Django contenttypes组件
Django包含一个contenttypes应用程序(app),可以跟踪Django项目中安装的所有模型(Model),提供用于处理模型的高级通用接口。
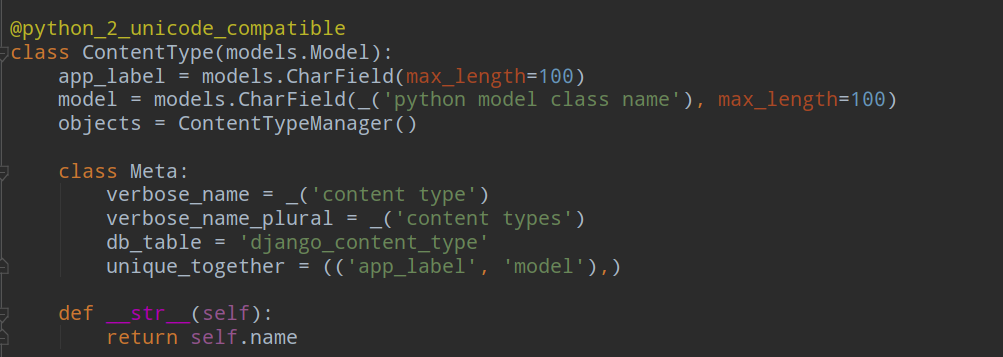
Contenttypes应用的核心是ContentType模型,位于django.contrib.contenttypes.models.ContentType。 ContentType的实例表示并保存项目中安装的模型的信息,每当有新的模型时会自动创建新的ContentType实例。
这个单独的app是在我们创建项目的时候就自动创建完成的;
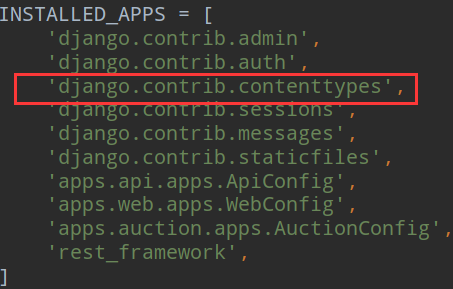
具体的逻辑代码:
在我们执行了数据库迁移的命令之后就会看到数据库中有一个名为django_content_type的表。
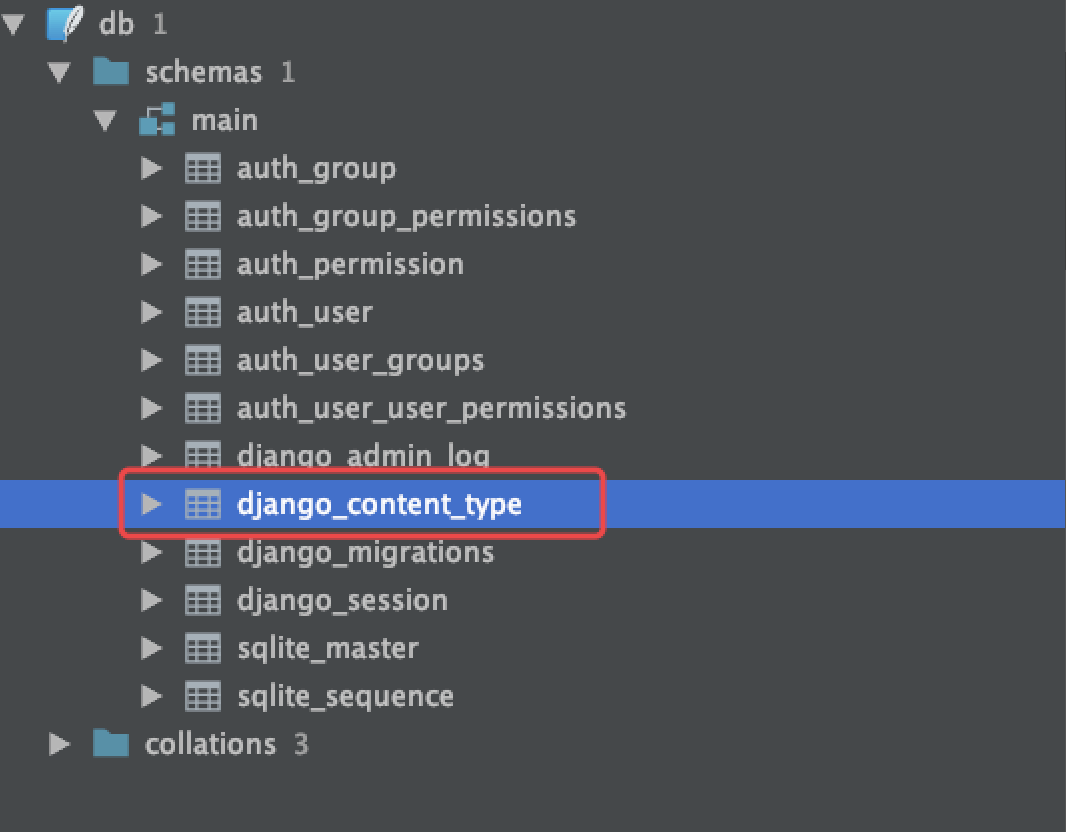
表结构如下图所示:
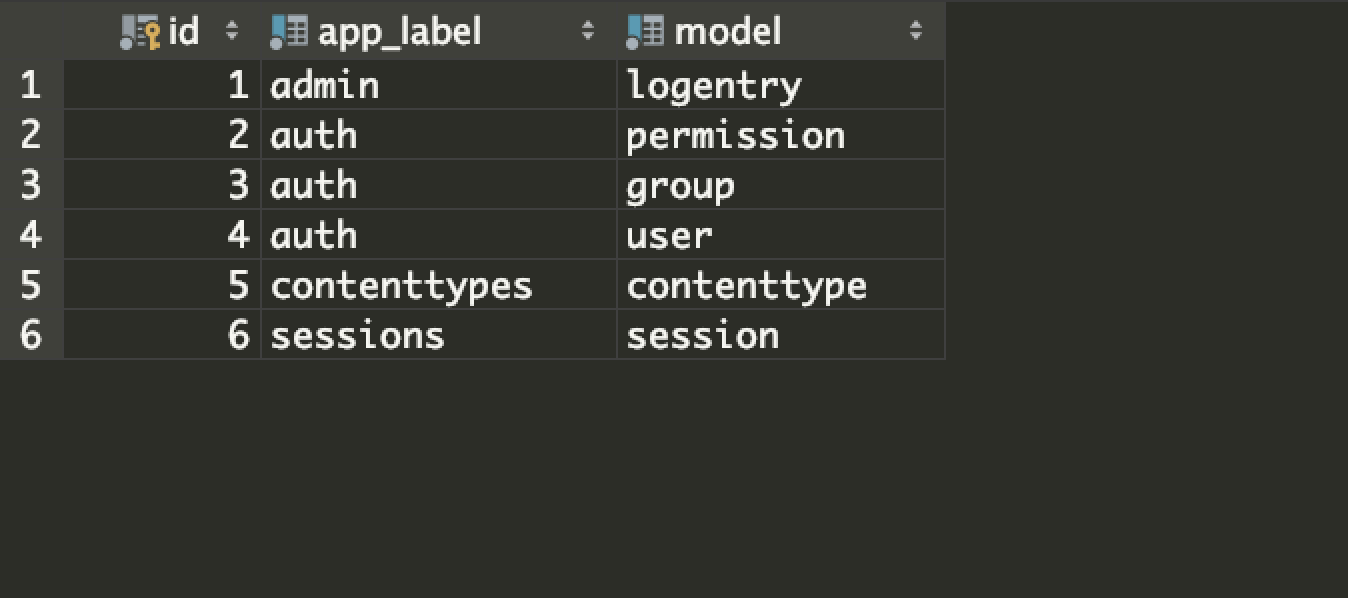
其中,app_label字段存储了APP的名称,model字段存储了APP下的具体的模型类的名称。
应用场景:
需求:课程&价格设计方案
正常的设计是:

这样的是设计没有问题,但是可以想到如果有很多的数据的话就会产生大量的空白格,造成资源的浪费;
所以我们有一种全新的设计方式:利用Django中自带的django_content_type表,来构造我们需要要的表关系;

这个时候我们就用上了前面讲到的contenttypes,借助contenttypes我们就能够在创建价格表的时候再决定和Development关联还是和Other关联。
创建的表结构:
from django.db import models
from django.contrib.contenttypes.models import ContentType
from django.contrib.contenttypes.fields import GenericForeignKey,GenericRelation
class Development(models.Model):
"""
开发课程表
"""
title = models.CharField(max_length=64)
price = GenericRelation('Price') # 支持反向查找评论数据(不会在数据库中创建字段)
class Other(models.Model):
"""
其他课程表
"""
title = models.CharField(max_length=64)
price = GenericRelation('Price') # 支持反向查找评论数据(不会在数据库中创建字段)
