两种实现方式继承Thread类或者实现Runnable接口
使用实现Runnable接口和继承Thread类这两种开辟新线程的方法的选择应该优先选择实现Runnable接口这种方式去开辟一个新的线程。因为接口的实现可以实现多个,而类的继承只能是单继承。因此在开辟新线程时能够使用Runnable接口就尽量不要使用从Thread类继承的方式来开辟新的线程。
1 public class mainTest { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 System.out.println("main Start....."); 4 //Thread有Runnable参数的构造方法 5 new Thread(new Runnable() { 6 public void run() { 7 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { 8 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"--->["+i+"]"); 9 } 10 } 11 }).start(); 12 //继承Thread类 13 new Mythread().start(); 14 System.out.println("main End...."); 15 } 16 17 static class Mythread extends Thread{ 18 @Override 19 public void run() { 20 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { 21 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"===>["+i+"]"); 22 } 23 } 24 } 25 }
Thread的常用方法
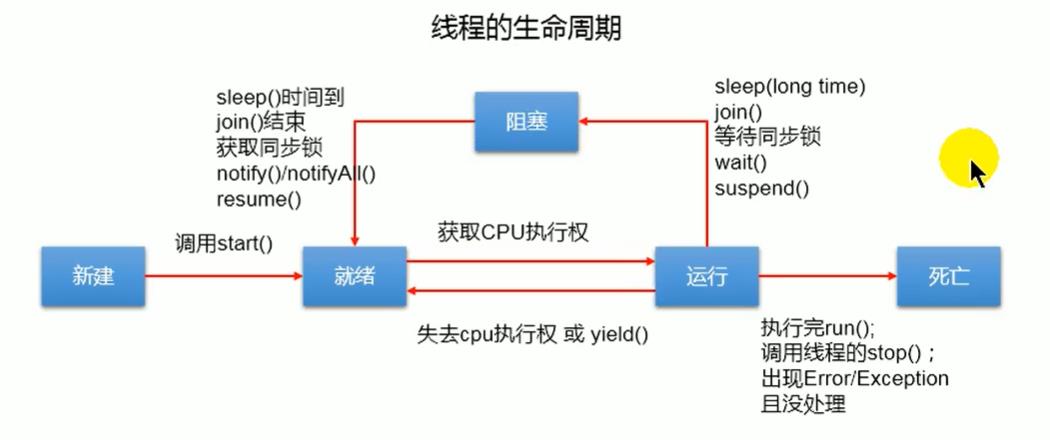
线程生命周期
线程同步synchronized
方法一:同步代码块
1 synchronized(同步监视器){ 2 需要被同步的代码 3 }
操作的共享数据即为需要被同步的代码
同步监视器又名锁,任意对象都可作为锁,为解决线程安全问题当多个线程操作共享数据时这些线程必须公用一把锁
通过实现Runnable可以用this作为锁,继承Thread类可以用子类的Class作为锁
1 public class mainTest { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 System.out.println("main Start....."); 4 //只有一个票池,作为成员变量的锁也只有一个 5 ticketPool pool = new ticketPool(); 6 Thread t1 = new Thread(pool,"t1"); 7 Thread t2 = new Thread(pool,"t2"); 8 Thread t3 = new Thread(pool,"t3"); 9 t1.start(); 10 t2.start(); 11 t3.start(); 12 13 //有多个票池,共享数据和锁应该用static修饰 14 new ticketPool02().start(); 15 new ticketPool02().start(); 16 new ticketPool02().start(); 17 System.out.println("main End...."); 18 } 19 20 static class ticketPool implements Runnable{ 21 //共享数据 22 private int num = 20; 23 //锁 24 Object obj = new Object(); 25 public void run() { 26 while(true){ 27 synchronized(this){ 28 if (num > 0){ 29 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"--->["+num+"]"); 30 num --; 31 try { 32 Thread.sleep(100); 33 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 34 e.printStackTrace(); 35 } finally { 36 } 37 } 38 } 39 } 40 } 41 } 42 43 static class ticketPool02 extends Thread{ 44 //共享数据 45 private static int num = 20; 46 //锁 47 private static Object obj = new Object(); 48 @Override 49 public void run() { 50 while (true){ 51 synchronized(ticketPool02.class){ 52 if(num > 0){ 53 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"--->["+num+"]"); 54 num --; 55 try { 56 Thread.sleep(100); 57 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 58 e.printStackTrace(); 59 } finally { 60 } 61 } 62 } 63 } 64 } 65 } 66 }
方法二:同步方法
仍然有锁,只是不需要自己显式地声明
非静态同步方法的锁是this
静态同步方法的锁是当前类的Class
