在NiceFish项目中,数据请求处理并没有用Promise的那一套方法,用的是Observable(观察者模式),我将其理解成生产者和消费者模式
如下简单例子:出自(https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000005051034)
var observable = Rx.Observable.create(function (observer) { observer.next(1); observer.next(2); observer.next(3); setTimeout(() => { observer.next(4); observer.complete(); }, 1000); }); console.log('just before subscribe'); observable.subscribe({ next: x => console.log('got value ' + x), error: err => console.error('something wrong occurred: ' + err), complete: () => console.log('done'), }); console.log('just after subscribe');
运行结果如下:
just before subscribe got value 1 got value 2 got value 3 just after subscribe got value 4 done
observer.complete()执行后observer.next()的执行是不会触发observable.subscribe里面的函数的。observer.complete()相当于终止了消费者与生产者之间的订阅关系。observable.subscribe()相当于消费者订阅了生产者的数据,一旦生产者产生了数据就会自动推送给消费者,这样会自动导致消费者根据推送过来的数据执行各自注册的函数。这是一种生产者主动,消费者被动的数据推送模式。类似于promise,但所不同的是observable能多点发射数据,能多次停止或执行subscribe里面注册的函数。
observable如何与用户点击事件关联起来呢: 参考:http://blog.csdn.net/tianjun2012/article/details/51246422
var allMoves = Rx.Observable.fromEvent(document, 'mousemove'); allMoves.subscribe(function(e) { console.log(e.clientX, e.clientY); }); var movesOnTheRight = allMoves.filter(function(e) { return e.clientX > window.innerWidth / 2; }); var movesOnTheLeft = allMoves.filter(function(e) { return e.clientX < window.innerWidth / 2; }); movesOnTheRight.subscribe(function(e) { console.log('Mouse is on the right:', e.clientX); }); movesOnTheLeft.subscribe(function(e) { console.log('Mouse is on the left:', e.clientX); });
以上就是observer的用法。add-comment.components组件在post-detail-main.components组件(属于post.module模块)中被引用,当add-comment.components被加载时
import ..... @Component({ selector: 'app-add-comment', templateUrl: './add-comment.component.html', styleUrls: ['./add-comment.component.scss'] }) export class AddCommentComponent implements OnInit { public comments: Array<Comment>; constructor( public commentService: CommentService, public activeRoute: ActivatedRoute) { } ngOnInit() { this.activeRoute.params.subscribe( params => this.getCommentList(params["postId"]) ); } public getCommentList(postId: number){ this.commentService.getCommentList(postId) .subscribe( data => { this.comments = data["items"] }, error => console.error(error) ); } }
constructor里面的两个参数:commentService和activeRoute是两个被注入的服务,ngOnInit表示一旦组件加载完成(这里的完成是指视图加载完成,组件被编译以及初始化之后即ngOnInit是在ngOnchanges执行完之后才调用)就会执行里面的内容,所以通常模板数据的初始化可以在ngOnInit方法内执行,即在里面请求服务器数据。
(ngOnInit纯粹是通知开发者组件/指令已经被初始化完成了,此时组件/指令上的属性绑定操作以及输入操作已经完成,也就是说在ngOnInit函数中我们已经能够操作组件/指令中被传入的数据了)
参考:https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000012095427,http://blog.csdn.net/u010730126/article/details/64486997,https://segmentfault.com/q/1010000006040976
this.activeRoute.params:
以下是activeRoute及其属性的定义
interface RouterState { snapshot: RouterStateSnapshot; //returns current snapshot root: ActivatedRoute; } interface ActivatedRoute { snapshot: ActivatedRouteSnapshot; //returns current snapshot url: Observable<UrlSegment[]>; params: Observable<{[name:string]:string}>; data: Observable<{[name:string]:any}>; queryParams: Observable<{[name:string]:string}>; fragment: Observable<string>; root: ActivatedRout; parent: ActivatedRout; firstchild: ActivatedRout; children: ActivatedRout[]; }
可以看到params是Observable的类型,事实上是angular路由监听了URL,一旦URL变化就会触发params注册的函数,那为什么params要是Observable的类型呢,在ngOnInt方法里面直接去获取URL里面的参数不可以吗,ngOnInt一定是在URl变化后执行的。
