调用fooTimerTask的业务代码
}
}
class FooTimerTask extends TimerTask {
@Override
public void run() {
// TODO 业务代码......
System.out.println("Hello Timer!");
}
}3 Timer函数和综合运用
3.1 Timer定时函数的用法
注意:Timer类在时间granularity(粒度)是毫秒级的,实际上Timer的schedule系列方法获取时间的方式是System.currentTimeMillis()(当前时间与Unix元年之差,类型为long),最多只能到毫秒级,而一些操作系统的计时精度会达到1/10毫秒。
3.1.1 schedule()方法的4种用法
- schedule(TimerTask task, Date time)
作用
在时间等于或超过time的时候执行且仅执行一次task (单次)。
源码
public void schedule(TimerTask task, Date time) {
sched(task, time.getTime(), 0);
}- schedule(TimerTask task, Date firstTime, long period)
作用
时间等于或超过firstTime时首次执行task,之后每隔peroid毫秒重复执行一次task (多次)。
源码
public void schedule(TimerTask task, long delay, long period) {
if (delay < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Negative delay.");
if (period <= 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Non-positive period.");
sched(task, System.currentTimeMillis()+delay, -period);
}- schedule(TimerTask task, long delay)
作用
等待delay毫秒后执行且仅执行一次task (单次)。
源码
public void schedule(TimerTask task, long delay) {
if (delay < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Negative delay.");
sched(task, System.currentTimeMillis()+delay, 0);
}- schedule(TimerTask task, long delay, long period)
作用
等待delay毫秒后首次执行task, 之后每个period毫秒重复执行一次task (多次)。
源码
public void scheduleAtFixedRate(TimerTask task, long delay, long period) {
if (delay < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Negative delay.");
if (period <= 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Non-positive period.");
sched(task, System.currentTimeMillis()+delay, period);
}3.1.2 scheduleAfixRate()的2种用法
- scheduleAtFixedRate(TimerTask task, Date firstTime, long period)
作用
时间等于或超过time时首次执行task,之后每隔peroid毫秒重复执行一次task (多次, 同schedule第2种用法)。
源码
public void scheduleAtFixedRate(TimerTask task, long delay, long period) {
if (delay < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Negative delay.");
if (period <= 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Non-positive period.");
sched(task, System.currentTimeMillis()+delay, period);
}- scheduleAtFixedRate(TimerTask task, long delay, long period)
作用
等待delay毫秒后首次执行task, 之后每个period毫秒重复执行一次task (多次, 同schedule第4种用法)。
源码
public void scheduleAtFixedRate(TimerTask task, Date firstTime, long period) {
if (period <= 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Non-positive period.");
sched(task, firstTime.getTime(), period);
}笔记:
- schedule()和scheduleAtFixedRate()方法都能实现对任务的一次或多次调度。
- schedule()按是否可重复执行分为单次和多次,按任务初次执行计算方式分为delay(long型延迟毫秒数)和time(Date型时间)。
- schedule()和scheduleAtFixedRate()最终都是调用Timer类下的sched()方法实现的。
演示代码包含DemoTimer.java和TimerUtils.java,代码清单:
/*
* DemoTimer.java -- JDK 1.8
*/
package timer;
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.Timer;
import java.util.TimerTask;
/**
* Description:
* <p>
* <p>
* @author ascribed
* @date 2019-04-03 Wed PM 18:37:03
*/
public class DemoTimer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Calendar calendar = TimerUtils.current();
TimerUtils.miscellaneous("Current time is : ", calendar.getTime());
calendar.add(Calendar.SECOND, 3); // 当前时间加3秒
Timer timer = new Timer();
DemoTimerTask demoTimerTask = new DemoTimerTask("No. 1");
demoTimerTask.setName("schedule1");
timer.schedule(demoTimerTask, calendar.getTime()); // 3.1.1.1
// demoTimerTask.setName("schedule2");
// timer.schedule(demoTimerTask, calendar.getTime(), 2000); // 3.1.1.2
//
// demoTimerTask.setName("schedule3");
// timer.schedule(demoTimerTask, 3000); // 3.1.1.3
//
// demoTimerTask.setName("schedule4");
