示例目录:
1.跑马灯效果
2.简单计数器
3.品牌案例(添加、删除、搜索)
4.过滤器的基本使用
5.全局过滤器与自定义过滤器
6.自定义按键修饰符和获取焦点
7.结合node手写JSONP服务器
1.跑马灯效果
代码如下:
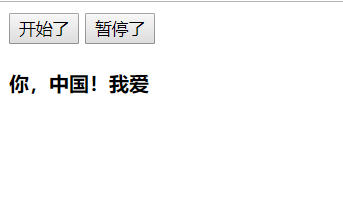
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <!--1.导入包--> <script src="vue.js"></script> </head> <body> <!--2.创建一个要控制的区域--> <div id="app"> <input type="button" value="开始了" @click="action"> <input type="button" value="暂停了" @click="stop"> <h4>{{ msg }}</h4> </div> <script> var vm = new Vue({ el:"#app", data:{ msg:'我爱你,中国!', intervalId:null //在data上定义定时器id }, methods:{ action(){ // 定时器方法1 // var _this = this // setInterval(function () { // var start = _this.msg.substring(0,1) //获取到头的第一个字符 // var end = _this.msg.substring(1) //获取到后面的所有字符 // _this.msg = end + start //重新拼接得到新的字符串,并赋值给 this.msg // },400) if (this.intervalId != null) return; //开始前判断是否为null,是的开始计时,不是就返回 //定时器方法2 this.intervalId = setInterval(()=>{ var start = this.msg.substring(0,1) //获取到头的第一个字符 var end = this.msg.substring(1) //获取到后面的所有字符 this.msg = end + start //重新拼接得到新的字符串,并赋值给 this.msg },400) }, stop(){ //停止定时器 clearInterval(this.intervalId) this.intervalId = null; //结束后重新定义为null } } }) </script> </body> </html>
渲染图:
2.简单计数器
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <script src="vue.js"></script> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <input type="text" v-model = "n1"> <select name="" id="" v-model = "opt"> <option value="+">+</option> <option value="-">-</option> <option value="*">*</option> <option value="/">/</option> </select> <input type="text" v-model="n2"> <input type="button" value="=" @click = "calc"> <input type="text" v-model = "result"> </div> <script> var vm = new Vue({ el:"#app", data:{ n1:0, n2:0, result:0, opt:'+', }, methods:{ calc(){ //计算器计数的方法 // switch(this.opt){ // case '+': // this.result = parseInt(this.n1) + parseInt(this.n2) // break // case '-': // this.result = parseInt(this.n1) - parseInt(this.n2) // break // case '*': // this.result = parseInt(this.n1) * parseInt(this.n2) // break // case '/': // this.result = parseInt(this.n1) / parseInt(this.n2) // break // } //投机取巧方式:少用 var codeStr = 'parseInt(this.n1)' + this.opt + 'parseInt(this.n2)' this.result = eval(codeStr) } } }) </script> </body> </html>
渲染图:

3.品牌案例
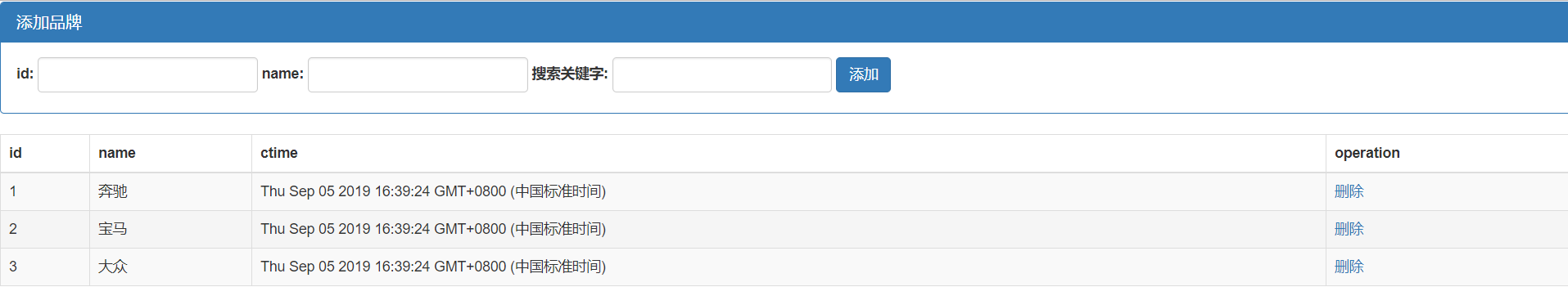
