原题,以不剪枝的决策树作为基学习器,对西瓜数据集实现Adaboost分类。
#!/usr/bin/python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn.ensemble import AdaBoostClassifier from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier file1 = open('c:quantwatermelon.csv','r') data = [line.strip(' ').split(',') for line in file1] data = np.array(data) #X = [[float(raw[-7]),float(raw[-6]),float(raw[-5]),float(raw[-4]),float(raw[-3]), float(raw[-2])] for raw in data[1:,1:-1]] X = [[float(raw[-3]), float(raw[-2])] for raw in data[1:]] y = [1 if raw[-1]=='1' else 0 for raw in data[1:]] X = np.array(X) y = np.array(y) # Create and fit an AdaBoosted decision tree,不剪枝决策树 bdt = AdaBoostClassifier(DecisionTreeClassifier(), algorithm="SAMME", n_estimators=200) bdt.fit(X, y) plot_colors = "br" plot_step = 0.02 class_names = "AB" plt.figure(figsize=(10, 5)) # Plot the decision boundaries plt.subplot(121) x_min, x_max = X[:, 0].min() - 1, X[:, 0].max() + 1 y_min, y_max = X[:, 1].min() - 1, X[:, 1].max() + 1 xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, plot_step), np.arange(y_min, y_max, plot_step)) Z = bdt.predict(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()]) Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape) cs = plt.contourf(xx, yy, Z, cmap=plt.cm.Paired) plt.axis("tight") # Plot the training points for i, n, c in zip(range(2), class_names, plot_colors): idx = np.where(y == i) plt.scatter(X[idx, 0], X[idx, 1], c=c, cmap=plt.cm.Paired, label="Class %s" % n) plt.xlim(x_min, x_max) plt.ylim(y_min, y_max) plt.legend(loc='upper right') plt.xlabel('Sugar rate') plt.ylabel('Density') plt.title('Decision Boundary') # Plot the two-class decision scores twoclass_output = bdt.decision_function(X) plot_range = (twoclass_output.min(), twoclass_output.max()) plt.subplot(122) for i, n, c in zip(range(2), class_names, plot_colors): plt.hist(twoclass_output[y == i], bins=10, range=plot_range, facecolor=c, label='Class %s' % n, alpha=.5) x1, x2, y1, y2 = plt.axis() plt.axis((x1, x2, y1, y2 * 1.2)) plt.legend(loc='upper right') plt.ylabel('Samples') plt.xlabel('Score') plt.title('Decision Scores') plt.tight_layout() plt.subplots_adjust(wspace=0.35) plt.show()
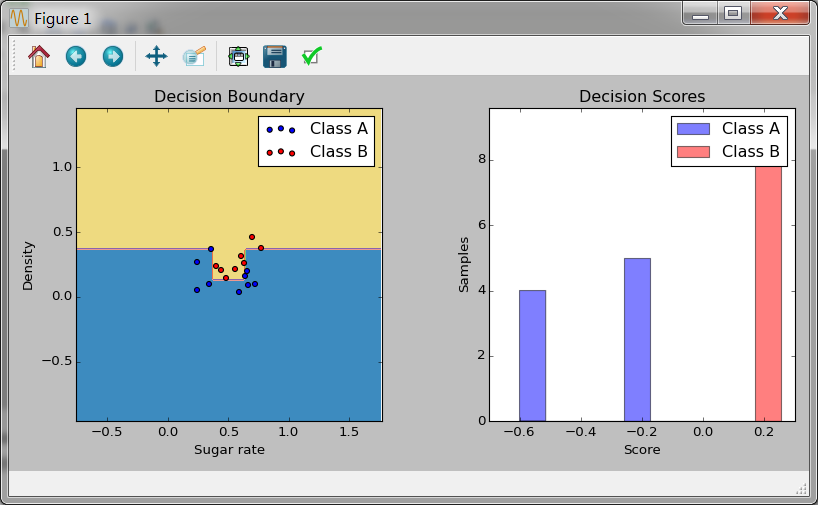
运行结果如下:
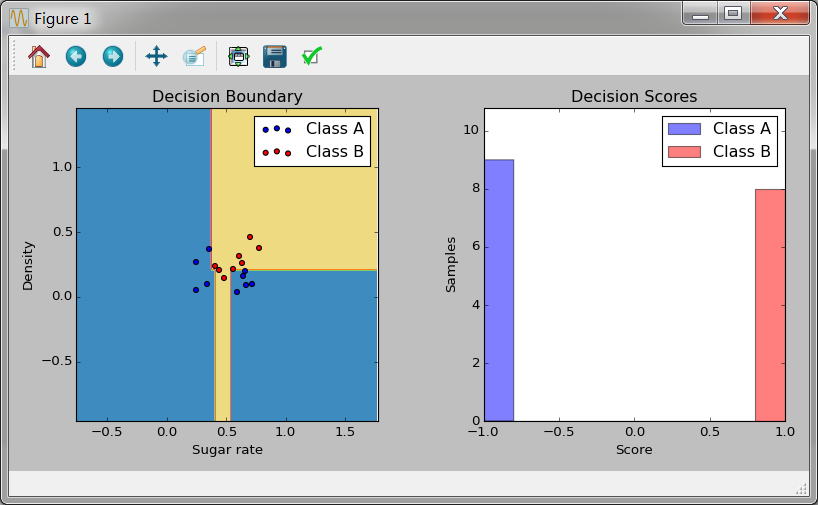
分类结果训练结果相当好。当然也测试了最大深度为1的决策树作为基学习器,结果如下: