1.字符串常用操作方法
1.str.find('xx',startIndex,endIndex)
没找到,返回-1
str.rfind()
2.str.index('xxx')
没找到,抛出异常
str.rindex()
3.str.count('xxx')
计算出现几次。
4.str.replace('xx','XX') 将替换后的字符串返回
5.str.split(' ') -->[] ***
应用:str="asff d s af d as f fdsf" 将空格和制表符去除
str.split() 按照不可见字符切割
6.str.capitalize() 将第一个字母变成大写
7.titile()

8.startWith('xxx') -->Ture or False
9.lower() , upper()
11.ljust (10) rjust() center() 对齐
12.lstrip() rstrip() strip() 去空格 ***
13.partition() 分割成三部分

14.splitlines() -->按行切
15. isXXX()
isdigit() 纯数字
isalpha() 纯字母
isalnum() 字母或数字
16.join()
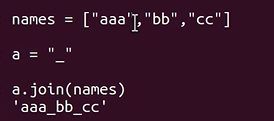
字典 <--->字符串
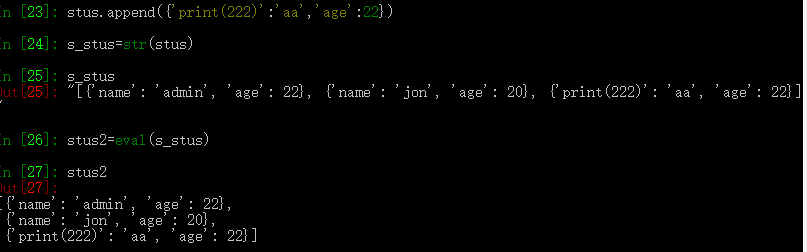
eval("[{'a':'admin''},{}]")

注意:代码注入,不执行?
本质就是将字符串放进代码中执行。 即 stu2=[{},{}],如果这个代码通过,则stu2=eval(s_stu)
也会通过。
17. cmp(str1, str2) 比较两个字符串
2. 正则表达式处理字符串
2.1 规则
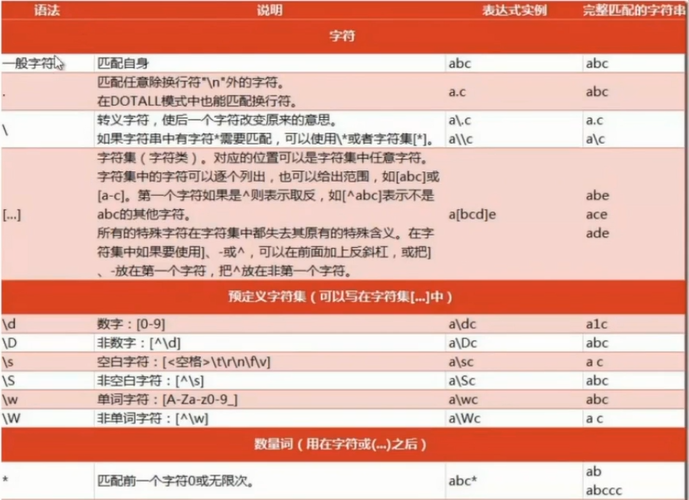
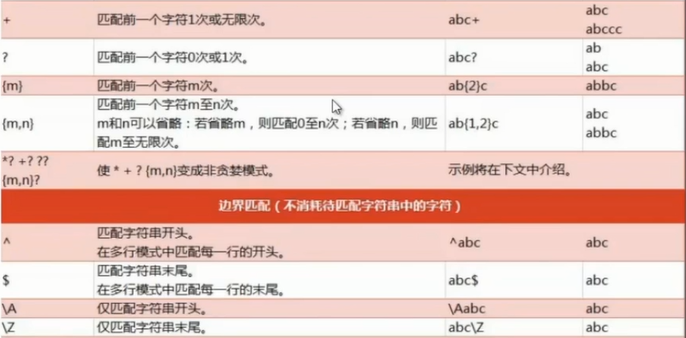
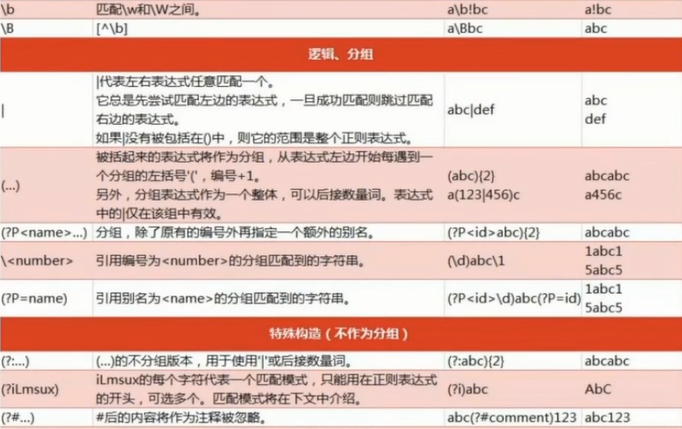
贪婪匹配:{2,6} 匹配2-6个字符,如果能找到6个,就先匹配6个
?:表示有或没有
*:表示>=0
+:表示>=1, 默认是贪婪匹配,尽量匹配多个
组合:/a(bc)+/
或者:(ab) | (cd)
2.2 python中使用正则
# coding:utf-8 import re # 将正则表达式编译成Pattern对象 pattern = re.compile('hello.*!') # 使用Pattern匹配文本,获取匹配结果,无匹配时返回None match = pattern.match('hello world!') if match: # 使用match获取分组信息 print(match.group)

