昨天忘记更新了,坚持做下去让自己越来越自信,把曾经没坚持做下去的事情,拿出来继续做。
现在是Java编程思想的第三章内容有关操作符的内容,下面根据书中所讲和大家分享下。
例1: 关系操作符 (大于 >,小于 <,大于等于 >=,小于等于 <=,等于 =,不等于 !=)
package com.date0530;
/**
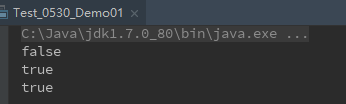
* == 和 !=比较的是对象的引用,所以即使内容相同,引用不同,所以n1 == n2 结果是false。
* 输出的是比较式的布尔值结果。
* 如果是比较两个对象的实际内容是否相同,则可以用方法equals(),但是不适用于基本类型
*/
public class Test_0530_Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer n1 = new Integer(47);
Integer n2 = new Integer(47);
System.out.println(n1 == n2);
System.out.println(n1 != n2);
System.out.println(n1.equals(n2));
}
}
运行结果:
例2 一定要恰当的定义equals()方法,看例子1 和2 做对比明白它的使用方法
package com.date0530;
class Value{
int i;
}
/**
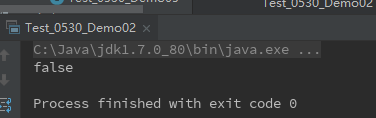
* 这里返回结果是false,因为equals()方法默认行为是比较引用
*/
public class Test_0530_Demo02 {
public static void main(String [] args){
Value v1 = new Value();
Value v2 = new Value();
v1.i = v2.i = 100;
System.out.println(v1.equals(v2));
}
}
运行结果:
例3 逻辑运算符
package com.date0530;
import java.util.Random;
public class Test_0530_Demo03 {
public static void main(String [] args){
Random rand = new Random(47);
int i = rand.nextInt(100);
int j = rand.nextInt(100);
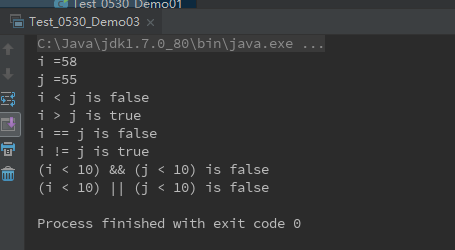
System.out.println("i =" + i);
System.out.println("j =" + j);
System.out.println("i < j is " + (i <= j));
System.out.println("i > j is " + (i >= j));
System.out.println("i == j is " + (i == j));
System.out.println("i != j is " + (i != j));
System.out.println("(i < 10) && (j < 10) is " + ((i < 10) && (j < 10) ));
System.out.println("(i < 10) || (j < 10) is " + ((i < 10) || (j < 10) ));
}
}
运行结果:
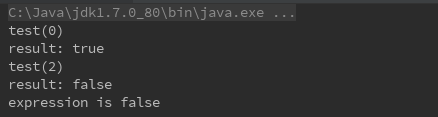
例4 短路
package com.date0530;
/**
* 短路 一但能够明确无误地确定整个表达式的值,就不再计算表达式余下部分。
*/
public class Test_0530_Demo04 {
static boolean test1(int val){
System.out.println("test(" + val + ")");
System.out.println("result: " + (val < 1));
return val < 1 ;
}
static boolean test2(int val){
System.out.println("test(" + val + ")");
System.out.println("result: " + (val < 2));
return val < 2 ;
}
static boolean test3(int val){
System.out.println("test(" + val + ")");
System.out.println("result: " + (val < 3));
return val < 3 ;
}
public static void main(String [] args){
boolean b = test1(0) && test2(2) && test3(3);
System.out.println("expression is " + b);
}
}
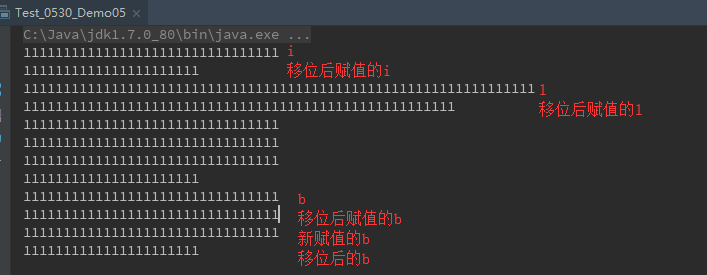
例5 移位操作符
package com.date0530;
/**
* 对于byte 和short 作移位运算得到的结果可能不正确,因为会先被转换成int类型,再进行右移动操作,然后被截断,赋值给原来的类型。
* 最后移位因为没重新赋值给b,所以运算结果是正确的。
*/
public class Test_0530_Demo05 {
public static void main(String [] args){
int i = -1;
System.out.println(Integer.toBinaryString(i));
i >>>= 10;
System.out.println(Integer.toBinaryString(i));
long l = -1;
System.out.println(Long.toBinaryString(l));
l >>>= 10;
System.out.println(Long.toBinaryString(l));
short r = -1;
System.out.println(Integer.toBinaryString(r));
r >>>= 10;
System.out.println(Integer.toBinaryString(r));
r = -1;
System.out.println(Integer.toBinaryString(r));
System.out.println(Integer.toBinaryString(r >>> 10));
byte b = -1;
System.out.println(Integer.toBinaryString(b));
b >>>= 10;
System.out.println(Integer.toBinaryString(b));
b = -1;
System.out.println(Integer.toBinaryString(b));
System.out.println(Integer.toBinaryString(b >>> 10));
}
}
先把昨天的例子补充上来,今天的晚上再说。