一、CursorAdapter介绍
CursorAdapter这个类是继承于BaseAdapter的它是一个虚类它为Cursor和ListView连接提供了桥梁
二、CursorAdapter详解
1.CursorAdapter的继承关系图
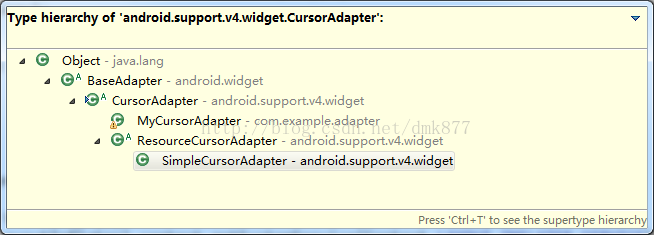
从图中可以看出CursorAdapter是继承于BaseAdapter的,它有一个直接的子类SimpleCursorAdapter
2.CursorAdapter的用法
我们首先看一下CursorAdapter的部分源码:
/** * @see android.widget.ListAdapter#getCount() */ public int getCount() { if (mDataValid && mCursor != null) { return mCursor.getCount(); } else { return 0; } } /** * @see android.widget.ListAdapter#getItem(int) */ public Object getItem( int position) { if (mDataValid && mCursor != null) { mCursor.moveToPosition(position); return mCursor; } else { return null; } } /** * @see android.widget.ListAdapter#getItemId(int) */ public long getItemId( int position) { if (mDataValid && mCursor != null) { if ( mCursor.moveToPosition(position)) { return mCursor.getLong( mRowIDColumn); } else { return 0; } } else { return 0; } } /** * @see android.widget.ListAdapter# getView(int, View, ViewGroup) */ public View getView( int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent) { if (!mDataValid) { throw new IllegalStateException( "this should only be called when the cursor is valid"); } if (!mCursor.moveToPosition(position)) { throw new IllegalStateException( "couldn't move cursor to position " + position); } View v; if (convertView == null) { v = newView( mContext, mCursor, parent); } else { v = convertView; } bindView(v, mContext, mCursor); return v; } 从源码中可以看出CursorAdapter是继承了BaseAdapter后覆盖它的getView方法在getView方法中调用了newView和bindView方法,我们在写CursorAdapter时必须实现它的两个方法 /** * Makes a new view to hold the data pointed to by cursor. * @param context Interface to application's global information * @param cursor The cursor from which to get the data. The cursor is already * moved to the correct position. * @param parent The parent to which the new view is attached to * @return the newly created view. */ public abstract View newView (Context context, Cursor cursor, ViewGroup parent); /** * Bind an existing view to the data pointed to by cursor * @param view Existing view, returned earlier by newView * @param context Interface to application's global information * @param cursor The cursor from which to get the data. The cursor is already * moved to the correct position. */ public abstract void bindView(View view, Context context, Cursor cursor);
从源码的 getView( int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent)方法中我们可以看出:
(1)newView:并不是每次都被调用的,它只在实例化的时候调用,数据增加的时候也会调用,但是在重绘(比如修改条目里的TextView的内容)的时候不会被调用
(2)bindView:从代码中可以看出在绘制Item之前一定会调用bindView方法它在重绘的时候也同样被调用
3.CursorAdapter还有一个重要的方法 public void changeCursor (Cursor cursor)
源码如下:
/** * Change the underlying cursor to a new cursor. If there is an existing cursor it will be * closed. * * @param cursor The new cursor to be used */ public void changeCursor (Cursor cursor) { Cursor old = swapCursor(cursor); if (old != null) { old.close(); } } swapCursor(cusor)的源码如下: /** * Swap in a new Cursor, returning the old Cursor. Unlike * {@link #changeCursor(Cursor)}, the returned old Cursor is <em>not</em> * closed. * * @param newCursor The new cursor to be used. * @return Returns the previously set Cursor, or null if there wasa not one. * If the given new Cursor is the same instance is the previously set * Cursor, null is also returned. */ public