// timer.schedule(demoTimerTask, 3000, 2000); // 3.1.1.4
//
// demoTimerTask.setName("scheduleAtFixedRate1");
// timer.scheduleAtFixedRate(demoTimerTask, calendar.getTime(), 2000); // 3.1.2.1
//
// demoTimerTask.setName("scheduleAtFixedRate2");
// timer.scheduleAtFixedRate(demoTimerTask, 3000, 2000); // 3.1.2.2
}
}
class DemoTimerTask extends TimerTask {
String name; // 任务名
public DemoTimerTask(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public void run() {
TimerUtils.miscellaneous("Current time is : ", TimerUtils.current().getTime());
System.out.println("Current exec name is : " + name); // 打印当前name的内容
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
/*
* TimerUtils.java -- JDK 1.8
*/
package timer;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.TimerTask;
/**
* Description:
* <p>
* <p>
* @author ascribed
* @date 2019-04-03 Wed PM 18:40:26
*/
public class TimerUtils {
final static SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"); // 定义日期格式
static Calendar current() {
Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance(); // 通过静态工厂方法创建Calendar实例
return calendar;
}
static void schedtime(TimerTask task) {
System.out.println("scheduled time is " + sdf.format(task.scheduledExecutionTime()));
}
static void miscellaneous(String str, Date date) {
System.out.println(str + sdf.format(date));
}
}3.2 其他重要函数
3.2.1 TimerTask的cancel(), scheduledExecutionTime()
- cancel()
作用
终止此计时器,丢弃所有当前已安排(scheduled)的任务。
说明
通过查看源码,TimerTask的实现机制是通过设置标志位来记录timer task的状态,调用cancel()方法的timer task实例并没有从相应TaskQueue队列移除,这是和Timer类的cancel()方法不同之处。
源码
public boolean cancel() {
synchronized(lock) {
boolean result = (state == SCHEDULED);
state = CANCELLED;
return result;
}
}
- scheduledExecutionTime()
作用
从此计时器的任务队列中移除所有已取消(canceled)的任务。
返回值
从队列中移除的任务数。
源码
public long scheduledExecutionTime() {
synchronized(lock) {
return (period < 0 ? nextExecutionTime + period
: nextExecutionTime - period);
}
}不能与fixed-delay执行式的重复任务搭配使用,也就是不用于schedule方法,应为schedule方法的(scheduled execution time)计划执行时间会偏移理想的计划时间,对她使用这个方法没有无意义。
演示代码清单:
/*
* CancelTest.java -- JDK 1.8
*/
package timer;
import java.util.Timer;
import java.util.TimerTask;
/**
* Description:
* <p>
* <p>
* @author ascribed
* @date 2019-04-03 Wed PM 19:43:04
*/
public class CancelTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Timer timer = new Timer();
MyTimerTask myTimerTask = new MyTimerTask("schedule");
TimerUtils.miscellaneous("Current time is : ", TimerUtils.current().getTime());
timer.schedule(myTimerTask, 3000, 2000); // 3.2.1
// timer.schedule(myTimerTask, 3000); // 3.3.2
// TimerUtils.schedtime(myTimerTask);
}
}
class MyTimerTask extends TimerTask {
private String name;
private Integer count = 0;
public MyTimerTask(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public void run() {
if (count < 3) {
TimerUtils.miscellaneous("Current time is : ", TimerUtils.current().getTime());
System.out.println("Current exec name is : " + name);
count++;
} else {
cancel();
System.out.println("Task canceled");
System.exit(0);
}
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}3.2.2 Timer的cancel(), purge()
- cancel()
作用
终止此计时器,丢弃所有当前已安排的任务。
源码
public void cancel() {
synchronized(queue) {
thread.newTasksMayBeScheduled = false;
queue.clear();
queue.notify(); // 防止队列已为空的处理
}
}- purge()
作用
purge,意为净化;(将不需要的东西)从......清除,相比消灭显得优雅一些。从此计时器的任务队列中移除所有已取消的任务。
返回值
从队列中移除的任务数。
源码
public int purge() {
int result = 0;
synchronized(queue) {
for (int i = queue.size(); i > 0; i--) {
if (queue.get(i).state == TimerTask.CANCELLED) {
queue.quickRemove(i);
result++;
}
}
if (result != 0)
