- 提取一些经常使用的对象特征
1.长宽比
边界矩形的宽高比
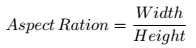
x,y,w,h = cv2.boundingRect(cnt)
aspect_ratio = floart(w)/h
2.Extent
轮廓面积与边界矩形面积的比。
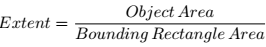
area = cv2.contourArea(cnt)
x,y,w,h = cv2.boundingRect(cnt)
rect_area = w*h
extent = float(area)/rect_area
3.Solidity
轮廓面积与凸包面积的比

area = cv2.contourtArea(cnt)
hull = cv2.convexHull(cnt)
hull_area = cv2.contourArea(hull)
solidity = float(area)/hull_area
4.Equivalent Diameter
与轮廓面积相等的圆形的直径
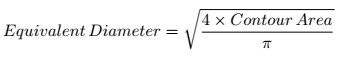
area = cv2.contourArea(cnt)
equi_diameter = np.sqrt(4*area/np.pi)
5.方向
对象的方向,下面的方法还会返回长轴和短轴的长度
(x,y),(MA,ma),angle = cv2.fitEllipse(cnt)
6.掩膜和像素点
有时我们需要构成对象的所有像素点,我们可以这样做:
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import numpy as np
import cv2
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
im = cv2.imread('10.png')
img = cv2.cvtColor(im,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)#用这个方式转换的原因是最后输出时希望能看到彩色的的轮廓图
ret,thresh = cv2.threshold(img,127,255,0)
img,contours,hierarchy = cv2.findContours(thresh,1,2)
cnt = contours[0]
mask = np.zeros(im.shape,np.uint8)
cv2.drawContours(mask,[cnt],0,255,-1)#使用-1可以绘制填充的轮廓
#transpose及noozero用法介绍
#Returns a tuple of arrays, one for each dimension of a,
#containing the indices of the non-zero elements in that dimension.
#The result of this is always a 2-D array, with a row for
#each non-zero element.
#To group the indices by element, rather than dimension, use:
#transpose(nonzero(a))
#>>> x = np.eye(3)
#>>> x
#array([[ 1., 0., 0.],
# [ 0., 1., 0.],
# [ 0., 0., 1.]])
#>>> np.nonzero(x)
#(array([0, 1, 2]), array([0, 1, 2]))
#>>> x[np.nonzero(x)]
#array([ 1., 1., 1.])
#>>> np.transpose(np.nonzero(x))
#array([[0, 0],
# [1, 1],
# [2, 2]]
pixelpoints = np.transpose(np.nonzero(mask))
#pixelpoints = cv2.findNonZero(mask)
#两种方法给出的结果相同,格式不同,前者是(row,column),后者是(x,y),所以这里row = x ,column = y
cv2.imshow('img',mask)
cv2.waitKey(0)
7.最大值最小值及它们的位置
利用上面得到的掩膜图像可以得到这些参数
min_val, max_val, min_loc, max_loc = cv2.minMaxLoc(imgray,mask = mask)
#试了一下,不使用掩膜反而能得到这些参数,使用了就得不到了。
8.平均颜色及平均灰度
可以使用相同的掩膜求一个对象的平均颜色或平均灰度
mean_val = cv2.mean(im,mask = mask)
9,.极点
一个对象最上面,最下面,最左边,最右边的点
leftmost = tuple(cnt[cnt[:,:,0].argmin()][0])
rightmost = tuple(cnt[cnt[:,:,0].argmax()][0])
topmost = tuple(cnt[cnt[:,:,1].argmin()][0])
bottommost = tuple(cnt[cnt[:,:,1].argmax()][0])