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <script src="vue.js"></script> <link rel="stylesheet" href="bootstrap-3.3.7-dist/css/bootstrap.min.css"> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <div class="panel panel-primary"> <div class="panel-heading"> <h3 class="panel-title">添加品牌</h3> </div> <div class="panel-body form-inline"> <label for=""> id: <input type="text" class="form-control" v-model="id"> </label> <label for=""> name: <input type="text" class="form-control" v-model="name"> </label> <label for=""> 搜索关键字: <input type="text" class="form-control" v-model="keywords"> </label> <input type="button" value="添加" class="btn btn-primary" @click="add"> </div> </div> <table class="table table-bordered table-hover table-striped"> <thead> <tr> <th>id</th> <th>name</th> <th>ctime</th> <th>operation</th> </tr> </thead> <tbody> <!--搜索关键词:使用自定义search方法--> <tr v-for="item in search(keywords)" :key="item.id"> <td>{{item.id}}</td> <td v-text="item.name"></td> <td>{{item.ctime}}</td> <td> <a href="" @click.prevent="del(item.id)">删除</a> </td> </tr> </tbody> </table> </div> </body> <script> var vm = new Vue({ el:'#app', data:{ id:'', name:'', keywords:'', list:[ {id:1,name:'奔驰',ctime:new Date()}, {id:2,name:'宝马',ctime:new Date()}, {id:3,name:'大众',ctime:new Date()}, ] }, methods:{ add(){ //分析: //1.获取到id和name,直接从data上获取 //2.组织出一个对象 //3.吧这个对象,调用数组的相关方法,添加到当前data上的list中 //4.注意:在Vue中,已经实现了双向绑定,每当更新数据都会在页面上渲染更新。 //5.当我们意识到里面的第四步时,就入门vue了,更多的是在model数据的操作,同时,指定业务逻辑数据操作 var car ={id:this.id,name:this.name,ctime:new Date()} this.list.push(car) this.id = this.name = '' }, del(id){ //分析: //1.如何根据id,找到要删除这一项的索引 //2.找到后,直接调用数组的splice方法 //通过some方法来查找id并删除 // this.list.some((item,i)=>{ // if(item.id == id){ // this.list.splice(i,1) // return true; // } // }) //通过findindex()来查找索引并删除 var index = this.list.findIndex(item =>{ if(item.id == id){ return true; } }) // console.log(index) this.list.splice(index,1 ) }, search(keywords){ // var newList=[] // this.list.forEach(item=>{ // if(item.name.indexOf(keywords)!= -1){ // newList.push(item) // } // }) // return newList //注意:forEach、some、filter、findindex 都会对数组中的每一项进行遍历 return this.list.filter(item=>{ if(item.name.includes(keywords)){ return item } }) } }, }) //过滤器的定义语法 //Vue.filter('过滤器的名称',function(){}) </script> </html>
实现功能:
添加,删除,查询
4.过滤器的基本使用
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <script src="vue.js"></script> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <p>{{msg|msgFormat('疯狂','123') |text}}</p> </div> <script> Vue.filter('msgFormat',function (msg,arg1,arg2) { // return msg.replace('单纯',arg) return msg.replace(/单纯/g,arg1+arg2) }) Vue.filter('text',function (msg) { return msg+ '=============' }) var vm = new Vue({ el:'#app', data:{ msg:'曾经,我也是一个单纯的少年,单纯的我,傻傻的问,谁是世界上最单纯的男人' }, methods:{}, }) </script> </body> </html>
实现如下:

5.全局过滤器和私有过滤器
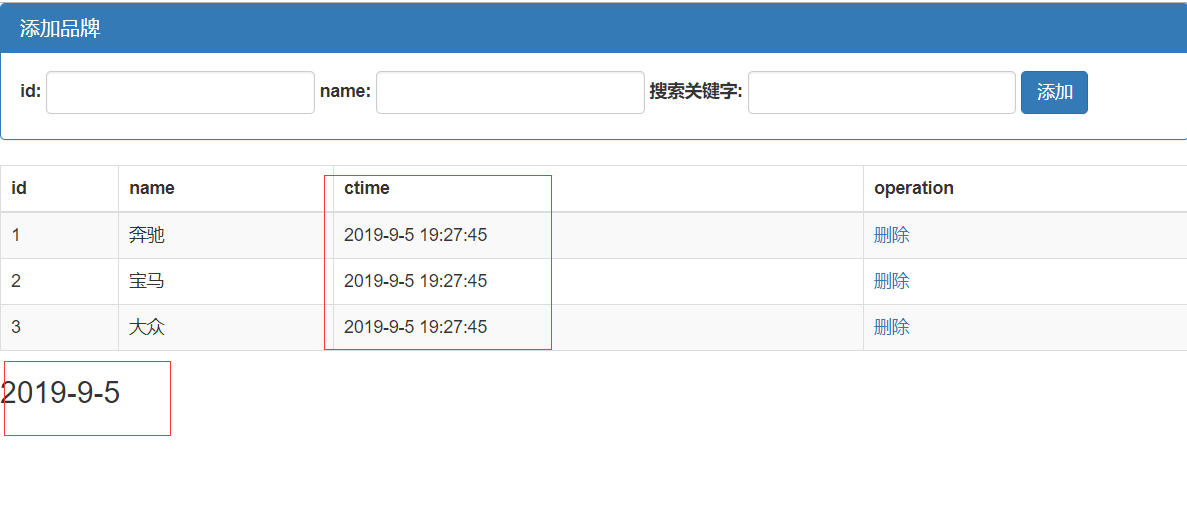