queue.heapify();
}
return result;
}
}演示代碼:
/*
* CancelTest.java -- JDK 1.8
*/
package timer;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.Timer;
import java.util.TimerTask;
/**
* Description:
* <p>
* <p>
* @author ascribed
* @date 2019-04-03 Wed PM 19:43:04
*/
public class CancelTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Timer timer = new Timer();
MyTimerTask task1 = new MyTimerTask("task1");
MyTimerTask task2 = new MyTimerTask("task2");
TimerUtils.miscellaneous("start time is : ", new Date());
// task1首次执行是距离现在时间2秒后,之后每隔2秒执行一次
// task2首次执行是距离现在时间1秒后,之后每隔2秒执行一次
timer.schedule(task1, 1000, 2000); // 奇数次执行
timer.schedule(task2, 2000, 2000); // 偶数次执行
// System.out.println("current canceled task number is : " + timer.purge());
Thread.sleep(5000); // 当前线程休眠5秒后cancel生效,没有此句立即触发cancel
TimerUtils.miscellaneous("cancel time is : ", new Date());
/*3.2.2.1
下面两句执行完后程序只剩下后台线程,JRE判定当前程序结束
因为当前程序只有后台线程,所有前台线程结束,后台的工作无前台线程使用就是没有意义的
*/
timer.cancel(); // 当前线程若检测到timer对队列中的任务进行调度则终止timer并从任务队列移除所有任务
System.out.println("Tasks all canceled!"); // 若此句输出后看到还有任务运行则停止所有运行的程序,这可能是之前运行的程序未终止
// 3.2.2.2
// task1.cancel(); // 当前线程每次检测到timer对task1进行schedule取消task1
// System.out.println("current canceled task number is : " + timer.purge());
}
}
class MyTimerTask extends TimerTask {
private String name;
private Integer count = 0;
public MyTimerTask(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public void run() {
if (count < 3) {
TimerUtils.miscellaneous("Current time is : ", TimerUtils.current()
.getTime());
System.out.println("Current exec name is : " + name);
count++;
} else {
cancel();
System.out.println("Task canceled");
System.exit(0);
}
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}3.3 schedule()和scheduledAtFixedRate()的区别
两种情况看区别一览表
| 方法 | schedule | scheduleAtFixedRate |
|---|---|---|
| 首次计划执行时间早于当前时间 | "fixed-delay",用代码的形式理解就是scheduleAtfixedDelay();如果第一次执行时间被delay了,随后的执行时间按照上一次实际执行完成的时间点进行计算。 |
"fixed-rate",义如其名;如果第一次执行时间按照上一次开始的时间点进行计算,并且为了赶上进度会多次执行任务,因此TimerTask中的执行体需要考虑同步。 |
| 任务执行所需的时间超出任务的执行周期间隔 | 下一次执行时间相对于上一次实际执行完成的时间点,因此执行时间会不断延后。 |
下一次执行时间相对于上一次开始的时间点,因此执行时间一般不会延后,因此存在并发性。 |
fixed-delay和fixed-rate执行的区别
- 对于fixed-delay执行讲解:
如当前时间2020-01-01 00:01:00,period为2000毫秒,将开始执行时间提前6秒即2020-01-01 00:01:57秒,首次执行时间为2020-01-01 00:01:00而不是2020-01-01 00:01:57,代码snippet:
Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance();
calendar.add(Calendar.SECOND, -6); // L1
Timer timer = new Timer();
// 第一次执行为6秒前,之后么个两秒钟执行一次
timer.schedule(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() { // L2
System.out.println("Scheduled exec time is : " + TimerUtils.sdf.format(scheduledExecutionTime()));
System.out.println("Task is being executed!");
}
}, calendar.getTime(), 2000);如果任务时间为3000毫秒,第一次执行开始时间2020-01-01 00:01:00,第二次为2020-01-01 00:01:03而不是2020-01-01 00:01:02。
这里使用在任务线程休眠三秒来实现,注释掉L1行代码,在L1处添加代码休眠三秒,代码snippet:
Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance();
Timer timer = new Timer();
timer.schedule(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("Scheduled exec time is : " + TimerUtils.sdf.format(scheduledExecutionTime()));
System.out.println("Task is being executed!");
}
}, calendar.getTime(), 2000);- 对于fixed-reate执行讲解:
如当前时间2019-04-03 23:02:58,period为2000毫秒,将开始执行时间提前6秒即2019-04-03 23:02:52秒,首次执行时间为2019-04-03 23:02:52,控制台会看到开始会一下子执行如下4次任务:
Current time is : 2019-04-03 23:02:58
Scheduled exec time is : 2019-04-03 23:02:52
Task is being executed!
Scheduled exec time is : 2019-04-03 23:02:54
Task is being executed!
Scheduled exec time is : 2019-04-03 23:02:56
Task is being executed!