# coding:utf-8 import re # 将正则表达式编译成Pattern对象 pattern = re.compile('(he)llo(.*)!') # 使用Pattern匹配文本,获取匹配结果,无匹配时返回None match = pattern.match('hello world!lsdjl') if match: # 使用match获取分组信息 print(match.group(1,2))
split分割:安装正则方式做分割
p = re.compile(r'd+') print(p.split('aa12bb34cc'))
findall:按照正则方式查询所有匹配的子串,返回列表
p = re.compile(r'd+') print(p.findall('hello 123world456'))
sub:字符串替换
将字符串 hello world, good morning! 替换为world hello, moring good!
p = re.compile(r'(w+) (w+)') print(p.sub(r'2 1', 'hello world, good morning! '))
def func(m):
return m.group(1).title()+' '+m.group(2).title()
print(p.sub(func, 'hello world, good morning! '))
subn:返回替换结果,和替换次数
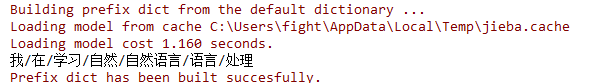
3. jieba中文分词
jieba.cut接受3个参数:
需要分词的字符串
cut_all参数决定是否采用全模式
HMM控制是否HMM模式
import jieba reg_list = jieba.cut('我在学习自然语言处理', cut_all=True) print('/'.join(reg_list))
jieba.cut_search:粒度比较细,所有有意义的词
字符串
是否HMM模式
用户自定义词典,例如专业名词,品牌名词等
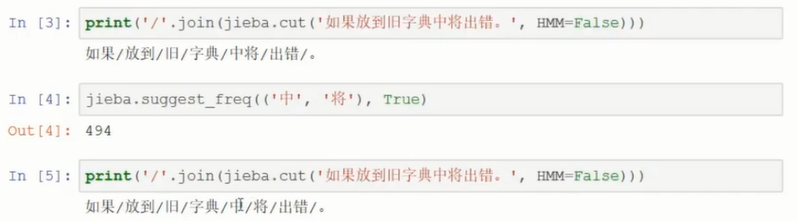
动态添加分词,只对本次程序生效,并且HMM必须设为False
3.1 关键词提取(特征提取)
基于TF-IDF算法的guanjian关键词提取
key_words = analyse.extract_tags(u'', topK=20, withWeight=False, allowPOS=('ns')) print(key_words) # topK:返回多少个关键词 # withWeight:是否返回关键词的权重 # allowPOS:仅仅包好指定的词,默认为空

基于textrank算法的关键词抽取
# 和extract_tags用法相同 jieba.analyse.textrank('', topK=20, withWeight=True, allowPOS=())

词性标注,POS tag

并行分词,提高运行效率
jieba.enable_parallel() words = jieba.cut('我在学习自然语言处理')
在Linux环境下可以使用。
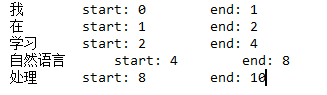
tokenize:返回词语在原文中的起始位置
result = jieba.tokenize(u'我在学习自然语言处理') for tk in result: print('%s start: %d end: %d'%(tk[0], tk[1], tk[2]))
ChineseAnalyzer for Whoosh 搜索引擎
end