背景
在OOP(面向对象编程)中处处是对象,我们当然希望可以有一种数据格式来存储这种对象的集合,以实现持久化。比如部门类所形成的部门对象集合,员工类所形成的员工对象集合,甚至是这样一个类所形成的对象:公司中有多个部门,每个部门有多个员工,我们希望将这样一个对象以文件的方式实现持久化保存。
对象流的概念
为实现对象的持久化保存,我们需要引入Java语言的对象序列化(object serialization)机制,这种机制可以将任何对象输出到流中:比如
/**
*流对象
*/
Object object = new Object();
//创建对象流并输出到文件object.dat
ObjectOutputStream output = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("c:\object.dat"));
//将object对象写到文件中
output.writeObject(object);
ObjectInputStream input = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("c:\object.dat"));
object = input.readObject();
对象流实例
引入一张组织结构图

定义组织架构图的类
- 公司:代表了组织架构的外在存在;公司是由部门和职员组成的一个完整实体。
- 部门:代表了组织架构中的运作单位;部门按类型不同可以分为不同的业务部门。
- 职员:代表了组织架构中的最小单位;职员按职位不同存在于不同的业务部门。
/**
* 用对象流保存信息--公司类
*
* @author zhuhuix
* @date 2020-05-27
*/
class Company implements Serializable {
//公司id
private int id;
//公司名称
private String name;
//公司部门列表
private List<Department> departments;
//默认构造函数
Company() {
}
//初始化构造函数
Company(int id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.departments = new ArrayList<>();
}
//增加部门
public void addDepartment(Department department) {
this.departments.add(department);
}
//裁撤部门
public void deleteDepartment(Department department) {
this.departments.remove(department);
}
//定位部门
Department findDepartmentByName(String departmentName) {
Optional<Department> optional = departments.stream().filter(department ->
department.getName().equals(departmentName)).findFirst();
return optional.get();
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public List<Department> getDepartments() {
return departments;
}
public void setDepartments(List<Department> departments) {
this.departments = departments;
}
}
/**
* 用对象流保存信息--部门类
*
* @author zhuhuix
* @date 2020-05-27
*/
class Department implements Serializable {
//部门id
private int id;
//部门名称
private String name;
//上级部门
private Integer parentId;
//部门职员列表
private List<Employee> employees;
//默认构造函数
Department(){}
//初始化构造函数
Department(int id,String name,Integer parentId){
this.id=id;
this.name=name;
this.parentId=parentId;
this.employees = new ArrayList<>();
}
//增加职员
public void addEmployee(Employee employee){
this.employees.add(employee);
}
//裁撤职员
public void deleteEmployee(Employee employee){
this.employees.remove(employee);
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getParentId() {
return parentId;
}
public void setParentId(Integer parentId) {
this.parentId = parentId;
}
public List<Employee> getEmployees() {
return employees;
}
public void setEmployees(List<Employee> employees) {
this.employees = employees;
}
}
/**
* 用对象流保存信息--职员类
*
* @author zhuhuix
* @date 2020-05-27
*/
class Employee implements Serializable {
//职员id
private int id;
//职员姓名
private String name;
//职员性别
private String sex;
//职员年龄
private int age;
//职员职位
private String position;
//入职日期
private Date hireDate;
//当前薪水
private BigDecimal salary;
//默认构造函数
Employee(){}
//初始化构造函数
public Employee(int id, String name, String sex, int age, String position, Date hireDate, BigDecimal salary) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.sex = sex;
