Given a string s, find the longest palindromic substring in s. You may assume that the maximum length of s is 1000.
寻找最长回文子串
Example:
Input: "babad" Output: "bab" Note: "aba" is also a valid answer.
Example:
Input: "cbbd" Output: "bb"
Brute Force
Time complexity O(n3)
判断每个子串是否是回文字符串,遍历每个子串O(n2),判断是否回文串O(n)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 | class Solution {public: string longestPalindrome(string s) { int max = 0, maxi = 0, maxc = 0; for (int i = 0; i< s.size(); ++i) { for (int j = 1; i + j - 1< s.size(); ++j) { if (isPalindromic(s.substr(i, j))) if (j> max) { max = j; maxi = i; maxc = j; } } } return s.substr(maxi, maxc); } bool isPalindromic(string s) { for (int i = 0; i < s.size() / 2; ++i) { if (s[i] != s[s.size() - 1- i]) return false; } return true; }}; |
Dynamic Programming
time O(n2), Space O(n2)
递推关系,描述如下:
定义 P[ i, j ] ← 如果子串Si … Sj 是一个回文,那么该项为true, 否则为false
因此递推如下:
P[ i, j ] 为 true ← ( P[ i+1, j-1 ]为true,并且Si = Sj )
基本条件是:
P[ i, i ] 一定是trueP[ i, i+1 ] 为true ← ( Si = Si+1 )
这便是一个典型的DP问题解法。首先初始化长度为1,2的回文字符判断表,即P。然后以它为基础,逐个找出长度为3,4,5……的回文。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 | string longestPalindromeDP(string s) { int n = s.length(); int longestBegin = 0; int maxLen = 1; bool table[1000][1000] = {false}; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { table[i][i] = true; } for (int i = 0; i < n-1; i++) { if (s[i] == s[i+1]) { table[i][i+1] = true; longestBegin = i; maxLen = 2; } } for (int len = 3; len <= n; len++) {//对长度为3,4,5……的子串进行遍历 for (int i = 0; i < n-len+1; i++) {//以len为窗口,在s上进行平移,判断是否符合递推条件 int j = i+len-1; if (s[i] == s[j] && table[i+1][j-1]) { table[i][j] = true; longestBegin = i; maxLen = len; } } } return s.substr(longestBegin, maxLen);} |
举例:cabccbad
第一次循环以后,table值如下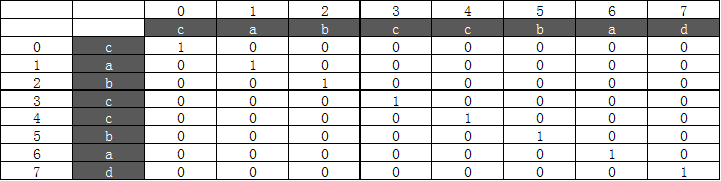
第二次循环以后,table值如下: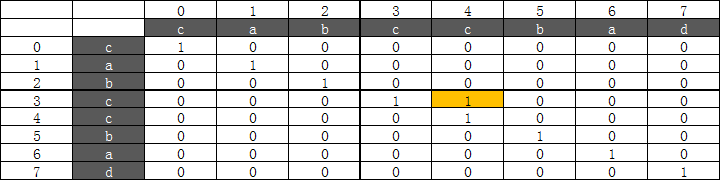
下面开始长度为3,4,5……的循环:
1. len=3:

窗口里的子串为cab,i=0,j=2,这时候判断 Table[1][1] 是否 true(是),并且 s[0] 和 s[2] 是否相等( 不相等)所以不满足。窗口平移:

一样的判断,同理还是不满足。
……
len=3循环结束,table值不变,因为没有长度为3的回文串。
2. len=4:
窗口子串为”cabc“,此时i=0,j=3,Table[1][2] false,不匹配。窗口平移。
窗口子串为”abcc“,此时i=1,j=4,Table[2][3] false,不匹配。窗口平移。

窗口子串为”bccb“,此时i=2,j=5,Table[3][4] true,且 s[2]==s[5],maxlen=4,longestBegin=2,Table更新