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <script src="vue.js"></script> <link rel="stylesheet" href="bootstrap-3.3.7-dist/css/bootstrap.min.css"> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <div class="panel panel-primary"> <div class="panel-heading"> <h3 class="panel-title">添加品牌</h3> </div> <div class="panel-body form-inline"> <label for=""> id: <input type="text" class="form-control" v-model="id"> </label> <label for=""> name: <input type="text" class="form-control" v-model="name"> </label> <label for=""> 搜索关键字: <input type="text" class="form-control" v-model="keywords"> </label> <input type="button" value="添加" class="btn btn-primary" @click="add"> </div> </div> <table class="table table-bordered table-hover table-striped"> <thead> <tr> <th>id</th> <th>name</th> <th>ctime</th> <th>operation</th> </tr> </thead> <tbody> <!--搜索关键词:使用自定义search方法--> <tr v-for="item in search(keywords)" :key="item.id"> <td>{{item.id}}</td> <td v-text="item.name"></td> <td>{{item.ctime | dateFormat('')}}</td> <td> <a href="" @click.prevent="del(item.id)">删除</a> </td> </tr> </tbody> </table> </div> <div id="app2"> <h3>{{dt | dateFormat}}</h3> </div> </body> <script> //全局过滤器 Vue.filter('dateFormat',function (dateStr,pattern="") { var dt = new Date(dateStr); var y = dt.getFullYear().toString().padStart(2,'0'); var m = (dt.getMonth() + 1).toString().padStart(2,'0'); var d = dt.getDate().toString().padStart(2,'0'); // return y+ '-' + m + '-' +d // return `${y}-${m}-${d}` if (pattern & pattern.toLowerCase() === 'yyyy-mm-dd'){ return `${y}-${m}-${d}` }else{ var hh = dt.getHours().toString().padStart(2,'0') var mm = dt.getMinutes().toString().padStart(2,'0') var ss = dt.getSeconds().toString().padStart(2,'0') return `${y}-${m}-${d} ${hh}:${mm}:${ss}` } }) var vm = new Vue({ el:'#app', data:{ id:'', name:'', keywords:'', list:[ {id:1,name:'奔驰',ctime:new Date()}, {id:2,name:'宝马',ctime:new Date()}, {id:3,name:'大众',ctime:new Date()}, ] }, methods:{ add(){ //分析: //1.获取到id和name,直接从data上获取 //2.组织出一个对象 //3.吧这个对象,调用数组的相关方法,添加到当前data上的list中 //4.注意:在Vue中,已经实现了双向绑定,每当更新数据都会在页面上渲染更新。 //5.当我们意识到里面的第四步时,就入门vue了,更多的是在model数据的操作,同时,指定业务逻辑数据操作 var car ={id:this.id,name:this.name,ctime:new Date()} this.list.push(car) this.id = this.name = '' }, del(id){ //分析: //1.如何根据id,找到要删除这一项的索引 //2.找到后,直接调用数组的splice方法 //通过some方法来查找id并删除 // this.list.some((item,i)=>{ // if(item.id == id){ // this.list.splice(i,1) // return true; // } // }) //通过findindex()来查找索引并删除 var index = this.list.findIndex(item =>{ if(item.id == id){ return true; } }) // console.log(index) this.list.splice(index,1 ) }, search(keywords){ // var newList=[] // this.list.forEach(item=>{ // if(item.name.indexOf(keywords)!