this.age = age;
this.position = position;
this.hireDate = hireDate;
this.salary = salary;
}
//升职、调岗、调动
public void setPosition(String position){
this.position = position;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getPosition() {
return position;
}
public Date getHireDate() {
return hireDate;
}
public void setHireDate(Date hireDate) {
this.hireDate = hireDate;
}
public BigDecimal getSalary() {
return salary;
}
public void setSalary(BigDecimal salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
}
类的完整结构
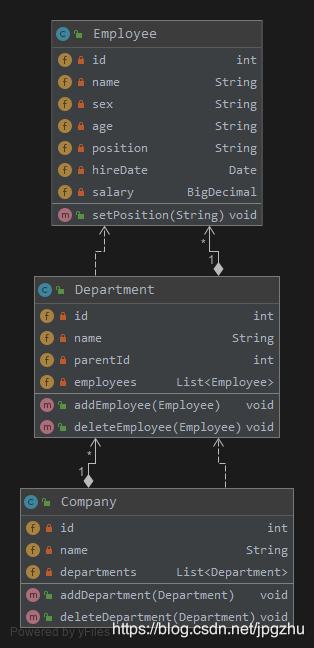
用对象流保存组织架构的对象信息
有了类及构造函数完成对象的初始化过程,我们就具备了建立整个组织架构的能力,接下来我们完整地建立一个公司的组织架构:
/**
1. 用对象流保存组织架构信息
2. * @author zhuhuix
3. @date 2020-05-27
*/
public class ObjectStreamSave {
//定义一个全局静态变量,作为控制组织架构的id
public static int id = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//设立公司
Company company = new Company(id++, "互联网股份有限公司");
//公司设立总经理室
Department manageDept = new Department(id++, "总经理室", null);
company.addDepartment(manageDept);
//在总经理室下设立产品部
Department productDept = new Department(id++, "产品部", manageDept.getId());
company.addDepartment(productDept);
//在产品部下设立产品A、B组
company.addDepartment(new Department(id++, "产品A组", productDept.getId()));
company.addDepartment(new Department(id++, "产品B组", productDept.getId()));
//在总经理室下设立研发部
Department developmentDept = new Department(id++, "研发部", manageDept.getId());
company.addDepartment(developmentDept);
//在研发部下设立软件组与硬件组
company.addDepartment(new Department(id++, "软件组", developmentDept.getId()));
company.addDepartment(new Department(id++, "硬件组", developmentDept.getId()));
//在总经理室下设立市场部
Department marketDept = new Department(id++, "市场部", manageDept.getId());
company.addDepartment(marketDept);
//在市场部下设立创意组与渠道组
company.addDepartment(new Department(id++, "创意组", marketDept.getId()));
company.addDepartment(new Department(id++, "渠道组", marketDept.getId()));
//总经理室人事任命
manageDept.addEmployee(new Employee(id++, "Mike", "男", 35, "总经理",
new Date(), BigDecimal.valueOf(100000)));
manageDept.addEmployee(new Employee(id++, "Tom", "男", 34, "副总经理",
new Date(), BigDecimal.valueOf(60000)));
//研发部人事任命
developmentDept.addEmployee(new Employee(id++, "Jack", "男", 30, "研发部主管",
new Date(), BigDecimal.valueOf(40000)));
company.findDepartmentByName("软件组")
.addEmployee(new Employee(id++, "Kate", "女", 26, "组员",
new Date(), BigDecimal.valueOf(20000)));
company.findDepartmentByName("硬件组")
.addEmployee(new Employee(id++, "Will", "男", 24, "组员",
new Date(), BigDecimal.valueOf(20000)));
//产品部人事任命
productDept.addEmployee(new Employee(id++, "Jerry", "男", 28, "产品部主管",
new Date(), BigDecimal.valueOf(40000)));
company.findDepartmentByName("产品A组")
.addEmployee(new Employee(id++, "Merry", "女", 28, "组员",
new Date(), BigDecimal.valueOf(20000)));
company.findDepartmentByName("产品B组")
.addEmployee(new Employee(id++, "Leo", "男", 27, "组员",
new Date(), BigDecimal.valueOf(20000)));
//市场部人事任命
marketDept.addEmployee(new Employee(id++, "Rose", "女", 29, "市场部主管",
new Date(), BigDecimal.valueOf(40000)));
company.findDepartmentByName("创意组")
.addEmployee(new Employee(id++, "Amy", "", 25, "组员",
new Date(), BigDecimal.valueOf(20000)));
company.findDepartmentByName("渠道组")
.addEmployee(new Employee(id++, "Tony", "男", 23, "组员",
new Date(), BigDecimal.valueOf(20000)));
//遍历公司组织结构
int deptCount = 0;
int empCount = 0;
Iterator<Department> deptIterator = company.getDepartments().iterator();
while (deptIterator.hasNext()) {
deptCount++;
Department department = deptIterator.next();
System.out.println("部门:" + department.getName());
if (department.getEmployees() != null) {
Iterator<Employee> empIterator = department.getEmployees().iterator();
while (empIterator.hasNext()) {
empCount++;
Employee employee = empIterator.next();
System.out.print(" 人员:" + employee.getName() + " 职位:" + employee.getPosition() + ",");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
System.out.println("总共部门数:" + deptCount);
System.out.println("总共职员数:" + empCount);
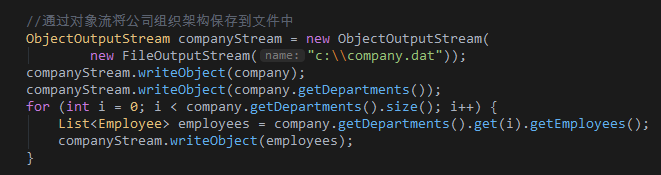
//通过对象流将公司组织架构保存到文件中
ObjectOutputStream companyStream = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("c:\company.dat"));
companyStream.writeObject(company);
companyStream.writeObject(company.getDepartments());
for (int i = 0; i < company.getDepartments().size(); i++) {
List<Employee> employees = company.getDepartments().get(i).getEmployees();
companyStream.writeObject(employees);
}
}
}
核心代码
- 通过对象流的方式建立一个company.dat文件
- 将公司对象写入文件
- 将公司对象中的部门列表集合写入文件
- 遍历部门列表,将每个部门下的职员列表集合写入文件
生成的文件如下:

二进制信息:
用对象流读取文件并输出
/**
* 用对象流读取信息
*
* @author zhuhuix
* @date 2020-05-27
*/
public class ObjectStreamRead {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
ObjectInputStream companyStream = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("c:\company.dat"));
if (companyStream!=null){
Company company=(Company) companyStream.readObject();
//遍历公司组织结构
int deptCount = 0;
int empCount = 0;
Iterator<Department> deptIterator = company.getDepartments().iterator();
while (deptIterator.hasNext()) {
deptCount++;
Department department = deptIterator.next();
System.out.println("部门:" + department.getName());
if (department.getEmployees() != null) {
Iterator<Employee> empIterator = department.getEmployees().iterator();
while (empIterator.hasNext()) {
empCount++;
Employee employee = empIterator.next();
System.out.print(" 人员:" + employee.getName() + " 职位:" + employee.getPosition() + ",");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
System.out.println("总共部门数:" + deptCount);
System.out.println("总共职员数:" + empCount);
}
}
}
核心代码
- 通过对象流的方式获取company.dat文件
- 读取对象信息
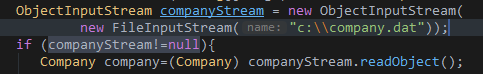
输出如下:
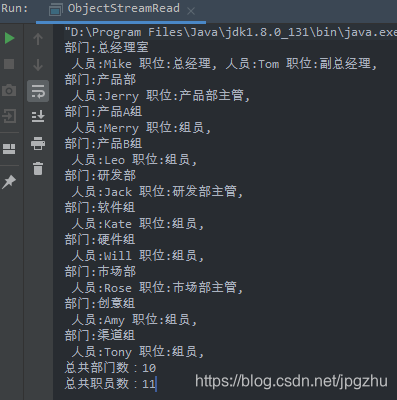
总结
在本文中,我们使用序列化将对象集合保存到磁盘文件中,并按照它们被存储的样子获取它们,我们学习到了如下信息:
- ObjectOutputStream(OutputStream out) 创建一个ObjectOutputStream使得你可以将对象写出到指定的OutputStream。
- void writeObject(Object obj) 写出指定的对象到ObjectOutputStream,这个方法将存储指定对象的类、类的签名以及这个类及其超类中所有非静态和非瞬时的域的值。
- ObjectInputStream(InputStream in) 创建一个ObjectInputStream用于从指定的InputStream中读回对象信息。
- Object readObject()从ObjectInputStream中读入一个对象。特别是,这个方法会读回对象的类、类的签名以及这个类及其超类中所有非静态和非瞬时的域的值。它执行的反序列化允许恢复多个对象引用。