Scheduled exec time is : 2019-04-03 23:02:58
Task is being executed!代码snippet:
Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance();
calendar.add(Calendar.SECOND, -6); // L1
Timer timer = new Timer();
timer.scheduleAtFixedRate(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {// L3
System.out.println("Scheduled exec time is : " + TimerUtils.sdf.format(scheduledExecutionTime()));
System.out.println("Task is being executed!");
}
}, calendar.getTime(), 2000);
}如果任务时间为3000毫秒,period为2000毫秒,当前时间2019-04-03 23:23:22,第一次执行开始时间2019-04-03 23:23:22,第二次执行时间2019-04-03 23:23:24,两个任务执行时间段有交集。
注释掉L1所在行,在L3处让任务线程休眠三秒模仿执行时间为3秒的任务,代码snippet:
Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance();
calendar.add(Calendar.SECOND, -6); // L1
Timer timer = new Timer();
timer.scheduleAtFixedRate(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(3000); // L3
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("Scheduled exec time is : " + TimerUtils.sdf.format(scheduledExecutionTime()));
System.out.println("Task is being executed!");
}
}, calendar.getTime(), 2000);注释掉不需要的代码观察效果,演示代码:
/*
* DifferenceTest.java -- JDK 1.8
*/
package timer;
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.Timer;
import java.util.TimerTask;
/**
* Description:
* <p>
* <p>
* @author ascribed
* @date 2019-04-03 Wed PM 21:47:38
*/
public class DifferenceTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Calendar calendar = TimerUtils.current();
TimerUtils.miscellaneous("Current time is : ", calendar.getTime());
// 设置成6秒前的时间,若当前时间为2016-12-28 00:00:06
// 那么设置之后时间变成2016-12-28 00:00:00
calendar.add(Calendar.SECOND, -6); // L1
Timer timer = new Timer();
// 第一次执行为6秒前,之后么个两秒钟执行一次
timer.schedule(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(3000); // L2
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("Scheduled exec time is : " + TimerUtils.sdf.format(scheduledExecutionTime()));
System.out.println("Task is being executed!");
}
}, calendar.getTime(), 2000); // 此处有个语法糖,编译器生成一个匿名类继承抽象类TimerTask通过new实例化,这并不违反抽象类不能实例化这一原则
timer.scheduleAtFixedRate(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(3000); // L3
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("Scheduled exec time is : " + TimerUtils.sdf.format(scheduledExecutionTime()));
System.out.println("Task is being executed!");
}
}, calendar.getTime(), 2000);
}
}4 实战
实现两个机器人
跳舞机器人:每隔两秒打印最近一次计划的时间和执行内容
灌水机器人:模拟往桶里倒水,直到桶里的水满为止
灌水机器人工作流程
灌水,如果水不满,则一直工作;如果水满,则停止工作。
跳舞机器人
跳舞,如果水不满,则一直工作;如果水满,则跳舞两秒后停止工作。
代码清单
DancingRobot.java、WaterRobot.java和Executor.java。
/*
* WaterRobot.java -- JDK 1.8
*/
package timer;
import java.util.Timer;
import java.util.TimerTask;
/**
* Description:
* <p>
* <p>
* @author ascribed
* @date 2019-04-02 Tue PM 16:44:17
*/
public class WaterRobot extends TimerTask {
private Timer timer;
// 最大容量5L
private Integer bucketCapacity = 0;
private final String unit = "L";
public WaterRobot(Timer timer) {
this.timer = timer;
}
@Override
public void run() {
// 灌水到桶满为止
if (bucketCapacity < 5) {
System.out.println("Add 1L water into the bucket!");
bucketCapacity++;
} else {
// 水满之后停止执行
System.out.println("The number of canceled task in timer is : " + timer.purge());
cancel();
System.out.println("The waterRot has been aborted");
System.out.println("The number of canceled task in timer is : " + timer.purge());
System.out.println("Current water is " + bucketCapacity + unit);
// 等待两秒钟,终止timer里面的所有内容
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
timer.cancel();
}
}
}
/*
* DancingRobot.java -- JDK 1.8
*/
package timer;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.TimerTask;
/**
* Description:
* <p>
* <p>
* @author ascribed
* @date 2019-04-02 Tue PM 16:35:12
*/
public class DancingRobot extends TimerTask {
@Override
public void run() {
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat(TimeConstants.DATE_FORMAT);
System.out.println("Scheduled exec time is : " + sdf.format(scheduledExecutionTime())); // 获得最近一次任务执行的计划时间
System.out.println("Dancing happily!");
}
}
/*
* Executor.java -- JDK 1.8
*/
package timer;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.Timer;
/**
* Description:
* <p>
* <p>
* @author ascribed
* @date 2019-04-02 Tue PM 16:54:04
*/
public class Executor {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Timer timer = new Timer();
Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance();
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat(TimeConstants.DATE_FORMAT);
System.out.println("Current time is : " + sdf.format(calendar.getTime()));
DancingRobot dr = new DancingRobot();
WaterRobot wr = new WaterRobot(timer);
timer.schedule(dr, calendar.getTime(), 2000);
timer.scheduleAtFixedRate(wr, calendar.getTime(), 1000);
}
}执行结果
Current time is : 2019-04-04 01:19:20
Scheduled exec time is : 2019-04-04 01:19:21
Dancing happily!