= -1){ // newList.push(item) // } // }) // return newList //注意:forEach、some、filter、findindex 都会对数组中的每一项进行遍历 return this.list.filter(item=>{ if(item.name.includes(keywords)){ return item } }) } }, }) var vm2 = new Vue({ el:'#app2', data:{ dt:new Date() }, methods:{}, filters:{//定义私有过滤器,过滤器有两个条件:过滤器名称和处理函数,全局和私有同名,就近原则,先使用私有过滤器 dateFormat:function (dateStr,pattern = '') { var dt = new Date(dateStr); var y = dt.getFullYear().toString().padStart(2,'0'); var m = (dt.getMonth() + 1).toString().padStart(2,'0'); var d = dt.getDate().toString().padStart(2,'0'); return y+ '-' + m + '-' +d } }, }) </script> </html>
实现效果:
6.自定义按键修饰符和获取焦点
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <script src="vue.js"></script> <link rel="stylesheet" href="bootstrap-3.3.7-dist/css/bootstrap.min.css"> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <div class="panel panel-primary"> <div class="panel-heading"> <h3 class="panel-title">添加品牌</h3> </div> <div class="panel-body form-inline"> <label for=""> id: <input type="text" class="form-control" v-model="id"> </label> <label for=""> name: <input type="text" class="form-control" v-model="name" @keyup.f2="add"> </label> <label for=""> 搜索关键字: <!--注意:vue所有的指令,在调用的时候都以v-开头。。。--> <input type="text" class="form-control" v-model="keywords" id="search" v-focus v-color="'red'"> </label> <input type="button" value="添加" class="btn btn-primary" @click="add"> </div> </div> <table class="table table-bordered table-hover table-striped"> <thead> <tr> <th>id</th> <th>name</th> <th>ctime</th> <th>operation</th> </tr> </thead> <tbody> <!--搜索关键词:使用自定义search方法--> <tr v-for="item in search(keywords)" :key="item.id"> <td>{{item.id}}</td> <td v-text="item.name"></td> <td>{{item.ctime | dateFormat('')}}</td> <td> <a href="" @click.prevent="del(item.id)">删除</a> </td> </tr> </tbody> </table> </div> <div id="app2"> <h3>{{dt | dateFormat}}</h3> </div> </body> <script> //全局过滤器 Vue.filter('dateFormat',function (dateStr,pattern="") { var dt = new Date(dateStr); var y = dt.getFullYear().toString().padStart(2,'0'); var m = (dt.getMonth() + 1).toString().padStart(2,'0'); var d = dt.getDate().toString().padStart(2,'0'); // return y+ '-' + m + '-' +d // return `${y}-${m}-${d}` if (pattern & pattern.toLowerCase() === 'yyyy-mm-dd'){ return `${y}-${m}-${d}` }else{ var hh = dt.getHours().toString().padStart(2,'0') var mm = dt.getMinutes().toString().padStart(2,'0') var ss = dt.getSeconds().toString().padStart(2,'0') return `${y}-${m}-${d} ${hh}:${mm}:${ss}` } }) //自定义全局按键修饰符 Vue.config.keyCodes.f2 = 113 // document.getElementById('search').focus() //使用Vue.directive() 定义全局指令 //其中:参数1:指令的名称,注意:在定义的时候指令的名称不需要加v- //参数2:是一个钩子函数,可以增加相关的操作 Vue.directive('focus',{ bind:function(el){ //每当指令绑定到元素上的时候,会立即执行这个bind函数只执行一次 //注意:每个函数中,第一个参数永远是el,el是原生js的对象 //一个元素只有插入dom之后,才能获取焦点 // el.focus() }, inserted:function(el){ //inseted表示元素插入到dom中时候,会执行inserted函数触发1次 el.focus() }, updated:function(el){ //当vnode更新的时候,会执行updated,可能会触发多次 }, }) Vue.directive('color',{ bind:function (el,binding) { el.style.color = binding.value } }) var vm = new Vue({ el:'#app', data:{ id:'', name:'', keywords:'', list:[ {id:1,name:'奔驰',ctime:new Date()}, {id:2,name:'宝马',ctime:new Date()}, {id:3,name:'大众',ctime:new Date()}, ] }, methods:{ add(){ //分析: //1.获取到id和name,直接从data上获取 //2.组织出一个对象 //3.吧这个对象,调用数组的相关方法,添加到当前data上的list中 //4.注意:在Vue中,已经实现了双向绑定,每当更新数据都会在页面上渲染更新。 //5.当我们意识到里面的第四步时,就入门vue了,更多的是在model数据的操作,同时,指定业务逻辑数据操作 var car ={id:this.id,name:this.name,ctime:new Date()} this.list.push(car) this.id = this.name = '' }, del(id){ //分析: //1.如何根据id,找到要删除这一项的索引 //2.找到后,直接调用数组的splice方法 //通过some方法来查找id并删除 // this.list.some((item,i)=>{ // if(item.id == id){ // this.list.splice(i,1) // return true; // } // }) //通过findindex()来查找索引并删除 var index = this.list.findIndex(item =>{ if(item.id == id){ return true; } }) // console.log(index) this.list.splice(index,1 ) }, search(keywords){ // var newList=[] // this.list.forEach(item=>{ // if(item.name.indexOf(keywords)!= -1){ // newList.push(item) // } // }) // return newList //注意:forEach、some、filter、findindex 都会对数组中的每一项进行遍历 return this.list.filter(item=>{ if(item.name.includes(keywords)){ return item } }) } }, }) var vm2 = new Vue({ el:'#app2', data:{ dt:new Date() }, methods:{}, filters:{//定义私有过滤器,过滤器有两个条件:过滤器名称和处理函数,全局和私有同名,就近原则,先使用私有过滤器 dateFormat:function (dateStr,pattern = '') { var dt = new Date(dateStr); var y = dt.getFullYear().toString().padStart(2,'0'); var m = (dt.getMonth() + 1).toString().padStart(2,'0'); var d = dt.getDate().toString().padStart(2,'0'); return y+ '-' + m + '-' +d } }, }) </script> </html>
7.结合node手写JSONP服务器
node.js
const http = require('http') //1.导入http内置模块 const urlModule = require('url') //2.这个核心模块,可以解析url地址,从而拿到pathname const server = http.createServer() // 3.创建一个http服务器 server.on('request',function (req,res) { //4.监听http服务器的request请求 // const url = req.url const{pathname:url,query} = urlModule.parse(req.rul,true) if (url === '/getscript'){ // var scriptStr = 'show()' var data = { name:'zxc', age:18, gender:'male' } var scriptStr = `${query.callback}(${JSON.stringify(data)})` res.end(scriptStr) }else{ res.end('404') } })
http客户端:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <script> function showInfo123(data) { console.log(data) } </script> <script src="http://127.0.0.1:30000/getscript?callback=showInfo123"> </script> </body> </html>