Cursor swapCursor (Cursor newCursor) { if (newCursor == mCursor) { return null; } Cursor oldCursor = mCursor; if (oldCursor != null) { if ( mChangeObserver != null) oldCursor.unregisterContentObserver(mChangeObserver ); if ( mDataSetObserver != null) oldCursor.unregisterDataSetObserver(mDataSetObserver ); } mCursor = newCursor; if (newCursor != null) { if ( mChangeObserver != null) newCursor.registerContentObserver(mChangeObserver ); if ( mDataSetObserver != null) newCursor.registerDataSetObserver(mDataSetObserver ); mRowIDColumn = newCursor.getColumnIndexOrThrow("_id" ); mDataValid = true; // notify the observers about the new cursor notifyDataSetChanged(); } else { mRowIDColumn = -1; mDataValid = false; // notify the observers about the lack of a data set notifyDataSetInvalidated(); } return oldCursor; }
从源码中可以看出调用此方法后会把当前的mCursor置为新传过来的cursor把原来的cursor返回去并关掉
作用:当我们的Cursor变化时调用此方法
adapter.changeCursor(cursor),它的功能类似于adapter.notifyDataSetChanged()方法
4.之前的疑惑
之前我一直对cursor是怎么移动的疑惑,比方说cursor中有40条数据,那么它是怎样一行一行移动cursor把这40条数据显示出来的,看过源码后发现其实很简单,
之前我一直对cursor是怎么移动的疑惑,比方说cursor中有40条数据,那么它是怎样一行一行移动cursor把这40条数据显示出来的,看过源码后发现其实很简单,
它在getCount()方法中return mCursor.getCount();然后在getView方法的时候调用了mCursor.moveToPosition(position)其实和BaseAdapter的原理是一样的,这样就可以一条一条的绘制条目了。
三、源码小案例:
1.案例功能

在EditText中输入姓名和电话,点击保存后会显示在下面的listView中
2.代码片段
(1)MyCursorAdapter的主要代码:
@Override public View newView(Context context, Cursor cursor, ViewGroup parent) { ViewHolder viewHolder= new ViewHolder(); LayoutInflater inflater=(LayoutInflater)context.getSystemService(Context.LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE ); View view=inflater.inflate(R.layout.item_contacts ,parent,false); viewHolder. tv_name=(TextView) view.findViewById(R.id.tv_showusername ); viewHolder. tv_phonenumber=(TextView) view.findViewById(R.id.tv_showusernumber ); view.setTag(viewHolder); Log. i("cursor" ,"newView=" +view); return view; } @Override public void bindView(View view, Context context, Cursor cursor) { Log. i("cursor" ,"bindView=" +view); ViewHolder viewHolder=(ViewHolder) view.getTag(); //从数据库中查询姓名字段 String name=cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex(PersonInfo.NAME)); //从数据库中查询电话字段 String phoneNumber=cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex(PersonInfo.PHONENUMBER)); viewHolder. tv_name.setText(name); viewHolder. tv_phonenumber.setText(phoneNumber); }
调用newView方法实例化条目,然后调用bindView绘制条目,当只绘制时不会调用newView方法。
(2)点击保存按钮执行的方法
private void setClickListener() { btn_save.setOnClickListener( new OnClickListener() { public void onClick(View v) { userName=et_name.getText().toString(); userPhoneNumber=et_phonenumber .getText().toString(); if( userName.equals( "")){ Toast. makeText(MainActivity.this, "用户名不能为空!",0).show(); return; } if( userPhoneNumber.equals( "")){ Toast. makeText(MainActivity.this,"电话不能为空", 0).show(); return; } ContentValues contentValues= new ContentValues(); contentValues.put(PersonInfo. NAME, userName); contentValues.put(PersonInfo.PHONENUMBER ,userPhoneNumber ); //把EditText中的文本插入数据库 dataBase.insert(PersonInfo. PERSON_INFO_TABLE, null,contentValues); //根据 _id 降序插叙数据库保证最后插入的在最上面 Cursor myCursor = dataBase.query(PersonInfo. PERSON_INFO_TABLE, null, null, null, null, null, orderBy); //Cursor改变调用chanageCursor()方法 myCursorAdapter.changeCursor(myCursor); } }); }