介绍
Elasticsearch 是一个分布式可扩展的实时搜索和分析引擎,一个建立在全文搜索引擎 Apache Lucene(TM) 基础上的搜索引擎.当然 Elasticsearch 并不仅仅是 Lucene 那么简单,它不仅包括了全文搜索功能,还可以进行以下工作:
- 分布式实时文件存储,并将每一个字段都编入索引,使其可以被搜索。
- 实时分析的分布式搜索引擎。
- 可以扩展到上百台服务器,处理PB级别的结构化或非结构化数据。
基本概念
先说Elasticsearch的文件存储,Elasticsearch是面向文档型数据库,一条数据在这里就是一个文档,用JSON作为文档序列化的格式,比如下面这条用户数据:
{ "name" : "John", "sex" : "Male", "age" : 25, "birthDate": "1990/05/01", "about" : "I love to go rock climbing", "interests": [ "sports", "music" ] }
用Mysql这样的数据库存储就会容易想到建立一张User表,有balabala的字段等,在Elasticsearch里这就是一个文档,当然这个文档会属于一个User的类型,各种各样的类型存在于一个索引当中。这里有一份简易的将Elasticsearch和关系型数据术语对照表:
关系数据库 ⇒ 数据库 ⇒ 表 ⇒ 行 ⇒ 列(Columns)
Elasticsearch ⇒ 索引(Index) ⇒ 类型(type) ⇒ 文档(Docments) ⇒ 字段(Fields)
一个 Elasticsearch 集群可以包含多个索引(数据库),也就是说其中包含了很多类型(表)。这些类型中包含了很多的文档(行),然后每个文档中又包含了很多的字段(列)。Elasticsearch的交互,可以使用Java API,也可以直接使用HTTP的Restful API方式,比如我们打算插入一条记录,可以简单发送一个HTTP的请求:
PUT /megacorp/employee/1
{ "name" : "John", "sex" : "Male", "age" : 25, "about" : "I love to go rock climbing", "interests": [ "sports", "music" ] }
安装
tar -zxf elasticsearch-6.3.2.tar.gz cd elasticsearch-6.3.2/bin ./elasticsearch 注意:不能以root用户运行elasticsearch
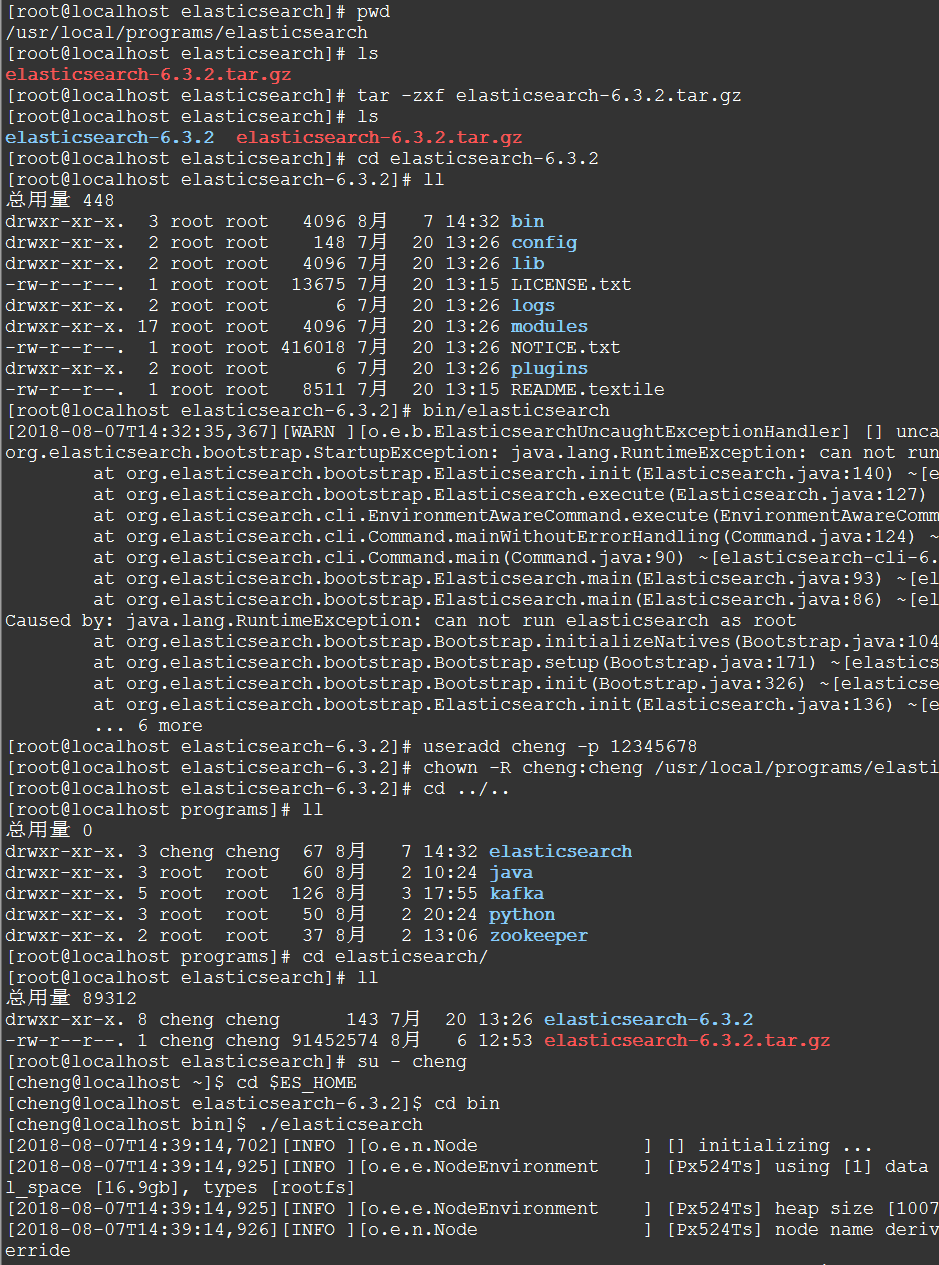
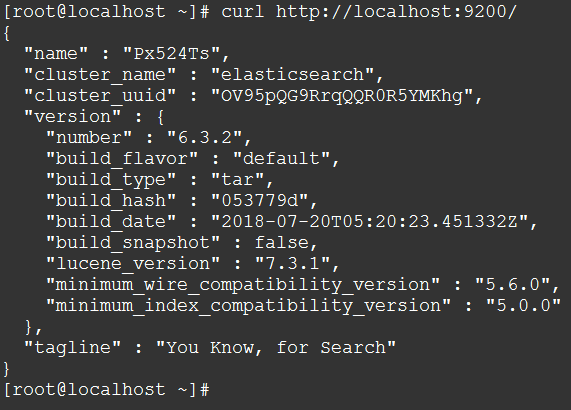
检查Elasticsearch是否正在运行:
curl http://localhost:9200/
查看全部索引
# 请求: curl -X GET "localhost:9200/_cat/indices?v" # 响应: # health status index uuid pri rep docs.count docs.deleted store.size pri.store.size
上面的输出意味着:我们在集群中没有索引
创建一个索引
现在,我们创建一个名字叫“customer”的索引,然后查看索引:
# 请求: curl -X PUT "localhost:9200/customer?pretty" # 响应: { "acknowledged" : true, "shards_acknowledged" : true, "index" : "customer" } # 再次请求查看全部索引 curl -X GET "localhost:9200/_cat/indices?v" # 响应: health status index uuid pri rep docs.count docs.deleted store.size pri.store.size yellow open customer rG5fxdruTNmD-bdYIF5zOg 5 1 0 0 1.1kb 1.1kb
结果的第二行告诉我们,我们现在有叫"customer"的索引,并且他有5个主分片和1个副本(默认是1个副本),有0个文档。
