本文以一个C语言版的hello world例子阐述编译系统四个阶段的工作内容。源程序hello.c如下:
#include <stdio.h> int main() { printf("hello world! "); }
作为一个精通各种语言的hello world的程序员,我相信你一定看得懂上面这段C代码。总所周知,像C语言这类的编译语言,都是将人类可读的源代码“编译”成机器能识别的“机器代码”,然后方能执行的。而我们通常所说的“编译”,实际上是指的是编译系统,一共包含4个阶段。即:预处理,编译,汇编,链接。而正是这四个阶段所需要的预处理器、编译器、汇编器、链接器构成了编译系统(compilation system)。下图是hello.c经过“编译”成为可执行的目标程序的过程示意图,接下来,将围绕此图阐述各个阶段的工作内容。
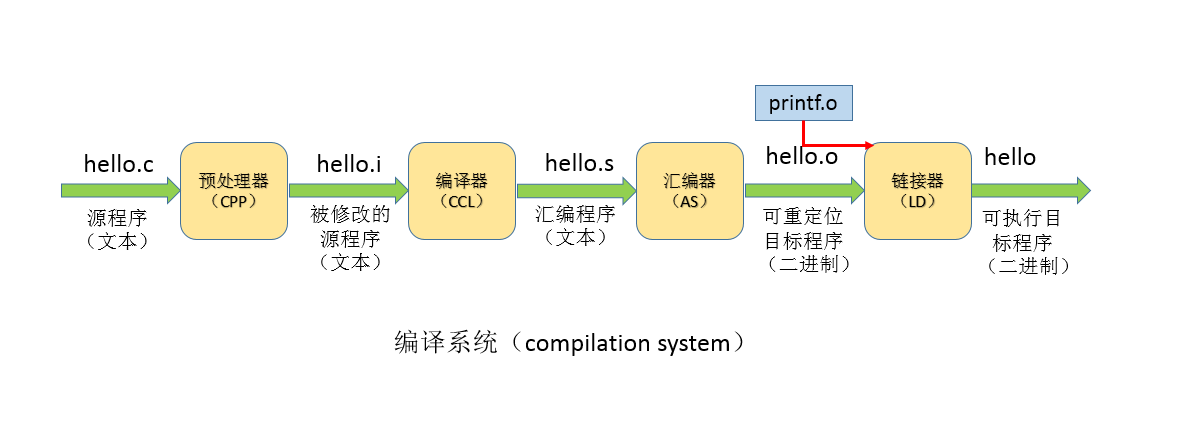
1. 预处理阶段
预处理器(cpp)根据以字符#号开头的命令,修改原始的c程序。比如hello.c中的第一行#include <stdio.h>命令告诉预处理器读取系统头文件stdio.h的内容,并把它直接插入到程序文本中,结果得到了另一个C程序,通常是以.i为扩展名。在Linux下我们用GCC命令:
gcc -E hello.c -o hello.i
得到一个hello.i文件,然后查看文件内容如下:

1 # 1 "hello.c" 2 # 1 "<built-in>" 3 # 1 "<command-line>" 4 # 1 "/usr/include/stdc-predef.h" 1 3 4 5 # 1 "<command-line>" 2 6 # 1 "hello.c" 7 # 1 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 1 3 4 8 # 27 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4 9 # 1 "/usr/include/features.h" 1 3 4 10 # 375 "/usr/include/features.h" 3 4 11 # 1 "/usr/include/sys/cdefs.h" 1 3 4 12 # 392 "/usr/include/sys/cdefs.h" 3 4 13 # 1 "/usr/include/bits/wordsize.h" 1 3 4 14 # 393 "/usr/include/sys/cdefs.h" 2 3 4 15 # 376 "/usr/include/features.h" 2 3 4 16 # 399 "/usr/include/features.h" 3 4 17 # 1 "/usr/include/gnu/stubs.h" 1 3 4 18 # 10 "/usr/include/gnu/stubs.h" 3 4 19 # 1 "/usr/include/gnu/stubs-64.h" 1 3 4 20 # 11 "/usr/include/gnu/stubs.h" 2 3 4 21 # 400 "/usr/include/features.h" 2 3 4 22 # 28 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 2 3 4 23 24 25 26 27 28 # 1 "/usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-redhat-linux/4.8.5/include/stddef.h" 1 3 4 29 # 212 "/usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-redhat-linux/4.8.5/include/stddef.h" 3 4 30 typedef long unsigned int size_t; 31 # 34 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 2 3 4 32 33 # 1 "/usr/include/bits/types.h" 1 3 4 34 # 27 "/usr/include/bits/types.h" 3 4 35 # 1 "/usr/include/bits/wordsize.h" 1 3 4 36 # 28 "/usr/include/bits/types.h" 2 3 4 37 38 39 typedef unsigned char __u_char; 40 typedef unsigned short int __u_short; 41 typedef unsigned int __u_int; 42 typedef unsigned long int __u_long; 43 44 45 typedef signed char __int8_t; 46 typedef unsigned char __uint8_t; 47 typedef signed short int __int16_t; 48 typedef unsigned short int __uint16_t; 49 typedef signed int __int32_t; 50 typedef unsigned int __uint32_t; 51 52 typedef signed long int __int64_t; 53 typedef unsigned long int __uint64_t; 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 typedef long int __quad_t; 62 typedef unsigned long int __u_quad_t; 63 # 130 "/usr/include/bits/types.h" 3 4 64 # 1 "/usr/include/bits/typesizes.h" 1 3 4 65 # 131 "/usr/include/bits/types.h" 2 3 4 66 67 68 typedef unsigned long int __dev_t; 69 typedef unsigned int __uid_t; 70 typedef unsigned int __gid_t; 71 typedef unsigned long int __ino_t; 72 typedef unsigned long int __ino64_t; 73 typedef unsigned int __mode_t; 74 typedef unsigned long int __nlink_t; 75 typedef long int __off_t; 76 typedef long int __off64_t; 77 typedef int __pid_t; 78 typedef struct { int __val[2]; } __fsid_t; 79 typedef long int __clock_t; 80 typedef unsigned long int __rlim_t; 81 typedef unsigned long int __rlim64_t; 82 typedef unsigned int __id_t; 83 typedef long int __time_t; 84 typedef unsigned int __useconds_t; 85 typedef long int __suseconds_t; 86 87 typedef int __daddr_t; 88 typedef int __key_t; 89 90 91 typedef int __clockid_t; 92 93 94 typedef void * __timer_t; 95 96 97 typedef long int __blksize_t; 98 99 100 101 102 typedef long int __blkcnt_t; 103 typedef long int __blkcnt64_t; 104 105 106 typedef unsigned long int __fsblkcnt_t; 107 typedef unsigned long int __fsblkcnt64_t; 108 109 110 typedef unsigned long int __fsfilcnt_t; 111 typedef unsigned long int __fsfilcnt64_t; 112 113 114 typedef long int __fsword_t; 115 116 typedef long int __ssize_t; 117 118 119 typedef long int __syscall_slong_t; 120 121 typedef unsigned long int __syscall_ulong_t; 122 123 124 125 typedef __off64_t __loff_t; 126 typedef __quad_t *__qaddr_t; 127 typedef char *__caddr_t; 128 129 130 typedef long int __intptr_t; 131 132 133 typedef unsigned int __socklen_t; 134 # 36 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 2 3 4 135 # 44 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4 136 struct _IO_FILE; 137 138 139 140 typedef struct _IO_FILE FILE; 141 142 143 144 145 146 # 64 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4 147 typedef struct _IO_FILE __FILE; 148 # 74 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4 149 # 1 "/usr/include/libio.h" 1 3 4 150 # 32 "/usr/include/libio.h" 3 4 151 # 1 "/usr/include/_G_config.h" 1 3 4 152 # 15 "/usr/include/_G_config.h" 3 4 153 # 1 "/usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-redhat-linux/4.8.5/include/stddef.h" 1 3 4 154 # 16 "/usr/include/_G_config.h" 2 3 4 155 156 157 158 159 # 1 "/usr/include/wchar.h" 1 3 4 160 # 82 "/usr/include/wchar.h" 3 4 161 typedef struct 162 { 163 int __count; 164 union 165 { 166 167 unsigned int __wch; 168 169 170 171 char __wchb[4]; 172 } __value; 173 } __mbstate_t; 174 # 21 "/usr/include/_G_config.h" 2 3 4 175 typedef struct 176 { 177 __off_t __pos; 178 __mbstate_t __state; 179 } _G_fpos_t; 180 typedef struct 181 { 182 __off64_t __pos; 183 __mbstate_t __state; 184 } _G_fpos64_t; 185 # 33 "/usr/include/libio.h" 2 3 4 186 # 50 "/usr/include/libio.h" 3 4 187 # 1 "/usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-redhat-linux/4.8.5/include/stdarg.h" 1 3 4 188 # 40 "/usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-redhat-linux/4.8.5/include/stdarg.h" 3 4 189 typedef __builtin_va_list __gnuc_va_list; 190 # 51 "/usr/include/libio.h" 2 3 4 191 # 145 "/usr/include/libio.h" 3 4 192 struct _IO_jump_t; struct _IO_FILE; 193 # 155 "/usr/include/libio.h" 3 4 194 typedef void _IO_lock_t; 195 196 197 198 199 200 struct _IO_marker { 201 struct _IO_marker *_next; 202 struct _IO_FILE *_sbuf; 203 204 205 206 int _pos; 207 # 178 "/usr/include/libio.h" 3 4 208 }; 209 210 211 enum __codecvt_result 212 { 213 __codecvt_ok, 214 __codecvt_partial, 215 __codecvt_error, 216 __codecvt_noconv 217 }; 218 # 246 "/usr/include/libio.h" 3 4 219 struct _IO_FILE { 220 int _flags; 221 222 223 224 225 char* _IO_read_ptr; 226 char* _IO_read_end; 227 char* _IO_read_base; 228 char* _IO_write_base; 229 char* _IO_write_ptr; 230 char* _IO_write_end; 231 char* _IO_buf_base; 232 char* _IO_buf_end; 233 234 char *_IO_save_base; 235 char *_IO_backup_base; 236 char *_IO_save_end; 237 238 struct _IO_marker *_markers; 239 240 struct _IO_FILE *_chain; 241 242 int _fileno; 243 244 245 246 int _flags2; 247 248 __off_t _old_offset; 249 250 251 252 unsigned short _cur_column; 253 signed char _vtable_offset; 254 char _shortbuf[1]; 255 256 257 258 _IO_lock_t *_lock; 259 # 294 "/usr/include/libio.h" 3 4 260 __off64_t _offset; 261 # 303 "/usr/include/libio.h" 3 4 262 void *__pad1; 263 void *__pad2; 264 void *__pad3; 265 void *__pad4; 266 size_t __pad5; 267 268 int _mode; 269 270 char _unused2[15 * sizeof (int) - 4 * sizeof (void *) - sizeof (size_t)]; 271 272 }; 273 274 275 typedef struct _IO_FILE _IO_FILE; 276 277 278 struct _IO_FILE_plus; 279 280 extern struct _IO_FILE_plus _IO_2_1_stdin_; 281 extern struct _IO_FILE_plus _IO_2_1_stdout_; 282 extern struct _IO_FILE_plus _IO_2_1_stderr_; 283 # 339 "/usr/include/libio.h" 3 4 284 typedef __ssize_t __io_read_fn (void *__cookie, char *__buf, size_t __nbytes); 285 286 287 288 289 290 291 292 typedef __ssize_t __io_write_fn (void *__cookie, const char *__buf, 293 size_t __n); 294 295 296 297 298 299 300 301 typedef int __io_seek_fn (void *__cookie, __off64_t *__pos, int __w); 302 303 304 typedef int __io_close_fn (void *__cookie); 305 # 391 "/usr/include/libio.h" 3 4 306 extern int __underflow (_IO_FILE *); 307 extern int __uflow (_IO_FILE *); 308 extern int __overflow (_IO_FILE *, int); 309 # 435 "/usr/include/libio.h" 3 4 310 extern int _IO_getc (_IO_FILE *__fp); 311 extern int _IO_putc (int __c, _IO_FILE *__fp); 312 extern int _IO_feof (_IO_FILE *__fp) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)); 313 extern int _IO_ferror (_IO_FILE *__fp) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)); 314 315 extern int _IO_peekc_locked (_IO_FILE *__fp); 316 317 318 319 320 321 extern void _IO_flockfile (_IO_FILE *) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)); 322 extern void _IO_funlockfile (_IO_FILE *) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)); 323 extern int _IO_ftrylockfile (_IO_FILE *) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)); 324 # 465 "/usr/include/libio.h" 3 4 325 extern int _IO_vfscanf (_IO_FILE * __restrict, const char * __restrict, 326 __gnuc_va_list, int *__restrict); 327 extern int _IO_vfprintf (_IO_FILE *__restrict, const char *__restrict, 328 __gnuc_va_list); 329 extern __ssize_t _IO_padn (_IO_FILE *, int, __ssize_t); 330 extern size_t _IO_sgetn (_IO_FILE *, void *, size_t); 331 332 extern __off64_t _IO_seekoff (_IO_FILE *, __off64_t, int, int); 333 extern __off64_t _IO_seekpos (_IO_FILE *, __off64_t, int); 334 335 extern void _IO_free_backup_area (_IO_FILE *) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)); 336 # 75 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 2 3 4 337 338 339 340 341 typedef __gnuc_va_list va_list; 342 # 90 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4 343 typedef __off_t off_t; 344 # 102 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4 345 typedef __ssize_t ssize_t; 346 347 348 349 350 351 352 353 typedef _G_fpos_t fpos_t; 354 355 356 357 358 # 164 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4 359 # 1 "/usr/include/bits/stdio_lim.h" 1 3 4 360 # 165 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 2 3 4 361 362 363 364 extern struct _IO_FILE *stdin; 365 extern struct _IO_FILE *stdout; 366 extern struct _IO_FILE *stderr; 367 368 369 370 371 372 373 374 extern int remove (const char *__filename) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)); 375 376 extern int rename (const char *__old, const char *__new) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)); 377 378 379 380 381 extern int renameat (int __oldfd, const char *__old, int __newfd, 382 const char *__new) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)); 383 384 385 386 387 388 389 390 391 extern FILE *tmpfile (void) ; 392 # 209 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4 393 extern char *tmpnam (char *__s) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ; 394 395 396 397 398 399 extern char *tmpnam_r (char *__s) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ; 400 # 227 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4 401 extern char *tempnam (const char *__dir, const char *__pfx) 402 __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) __attribute__ ((__malloc__)) ; 403 404 405 406 407 408 409 410 411 extern int fclose (FILE *__stream); 412 413 414 415 416 extern int fflush (FILE *__stream); 417 418 # 252 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4 419 extern int fflush_unlocked (FILE *__stream); 420 # 266 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4 421 422 423 424 425 426 427 extern FILE *fopen (const char *__restrict __filename, 428 const char *__restrict __modes) ; 429 430 431 432 433 extern FILE *freopen (const char *__restrict __filename, 434 const char *__restrict __modes, 435 FILE *__restrict __stream) ; 436 # 295 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4 437 438 # 306 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4 439 extern FILE *fdopen (int __fd, const char *__modes) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ; 440 # 319 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4 441 extern FILE *fmemopen (void *__s, size_t __len, const char *__modes) 442 __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ; 443 444 445 446 447 extern FILE *open_memstream (char **__bufloc, size_t *__sizeloc) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ; 448 449 450 451 452 453 454 extern void setbuf (FILE *__restrict __stream, char *__restrict __buf) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)); 455 456 457 458 extern int setvbuf (FILE *__restrict __stream, char *__restrict __buf, 459 int __modes, size_t __n) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)); 460 461 462 463 464 465 extern void setbuffer (FILE *__restrict __stream, char *__restrict __buf, 466 size_t __size) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)); 467 468 469 extern void setlinebuf (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)); 470 471 472 473 474 475 476 477 478 extern int fprintf (FILE *__restrict __stream, 479 const char *__restrict __format, ...); 480 481 482 483 484 extern int printf (const char *__restrict __format, ...); 485 486 extern int sprintf (char *__restrict __s, 487 const char *__restrict __format, ...) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__)); 488 489 490 491 492 493 extern int vfprintf (FILE *__restrict __s, const char *__restrict __format, 494 __gnuc_va_list __arg); 495 496 497 498 499 extern int vprintf (const char *__restrict __format, __gnuc_va_list __arg); 500 501 extern int vsprintf (char *__restrict __s, const char *__restrict __format, 502 __gnuc_va_list __arg) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__)); 503 504 505 506 507 508 extern int snprintf (char *__restrict __s, size_t __maxlen, 509 const char *__restrict __format, ...) 510 __attribute__ ((__nothrow__)) __attribute__ ((__format__ (__printf__, 3, 4))); 511 512 extern int vsnprintf (char *__restrict __s, size_t __maxlen, 513 const char *__restrict __format, __gnuc_va_list __arg) 514 __attribute__ ((__nothrow__)) __attribute__ ((__format__ (__printf__, 3, 0))); 515 516 # 412 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4 517 extern int vdprintf (int __fd, const char *__restrict __fmt, 518 __gnuc_va_list __arg) 519 __attribute__ ((__format__ (__printf__, 2, 0))); 520 extern int dprintf (int __fd, const char *__restrict __fmt, ...) 521 __attribute__ ((__format__ (__printf__, 2, 3))); 522 523 524 525 526 527 528 529 530 extern int fscanf (FILE *__restrict __stream, 531 const char *__restrict __format, ...) ; 532 533 534 535 536 extern int scanf (const char *__restrict __format, ...) ; 537 538 extern int sscanf (const char *__restrict __s, 539 const char *__restrict __format, ...) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)); 540 # 443 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4 541 extern int fscanf (FILE *__restrict __stream, const char *__restrict __format, ...) __asm__ ("" "__isoc99_fscanf") 542 543 ; 544 extern int scanf (const char *__restrict __format, ...) __asm__ ("" "__isoc99_scanf") 545 ; 546 extern int sscanf (const char *__restrict __s, const char *__restrict __format, ...) __asm__ ("" "__isoc99_sscanf") __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) 547 548 ; 549 # 463 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4 550 551 552 553 554 555 556 557 558 extern int vfscanf (FILE *__restrict __s, const char *__restrict __format, 559 __gnuc_va_list __arg) 560 __attribute__ ((__format__ (__scanf__, 2, 0))) ; 561 562 563 564 565 566 extern int vscanf (const char *__restrict __format, __gnuc_va_list __arg) 567 __attribute__ ((__format__ (__scanf__, 1, 0))) ; 568 569 570 extern int vsscanf (const char *__restrict __s, 571 const char *__restrict __format, __gnuc_va_list __arg) 572 __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) __attribute__ ((__format__ (__scanf__, 2, 0))); 573 # 494 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4 574 extern int vfscanf (FILE *__restrict __s, const char *__restrict __format, __gnuc_va_list __arg) __asm__ ("" "__isoc99_vfscanf") 575 576 577 578 __attribute__ ((__format__ (__scanf__, 2, 0))) ; 579 extern int vscanf (const char *__restrict __format, __gnuc_va_list __arg) __asm__ ("" "__isoc99_vscanf") 580 581 __attribute__ ((__format__ (__scanf__, 1, 0))) ; 582 extern int vsscanf (const char *__restrict __s, const char *__restrict __format, __gnuc_va_list __arg) __asm__ ("" "__isoc99_vsscanf") __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) 583 584 585 586 __attribute__ ((__format__ (__scanf__, 2, 0))); 587 # 522 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4 