3. 后面都不更新。
4. len=6:
当窗口滑到

串口子串为”abccba“,此时i=1,j=6,Table[2][5] true,且 s[1]==s[6],maxlen=6,longestBegin=1,Table更新
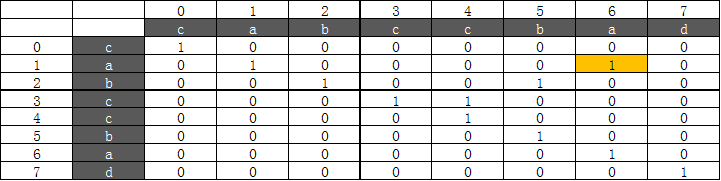
5. len=7:
不更新。
DP改进
事实上我们可以在O(N2)时间复杂度的前提下,不使用额外的存储空间。
可以观察到,一个回文是以中心点,镜像对称的。因此,一个回文可以从中心点展开,而这个中心点,有2N-1个。
可能你会问,为什么是2N-1个中心点,而不是N个。这是因为偶数串中心点是两个数中间,奇数串中心点是中间的数字。
因为在一个中心点展开回文,需要耗时O(N),总共时间复杂度也就是O(N2).
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 | class Solution {public: string longestPalindrome(string s) { int len = s.size(); if (len == 0) return ""; string longest; for(int i = 0; i < len; ++i){ string s1 = expand(s,i,i); if(s1.size() > longest.size()) longest = s1; string s2 = expand(s,i,i+1); if(s2.size() > longest.size()) longest = s2; } return longest; } string expand(string s, int l, int r){ int len = s.size(); while(l>=0 && r < len && s[l] == s[r]){ --l; ++r; } return s.substr(l+1, r - l -1); }}; |
举例:cabccbad
初始时,i=0 (奇 代表奇数长子串,偶 代表偶数长子串)
奇:

一次循环,l=-1,r=1
s.substr(l+1,r-l-1)==s.substr(0,1),即”c“->longest
偶:

不满足循环条件,l=0,r=1
substr(1,0) null.
i=1:
奇:

同上
偶:

同上
……
i=3:
奇:

同上
偶:

可以看出这是回文的对称点。
循环三次,第四次判断结束。
l=0,r=7
substr(1,6):”abccba“ -> longest
……
Manacher算法
see explaination here:http://articles.leetcode.com/longest-palindromic-substring-part-ii/
time complexity O(n)
space comlexity O(n)
1. 计算P[i]
2. 扩展P[i]
3. 扩展边界R,C
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 | // Transform S into T.// For example, S = "abba", T = "^#a#b#b#a#$".// ^ and $ signs are sentinels appended to each end to avoid bounds checkingstring preProcess(string s) { int n = s.length(); if (n == 0) return "^$"; string ret = "^"; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) ret += "#" + s.substr(i, 1); ret += "#$"; return ret;} string longestPalindrome(string s) { string T = preProcess(s); int n = T.length(); int *P = new int[n]; int C = 0, R = 0; for (int i = 1; i < n-1; i++) { int i_mirror = 2*C-i; // equals to i' = C - (i-C) P[i] = (R > i) ? min(R-i, P[i_mirror]) : 0; // Attempt to expand palindrome centered at i if(i + P[i] >= R) // There's no need to expand palindrome when i + P[i] < R while (T[i + 1 + P[i]] == T[i - 1 - P[i]]) P[i]++; // If palindrome centered at i expand past R, // adjust center based on expanded palindrome. if (i + P[i] > R) { C = i; R = i + P[i]; } } // Find the maximum element in P. int maxLen = 0; int centerIndex = 0; for (int i = 1; i < n-1; i++) { if (P[i] > maxLen) { maxLen = P[i]; centerIndex = i; } } delete[] P; return s.substr((centerIndex - 1 - maxLen)/2, maxLen);} |
初始化:
RCiT: ^ # b # a # b # c # b # a # b # c # b # a # c # c # b # a # $P:0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29
i = 1
RCiT: ^ # b # a # b # c # b # a # b # c # b # a # c # c # b # a # $P: 00 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29
i = 2
计算P[i]
RCiT: ^ # b # a # b # c # b # a # b # c # b # a # c # c # b # a # $P: 0 00 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29
扩展P[i]
RCiT: ^ # b # a # b # c # b # a # b # c # b # a # c # c # b # a # $P: 0 10 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29
扩展边界
RCiT: ^ # b # a # b # c # b # a # b # c # b # a # c # c # b # a # $P: 0 10 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29
i = 3
RCiT: ^ # b # a # b # c # b # a # b # c # b # a # c # c # b # a # $P: 0 1 00 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29
i = 4
RCiT: ^ # b # a # b # c # b # a # b # c # b # a # c # c # b # a # $P: 0 1 0 30 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29
i = 5
RCi' iT: ^ # b # a # b # c # b # a # b # c # b # a # c # c # b # a # $P: 0 1 0 3 00 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29
i = 6
RCi' iT: ^ # b # a # b # c # b # a # b # c # b # a # c # c # b # a # $P: 0 1 0 3 0 10 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29
i = 8
RCiT: ^ # b # a # b # c # b # a # b # c # b # a # c # c # b # a # $P: 0 1 0 3 0 1 0 70 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29
i = 9
RCi' iT: ^ # b # a # b # c # b # a # b # c # b # a # c # c # b # a # $P: 0 1 0 3 0 1 0 7 0 1 0 90 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29