Add 1L water into the bucket!
Add 1L water into the bucket!
Add 1L water into the bucket!
Scheduled exec time is : 2019-04-04 01:19:23
Dancing happily!
Add 1L water into the bucket!
Add 1L water into the bucket!
Scheduled exec time is : 2019-04-04 01:19:25
Dancing happily!
The number of canceled task in timer is : 0
The waterRot has been aborted
The number of canceled task in timer is : 1
Current water is 5L5 Timer的缺陷
天生的两种缺陷
- 管理并发任务的缺陷
Timer有且仅有一个线程去执行定时任务,如果存在多个任务,且任务时间过长,会导致执行结果与预期不符。
演示代码:
/*
* ExTimer.java -- JDK 1.8
*/
package timer;
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.Timer;
import java.util.TimerTask;
/**
* Description:
* <p>
* <p>
* @author ascribed
* @date 2019-04-03 Wed PM 23:37:41
*/
public class ConTimer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Timer timer = new Timer();
ConTimerTask exTimerTask1 = new ConTimerTask("No.1", 2000);
ConTimerTask exTimerTask2 = new ConTimerTask("No.2", 2000);
Calendar calendar = TimerUtils.current();
TimerUtils.miscellaneous("Current time is : ", calendar
.getTime());
timer.schedule(exTimerTask1, calendar.getTime());
timer.schedule(exTimerTask2, calendar.getTime());
// timer.scheduleAtFixedRate(exTimerTask1, calendar.getTime(), 2000);
// timer.scheduleAtFixedRate(exTimerTask2, calendar.getTime(), 2000);
}
}
class ConTimerTask extends TimerTask {
private String name;
private long costTime;
public ConTimerTask(String name, long costTime) {
this.setName(name);
this.costTime = costTime;
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(name + "'s current exec time is : " + TimerUtils.sdf.format(Calendar.getInstance()
.getTime())); // 输出当前时间
try {
Thread.sleep(costTime);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(name + "'s finish time is : " + TimerUtils.sdf.format(Calendar.getInstance()
.getTime())); // 输出costTime之后的时间
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}执行结果:
Current time is : 2019-04-04 01:04:24
No.1's current exec time is : 2019-04-04 01:04:24
No.1's finish time is : 2019-04-04 01:04:26
No.2's current exec time is : 2019-04-04 01:04:26
No.2's finish time is : 2019-04-04 01:04:28- 当任务抛出异常时的缺陷
如果TimerTask抛出RuntimeException,Timer会停止所有任务的运行。
演示代码:
/*
* ExTimer.java -- JDK 1.8
*/
package timer;
import java.util.Timer;
import java.util.TimerTask;
/**
* Description:
* <p>
* <p>
* @author ascribed
* @date 2019-04-04 Thu AM 00:33:14
*/
public class ExTimer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Timer timer = new Timer();
ExTimerTask task1 = new ExTimerTask("task1");
ExTimerTask task2 = new ExTimerTask("task2");
timer.scheduleAtFixedRate(task1, 1000, 1000);
timer.scheduleAtFixedRate(task2, 1000, 2000 );
}
}
class ExTimerTask extends TimerTask {
private String name;
public ExTimerTask(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(name);
throw new IllegalStateException();
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}执行结果:
task1
Exception in thread "Timer-0" java.lang.IllegalStateException
at timer.ExTimerTask.run(ExTimer.java:37)
at java.util.TimerThread.mainLoop(Timer.java:555)
at java.util.TimerThread.run(Timer.java:505)-
TimerTask是一次性
定时器(Timer)的TimerTask实例只能schedule一次,再次调用会抛出运行时异常IllegalStateException,这是一个运行时异常。
解决方法有二:一是反射修改state字段,二是每次用new一个TimerTask。Timer的使用禁区
- 对时效性要求较高的多任务并发作业
-
对复杂的任务的调度