这是因为比如一个A组件,它的路由路径是/post/details/1,当A组件第一次加载到页面时,ngOnInt方法会执行,这个时候直接获取URL里面的参数是可以做到的,如下:
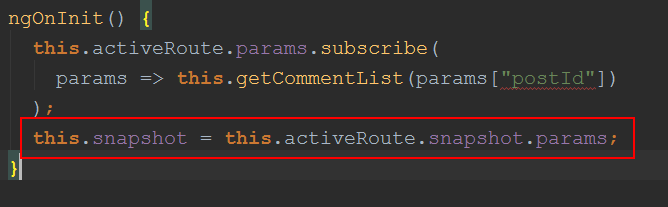
当某一时刻用户在页面触发了某一事件,或者js自动隔一段时间执行如下代码:this.router.navigate(['post/postdetail', '2']); 即希望URL跳转为/post/details/2;这个时候angular是不会重新加载组件的,因此ngOnInt以及constructor方法不会执行。this.snapshot的值不会变化。这个时候如果你在其他地方用到this.snapshot的引用的话是不正确的。 当然this.activeRoute.snapshot.params是变化的。如果你不介意重新像上面来一次赋值的话。
那么怎么样才能让this.snapshot的值随着URL变化而变化呢。可以将上面红框的赋值语句放到params.subscribe的参数方法里面去。这样一旦URL参数变化,this.activeRoute.params注册的方法就会执行,getCommentList()自动从服务器获取评论列表信息并显示在页面。this.snapshot这个路由参数信息随时都是有效正确的。
这里RouterStateSnapshot和ActiveRoute是对应的。它们都可以获取URl参数,但RouterStateSnapshot是一个快照,代表某一时刻页面的url参数信息。是一个固定的状态,可以通过直接赋值来获取URL的参数。URL的变化是不会触发它的更新的。而ActiveRoute是会随着URl变化而变化的路由信息状态。
注意:官网上对于params和queryParams这两个属性有了更新:
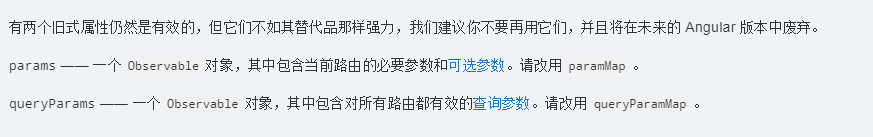
详细请参考:https://vsavkin.com/angular-router-understanding-router-state-7b5b95a12eab,https://angular.cn/guide/router,://juejin.im/entry/5822c9d6da2f60005d1af6ce
在实际页面查看两者的区别可以参考如下代码:
import { Component, OnInit, Input } from '@angular/core';
import { ActivatedRoute, Router, Params } from '@angular/router';
import { CommentService } from '../services/comment.service';
import { Comment } from '../model/comment-model';
@Component({
selector: 'app-add-comment',
templateUrl: './add-comment.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./add-comment.component.scss']
})
export class AddCommentComponent implements OnInit {
public comments: Array<Comment>;
public snapshot;
constructor(
public commentService: CommentService,
public activeRoute: ActivatedRoute,
public router: Router)
{
setTimeout(() => {
//this.router.navigate(['../', '2'], {relativeTo: this.activeRoute });
this.router.navigate(['post/postdetail', '2']);
}, 3000);
}
ngOnInit() {
this.activeRoute.params.subscribe(
params => this.getCommentList(params["postId"])
);
this.snapshot = this.activeRoute.snapshot.params;
}
public getCommentList(postId: number){
console.log('snapshot.params::::::::::::::::',this.snapshot);
console.log('getCommentList::::::::subscribe:::::::::::::::::::::',postId);
console.log('getCommentList:::::::::snapshot.params::::::::::::::::',this.activeRoute.snapshot.params);
this.commentService.getCommentList(postId)
.subscribe(
data => {
this.comments = data["items"]
},
error => console.error(error)
);
}
}
getCommentList方法调用了commentService服务来从服务器获取信息,那么commentService是如何发起请求的呢,里面有什么逻辑呢?
先上源码:
import { Injectable } from '@angular/core';
import { Http, Response, Headers, RequestOptions,URLSearchParams } from '@angular/http';
import { Observable } from 'rxjs/Rx';
import 'rxjs/add/operator/map';
import 'rxjs/add/operator/catch';
import { Comment } from '../model/comment-model';
@Injectable()
export class CommentService {
public commentListURL = "mock-data/comment-mock.json";
constructor(public http: Http) { }
public getCommentList(postId: number):Observable<Comment[]>{
return this.http.get(this.commentListURL)
.map((res: Response) => res.json())
}
}
Observable<Comment[]>是代表Observable的返回类型,一旦服务器发回了数据,触发的subscrible里面注册的函数的参数为一个数组,里面的元素是Comment类型。
Http是angular内置服务,这里在构造函数里面被注入。http.get()返回的也是Observable类型的对象,它有个属性map,这个map的作用是重构服务器传回来的信息(具体请参考Observable的相关文档)。
这里的map方法也返回一个Observable的对象。res.json()就是将服务器传回来的信息对象化。
以上是一个简单的请求服务器数据的demo,可以将这个demo作为基础种子放到我们的项目中去。