588 589 590 591 592 593 594 595 596 597 extern int fgetc (FILE *__stream); 598 extern int getc (FILE *__stream); 599 600 601 602 603 604 extern int getchar (void); 605 606 # 550 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4 607 extern int getc_unlocked (FILE *__stream); 608 extern int getchar_unlocked (void); 609 # 561 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4 610 extern int fgetc_unlocked (FILE *__stream); 611 612 613 614 615 616 617 618 619 620 621 622 extern int fputc (int __c, FILE *__stream); 623 extern int putc (int __c, FILE *__stream); 624 625 626 627 628 629 extern int putchar (int __c); 630 631 # 594 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4 632 extern int fputc_unlocked (int __c, FILE *__stream); 633 634 635 636 637 638 639 640 extern int putc_unlocked (int __c, FILE *__stream); 641 extern int putchar_unlocked (int __c); 642 643 644 645 646 647 648 extern int getw (FILE *__stream); 649 650 651 extern int putw (int __w, FILE *__stream); 652 653 654 655 656 657 658 659 660 extern char *fgets (char *__restrict __s, int __n, FILE *__restrict __stream) 661 ; 662 # 638 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4 663 extern char *gets (char *__s) __attribute__ ((__deprecated__)); 664 665 666 # 665 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4 667 extern __ssize_t __getdelim (char **__restrict __lineptr, 668 size_t *__restrict __n, int __delimiter, 669 FILE *__restrict __stream) ; 670 extern __ssize_t getdelim (char **__restrict __lineptr, 671 size_t *__restrict __n, int __delimiter, 672 FILE *__restrict __stream) ; 673 674 675 676 677 678 679 680 extern __ssize_t getline (char **__restrict __lineptr, 681 size_t *__restrict __n, 682 FILE *__restrict __stream) ; 683 684 685 686 687 688 689 690 691 extern int fputs (const char *__restrict __s, FILE *__restrict __stream); 692 693 694 695 696 697 extern int puts (const char *__s); 698 699 700 701 702 703 704 extern int ungetc (int __c, FILE *__stream); 705 706 707 708 709 710 711 extern size_t fread (void *__restrict __ptr, size_t __size, 712 size_t __n, FILE *__restrict __stream) ; 713 714 715 716 717 extern size_t fwrite (const void *__restrict __ptr, size_t __size, 718 size_t __n, FILE *__restrict __s); 719 720 # 737 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4 721 extern size_t fread_unlocked (void *__restrict __ptr, size_t __size, 722 size_t __n, FILE *__restrict __stream) ; 723 extern size_t fwrite_unlocked (const void *__restrict __ptr, size_t __size, 724 size_t __n, FILE *__restrict __stream); 725 726 727 728 729 730 731 732 733 extern int fseek (FILE *__stream, long int __off, int __whence); 734 735 736 737 738 extern long int ftell (FILE *__stream) ; 739 740 741 742 743 extern void rewind (FILE *__stream); 744 745 # 773 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4 746 extern int fseeko (FILE *__stream, __off_t __off, int __whence); 747 748 749 750 751 extern __off_t ftello (FILE *__stream) ; 752 # 792 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4 753 754 755 756 757 758 759 extern int fgetpos (FILE *__restrict __stream, fpos_t *__restrict __pos); 760 761 762 763 764 extern int fsetpos (FILE *__stream, const fpos_t *__pos); 765 # 815 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4 766 767 # 824 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4 768 769 770 extern void clearerr (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)); 771 772 extern int feof (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ; 773 774 extern int ferror (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ; 775 776 777 778 779 extern void clearerr_unlocked (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)); 780 extern int feof_unlocked (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ; 781 extern int ferror_unlocked (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ; 782 783 784 785 786 787 788 789 790 extern void perror (const char *__s); 791 792 793 794 795 796 797 # 1 "/usr/include/bits/sys_errlist.h" 1 3 4 798 # 26 "/usr/include/bits/sys_errlist.h" 3 4 799 extern int sys_nerr; 800 extern const char *const sys_errlist[]; 801 # 854 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 2 3 4 802 803 804 805 806 extern int fileno (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ; 807 808 809 810 811 extern int fileno_unlocked (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ; 812 # 873 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4 813 extern FILE *popen (const char *__command, const char *__modes) ; 814 815 816 817 818 819 extern int pclose (FILE *__stream); 820 821 822 823 824 825 extern char *ctermid (char *__s) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)); 826 # 913 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4 827 extern void flockfile (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)); 828 829 830 831 extern int ftrylockfile (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ; 832 833 834 extern void funlockfile (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)); 835 # 943 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4 836 837 # 2 "hello.c" 2 838 839 int main() { 840 printf("hello world! "); 841 }
该程序依然是C语言程序,只不过多了头文件stdio.h的内容。
2. 编译阶段
编译器(ccl)将文本文件hello.i翻译成文本文件hello.s,它包含一个汇编语言程序。汇编语言中每条语句都以一种标准的文本格式确切地描述了一条低级机器语言指令。其实汇编语言是非常有用的,它为所有的高级语言提供了一种通用的输出语言。比如C编译器和Fortran编译器产生的输出文件用的都是一样的汇编语言。在Linux下,我们用命令:
gcc -S hello.i -o hello.s
得到一个hello.s汇编程序,内容如下:

.file "hello.c" .section .rodata .LC0: .string "hello world!" .text .globl main .type main, @function main: .LFB0: .cfi_startproc pushq %rbp .cfi_def_cfa_offset 16 .cfi_offset 6, -16 movq %rsp, %rbp .cfi_def_cfa_register 6 movl $.LC0, %edi call puts popq %rbp .cfi_def_cfa 7, 8 ret .cfi_endproc .LFE0: .size main, .-main .ident "GCC: (GNU) 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-11)" .section .note.GNU-stack,"",@progbits
3. 汇编阶段
汇编器(as)将hello.s翻译成机器语言指令,把这些指令打包成一种叫做可定位目标程序的格式,并将结果保存在目标文件hello.o中,hello.o是一个二进制文件,它的字节编码是“机器语言指令”而不是“字符”,所以,我们用文本编辑器打开hello.o文件看到是回事一堆乱码。使用gcc命令:
gcc -c hello.s -o hello.o
将得到hello.o文件,用vim打开看一下是如下乱码:

4. 链接阶段
我们注意到,hello.c中有一个printf函数,它是每个C编译器都会提供的标准库中的一个函数。printf函数存在于一个名为printf.o的单独的预编译好的目标文件中,而这个文件必须以某种方式合并到我们的hello.o程序中。链接器(ld)就是负责处理这种合并。最后得到hello文件,一个可执行目标文件(可执行文件),可被加载到内存中,由系统执行。使用命令:
gcc hello.o -o hello
得到hello文件,内容如下:
自此,编译系统的整个过程大致如此。总结一下,从源程序到目标文件(可执行文件)的转化是通过编译系统完成的,编译系统包含四个阶段:预处理,编译,汇编,链接。一般的编译驱动程序如GCC都实现了编译系统的所有功能,我们用编译驱动程序直接就可以实现源程序到目标文件的转化。