class Price(models.Model):
"""
价格表
"""
price = models.CharField(max_length=32)
table_id = models.ForeignKey(ContentType)
object_id = models.PositiveIntegerField()
# 不会在数据库中创建字段,可以帮助你快速的查询
content_object = GenericForeignKey("table_id","object_id")
添加数据:
development_1 = model.Development.objects.create(title="python")
development_2 = model.Development.objects.create(title="JavaScript")
development_3 = model.Development.objects.create(title="go")
other_1 = model.Other.objects.create(title="linux")
other_2 = model.Other.objects.create(title="网络安全")
other_3 = model.Other.objects.create(title="数据库")
price_1 = model.Price.objects.create(price=1000,table_id=1,object_id=development_1.id)
price_2 = model.Price.objects.create(price=800,table_id=1,object_id=development_2.id)
price_3 = model.Price.objects.create(price=600,table_id=1,object_id=development_3.id)
price_4 = model.Price.objects.create(price=1000,table_id=2,object_id=other_1.id)
price_5 = model.Price.objects.create(price=800,table_id=2,object_id=other_2.id)
price_6 = model.Price.objects.create(price=600,table_id=2,object_id=other_3.id)
反向查询:price字段
development_1 = model.Development.objects.filter(id=1).first()
price_list = development_1.price.price