https://www.techtarget.com/searchnetworking/definition/BGP-Border-Gateway-Protocol
BGP(边界网关协议)是互联网全球路由系统的底层协议。它通过在边缘路由器之间交换路由和可达性信息来管理数据包如何从网络路由到网络。BGP 在自治系统 ( AS )之间引导数据包,自治系统是由单个企业或服务提供商管理的网络。
BGP 通过保证路由器能够适应路由故障来创建网络稳定性:当一条路径出现故障时,可以快速找到一条新路径。BGP 根据路径做出路由决策,这些路径由网络管理员设置的规则或网络策略定义。
BGP 如何工作?
每个路由器维护一个路由表,控制数据包的定向方式。路由表信息由路由器上的 BGP 进程根据来自其他路由器的传入信息以及 BGP 路由信息库 (RIB) 中的信息生成,该信息库是存储在 BGP 路由器上的服务器上的数据表。RIB 包含来自直接连接的外部对等体和内部对等体的信息,并根据应该使用什么路由和应该发布什么信息的策略,在发生变化时不断更新路由表。
BGP有什么用?
BGP 提供网络稳定性,确保路由器可以在一个 Internet 路径出现故障时快速适应通过另一次重新连接发送数据包。BGP 根据网络管理员配置的路径、规则或网络策略做出路由决策。每个 BGP 路由器都维护一个标准路由表,用于引导传输中的数据包。BGP 使用客户端-服务器拓扑来传递路由信息,客户端-服务器通过向服务器发送请求来启动 BGP 会话。
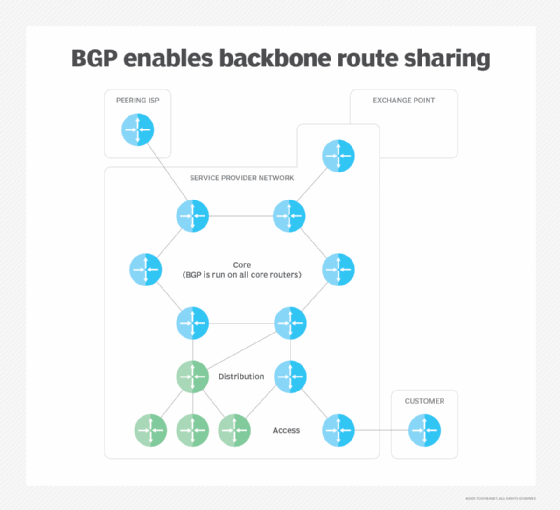
BGP 路由基础
BGP 仅在发生变化时发送更新的路由器表信息,并且仅发送受影响的信息。BGP 没有自动发现机制,这意味着必须手动建立对等体之间的连接,并在两端编程对等体地址。
BGP 根据当前可达性、跳数和其他路径特征做出最佳路径决策。在多条路径可用的情况下——比如在一个主要的托管设施内——BGP 策略传达了组织对流量应该遵循的路径进出的偏好。BGP 社区标签可以控制对等体之间的路由发布行为。
网络中的 BGP 是基于TCP/IP 的。它在OSI传输层(第 4 层)上运行以控制网络层(第 3 层)。如 RFC4271 中所述并于 2006 年批准,当前版本的 BGP-4 支持IPv6和无类别域间路由 ( CIDR ),这使 IPv4 具有持续的可行性。与当前的 IP 地址分配方案相比,使用 CIDR 是一种在网络中拥有更多地址的方法。
常见的 BGP 问题
BGP 的常见问题包括信息交换失败。信息交换并不总是成功,因为信息可能格式不正确或包含不正确的数据。路由器可能会耗尽内存或存储空间,或者响应更新速度太慢。路由器发送错误代码和子代码来传达问题,包括超时、格式错误的请求和处理问题。
BGP安全
BGP 也容易受到基于错误信息的攻击。例如,恶意行为者可以在拒绝服务攻击中用坏数据包淹没路由器。他们还可以声称自己是 AS 路由信息的来源,并(暂时)控制来自该 AS 的流量的去向,这种做法称为 BGP劫持。
内外BGP、OSPF的区别
当 BGP 用于在单个 AS 内进行路由时,称为内部 BGP,或 iBGP。当用于将一个 AS 连接到其他 AS 时,它被称为外部 BGP,或 eBGP。
的OSPF(开放最短路径优先)协议被用于仅在内部网络。OSPF 专注于查找节点之间可用的最短路由,并尽快故障转移到该最短路由。BGP 失败到新路由的速度较慢,但更具可扩展性。OSPF在结构上本质上是分层的,而BGP是一个mesh。一些网络正在用 iBGP 替换 OSPF。
脸书停电
社交媒体应用 Facebook、Instagram 和 WhatsApp于 2021 年 10 月 4 日离线 6 小时。 据报道,此次中断是由于没有有效的 BGP 路由进入社交媒体站点,并且 DNS 服务器离线。这基本上断开了社交媒体应用程序与互联网的连接。
BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) is the protocol underlying the global routing system of the internet. It manages how packets get routed from network to network through the exchange of routing and reachability information among edge routers. BGP directs packets between autonomous systems (AS), which are networks managed by a single enterprise or service provider.