可能你已经注意到这个"customer"索引的健康状态是yellow。回想一下我们之前的讨论,yellow意味着一些副本(尚未)被分配。
之所以会出现这种情况,是因为Elasticsearch默认情况下为这个索引创建了一个副本。由于目前我们只有一个节点在运行,所以直到稍后另一个节点加入集群时,才会分配一个副本(对于高可用性)。一旦该副本分配到第二个节点上,该索引的健康状态将变为green
索引并查询一个文档
现在,让我们put一些数据到我们的"customer"索引:
# 请求: curl -X PUT "localhost:9200/customer/_doc/1?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d'{"name": "John Doe"}' # 响应 { "_index" : "customer", "_type" : "_doc", "_id" : "1", "_version" : 1, "result" : "created", "_shards" : { "total" : 2, "successful" : 1, "failed" : 0 }, "_seq_no" : 0, "_primary_term" : 1 }
从上面的响应可以看到,我们在"customer"索引下成功创建了一个文档。这个文档还有一个内部id为1,这是我们在创建的时候指定的。
需要注意的是,Elasticsearch并不要求你在索引文档之前就先创建索引,然后才能将文档编入索引。在前面的示例中,如果事先不存在"customer"索引,Elasticsearch将自动创建"customer"索引。
(画外音:也就是说,在新建文档的时候如果指定的索引不存在则会自动创建相应的索引)
现在,让我重新检索这个文档:
# 请求 curl -X GET "localhost:9200/customer/_doc/1?pretty" # 响应 { "_index" : "customer", "_type" : "_doc", "_id" : "1", "_version" : 1, "found" : true, "_source" : { "name" : "John Doe" } }
可以看到除了"found"字段外没什么不同,"_source"字段返回了一个完整的JSON文档。
删除一个索引
现在,让我们删除前面创建的索引,然后查看全部索引
# 请求 curl -X DELETE "localhost:9200/customer?pretty" # 响应 { "acknowledged" : true }
接下来,查看一下
# 请求 curl -X GET "localhost:9200/_cat/indices?v" 响应 health status index uuid pri rep docs.count docs.deleted store.size pri.store.size
到现在为止,我们已经学习了创建/删除索引、索引/查询文档这四个命令
curl -X PUT "localhost:9200/customer" curl -X PUT "localhost:9200/customer/_doc/1" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d'{"name": "John Doe"}' curl -X GET "localhost:9200/customer/_doc/1" curl -X DELETE "localhost:9200/customer"