原文链接https://www.cnblogs.com/zhouzhendong/p/9246484.html
题目传送门 - Codeforces 1000G Two-Paths
题意
给定一棵有 $n(2leq nleq 3 imes 10^5)$ 个节点的树,其中节点 $i$ 有权值 $a_i$,边 $e$ 有权值 $w_e$。$(1leq a_i,w_eleq 10^9)$
现在给出 $q(1leq qleq 4 imes 10^5)$ 组询问,每组询问给定两个数 $x,y(1leq x,yleq n)$。
如果一条路径的起点和终点分别为 $x$ 和 $y$,而且这条路径重复经过同一条边最多 $2$ 次(点可以多次经过),那么这条路径合法。
一条合法路径 $P$ 的价值为 $Pr(p)$。$ ext{Pr}(p) = sumlimits_{v in ext{distinct vertices in } p}{a_v} - sumlimits_{e in ext{distinct edges in } p}{k_e cdot w_e}$。
其中 $k_e$ 为路径 $p$ 经过 $e$ 的次数。
每次询问问所有合法路径的最大价值。
题解
我们来跑一下树形dp。
求出以下值。(下面是示意图,有填色的部分表示被计算)
其中 $dp1,dp2,f1,sum$ 都表示所取的部分的合法最大值。
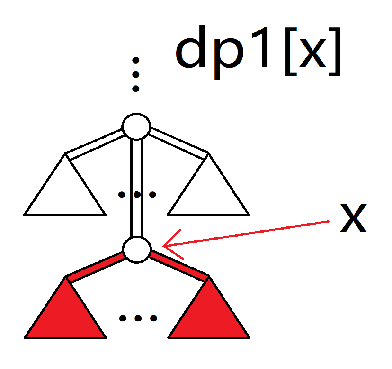
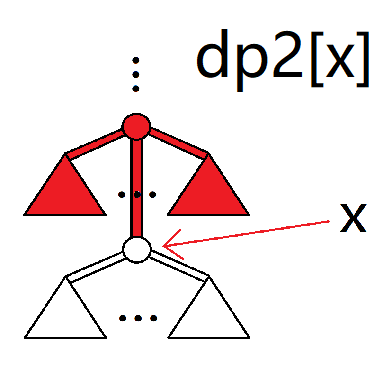
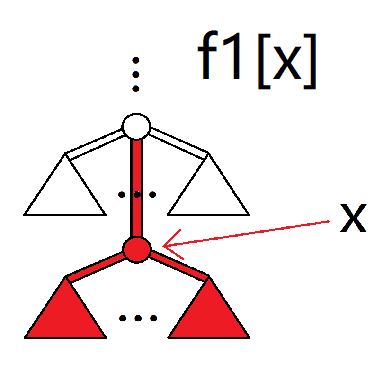
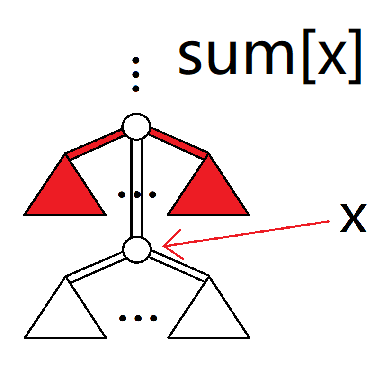
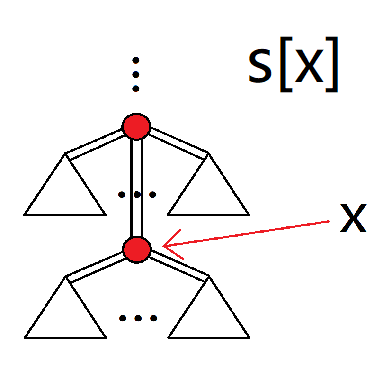
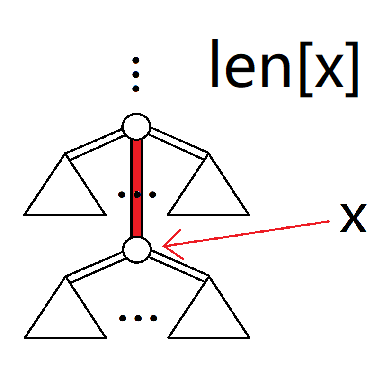
再描述一下上面六个量的意义:
dp1[x]:往 $x$ 的后代节点走最多可以赚多少。
dp2[x]:往 $x$ 的祖先走最多可以赚多少。
f1[x]:从 $x$ 的祖先向 $x$ 走最多可以赚多少。
sum[x]:令树根到 $x$ 父亲的链为主链,假设主链上行走没有任何消耗和获益,向主链走最多可以获益多少。
len[x]:$x$ 到根的距离(带边权)。
s[x]:$x$ 的深度。
在回答询问 $x,y$ 的时候,首先从 $x$ 到 $y$ 的路径一定被选,其中的边一定只走一次。
其他的我们根据之前维护的量分类讨论加加减减一下就可以了。
详见代码。
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N=300005,M=N*2;
LL read(){
LL x=0;
char ch=getchar();
while (!('0'<=ch&&ch<='9'))
ch=getchar();
while ('0'<=ch&&ch<='9')
x=x*10+ch-48,ch=getchar();
return x;
}
struct Gragh{
int cnt,y[M],nxt[M],fst[N];
LL z[M];
void clear(){
cnt=0;
memset(fst,0,sizeof fst);
}
void add(int a,int b,LL c){
y[++cnt]=b,z[cnt]=c,nxt[cnt]=fst[a],fst[a]=cnt;
}
}g;
int n,q,fa[N][20],depth[N],xx,yy;