BGP creates network stability by guaranteeing routers can adapt to route failures: when one path goes down, a new path is quickly found. BGP makes routing decisions based on paths, defined by rules or network policies set by network administrators.
How does BGP work?
Each router maintains a routing table controlling how packets are directed. Routing table information is generated by the BGP process on the router, based on incoming information from other routers, and information in the BGP routing information base (RIB), which is a data table stored on a server on the BGP router. The RIB contains information both from directly connected external peers, as well as internal peers, and based on policies for what routes should be used and what information should be published, continually updates the routing table as changes occur.
What is BGP used for?
BGP offers network stability that guarantees routers can quickly adapt to send packets through another reconnection if one internet path goes down. BGP makes routing decisions based on paths, rules or network policies configured by a network administrator. Each BGP router maintains a standard routing table used to direct packets in transit. BGP uses client-server topology to communicate routing information, with the client-server initiating a BGP session by sending a request to the server.
BGP routing basics
BGP sends updated router table information only when something changes, and only the affected information. BGP has no automatic discovery mechanism, which means connections between peers must be set up manually, with peer addresses programmed in at both ends.
BGP makes best-path decisions based on current reachability, hop counts and other path characteristics. In situations where multiple paths are available -- as within a major hosting facility -- BGP policies communicate an organization's preferences for what path traffic should follow in and out. BGP community tags can control route advertisement behavior among peers.
BGP in networking is based on TCP/IP. It operates on the OSI Transport Layer (Layer 4) to control the Network Layer (Layer 3). As described in RFC4271 and ratified in 2006, the current version of BGP-4 supports both IPv6 and Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR), which enables the continued viability of IPv4. Use of the CIDR is a way to have more addresses within the network than with the current IP address assignment scheme.

Common BGP issues
Common issues with BGP include information exchange failures. Information exchanges don't always succeed as information can be improperly formatted or contain incorrect data. Routers can run out of memory or storage, or be too slow to respond to updates. Routers send error codes and subcodes to communicate problems including timeouts, malformed requests and processing problems.
BGP security
BGP is also vulnerable to attacks based on misinformation. Malicious actors can flood a router with bad packets in a denial-of-service attack, for example. They can also claim to be the source of routing information for an AS, and (temporarily) control where traffic headed from that AS goes, a practice known as BGP hijacking.
Difference between internal and external BGP, OSPF
When BGP is used to route within a single AS, it is called internal BGP, or iBGP. When used to connect one AS to others, it is called external BGP, or eBGP.
The OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) protocol is used only in internal networks. OSPF is focused on finding the shortest route available between nodes, and on failing over to that shortest route as quickly as possible. BGP is slower to fail to a new route but is more scalable. OSPF is essentially hierarchical in structure, while BGP is a mesh. Some networks are replacing OSPF with iBGP.
Facebook outage
Social media applications Facebook, Instagram and WhatsApp went offline for six hours on Oct. 4, 2021. The outage was reportedly due to there being no working BGP routes into the social media sites and the DNS servers going offline. This essentially disconnected the social media apps from the internet.