LL a[N],dp1[N],f1[N],dp2[N],sum[N],fadis[N],len[N],s[N];
void dfs1(int x,int pre,int d,LL L){
fa[x][0]=pre;
depth[x]=d;
len[x]=L;
s[x]=s[pre]+a[x];
for (int i=1;i<20;i++)
fa[x][i]=fa[fa[x][i-1]][i-1];
dp1[x]=0;
for (int i=g.fst[x];i;i=g.nxt[i]){
int y=g.y[i];
LL z=g.z[i];
if (y!=pre){
dfs1(y,x,d+1,L+z);
fadis[y]=z;
f1[y]=max(dp1[y]+a[y]-z*2,0LL);
dp1[x]+=f1[y];
}
}
}
void dfs2(int x,int pre,LL v,LL v2){
dp2[x]=v;
sum[x]=v2;
for (int i=g.fst[x];i;i=g.nxt[i]){
int y=g.y[i];
LL z=g.z[i];
if (y!=pre){
LL _v=max(v+a[x]+dp1[x]-f1[y]-2*z,0LL);
LL _v2=max(v2+dp1[x]-f1[y],0LL);
dfs2(y,x,_v,_v2);
}
}
}
int LCA(int x,int y){
if (depth[x]<depth[y])
swap(x,y);
for (int i=19;i>=0;i--)
if (depth[x]-(1<<i)>=depth[y])
x=fa[x][i];
if (x==y)
return x;
for (int i=19;i>=0;i--)
if (fa[x][i]!=fa[y][i])
x=fa[x][i],y=fa[y][i];
xx=x,yy=y;
return fa[x][0];
}
int main(){
scanf("%d%d",&n,&q);
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++)
a[i]=read();
g.clear();
for (int i=1;i<n;i++){
int a=read(),b=read();
LL c=read();
g.add(a,b,c);
g.add(b,a,c);
}
dfs1(1,0,0,0);
dfs2(1,0,0,0);
while (q--){
int x,y,lca;
scanf("%d%d",&x,&y);
if (depth[x]>depth[y])
swap(x,y);
lca=LCA(x,y);
if (x==lca){
if (y==lca){
printf("%I64d
",dp1[x]+dp2[x]+a[x]);
continue;
}
LL ans=s[y]-s[x]+a[x];
ans-=len[y]-len[x];
ans+=sum[y]-sum[x];
ans+=dp2[x]+dp1[y];
printf("%I64d
",ans);
continue;
}
LL ans=s[x]+s[y]-s[lca]*2+a[lca];
ans-=len[x]+len[y]-len[lca]*2;
ans+=sum[x]+sum[y]-sum[xx]-sum[yy];
ans+=dp1[lca]-f1[xx]-f1[yy];
ans+=dp2[lca]+dp1[x]+dp1[y];
printf("%I64d
",ans);
}
return 0;
}