1 public class mainTest { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 System.out.println("main Start....."); 4 //只有一个票池,作为成员变量的锁也只有一个 5 ticketPool pool = new ticketPool(); 6 Thread t1 = new Thread(pool,"t1"); 7 Thread t2 = new Thread(pool,"t2"); 8 Thread t3 = new Thread(pool,"t3"); 9 t1.start(); 10 t2.start(); 11 t3.start(); 12 13 //有多个票池,共享数据和锁应该用static修饰 14 new ticketPool02().start(); 15 new ticketPool02().start(); 16 new ticketPool02().start(); 17 System.out.println("main End...."); 18 } 19 20 static class ticketPool implements Runnable{ 21 //共享数据 22 private int num = 20; 23 24 public void run() { 25 while(true){ 26 synMethod(); 27 } 28 } 29 30 //同步方法 31 public synchronized void synMethod(){//锁默认是this 32 if (num > 0){ 33 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"--->["+num+"]"); 34 num --; 35 try { 36 Thread.sleep(100); 37 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 38 e.printStackTrace(); 39 } finally { 40 } 41 } 42 } 43 } 44 45 static class ticketPool02 extends Thread{ 46 //共享数据 47 private static int num = 20; 48 49 @Override 50 public void run() { 51 while (true){ 52 synMethod(); 53 } 54 } 55 56 //因为有static修饰所以锁默认是当前类的Class即ticketPool02.class 57 public static synchronized void synMethod(){ 58 if(num > 0){ 59 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"--->["+num+"]"); 60 num --; 61 try { 62 Thread.sleep(100); 63 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 64 e.printStackTrace(); 65 } finally { 66 } 67 } 68 } 69 } 70 }
解决懒汉式单例模式的线程安全问题
1 @Data 2 class Student{ 3 private String name; 4 private Integer age; 5 private String studentNo; 6 7 private Student(){} 8 private static Student student; 9 /*1 10 public static synchronized Student getInstance(){ 11 if(student == null){ 12 student = new Student(); 13 } 14 return student; 15 }*/ 16 17 /*2、和上面方法1一样,都有效率低的弊端,当前面的线程实例化对象后后面的线程仍要等待获得锁 18 public static Student getInstance(){ 19 synchronized (Student.class) { 20 if(student == null){ 21 student = new Student(); 22 } 23 return student; 24 } 25 }*/ 26 27 //3、效率提高了,前面的线程实例化后,后面的线程就不用排队等锁了 28 public static Student getInstance(){ 29 if(student == null){ 30 synchronized (Student.class) { 31 if(student == null){ 32 student = new Student(); 33 } 34 } 35 } 36 return student; 37 } 38 }
死锁:不同线程分别占用对方线程需要的同步资源不放弃,都在等待对方释放自己需要的同步资源。死锁不会报异常也没有提示,相关线程都将处于阻塞状态,无法继续
开发中尽量减少同步资源的定义
尽量避免嵌套同步
应用专门的算法。
1 public class test02 { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 4 final StringBuffer s1 = new StringBuffer(); 5 final StringBuffer s2 = new StringBuffer(); 6 7 new Thread(){ 8 @Override 9 public void run() { 10 synchronized (s1){ 11 s1.append("A"); 12 try { 13 Thread.sleep(100); 14 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 15 e.printStackTrace(); 16 } 17 synchronized(s2){ 18 s2.append("B"); 19 System.out.println(s1.toString()+" "+s2.toString()); 20 } 21 } 22 } 23 }.start(); 24 25 new Thread(new Runnable() { 26 public void run() { 27 synchronized (s2){ 28 s2.append("F"); 29 try { 30 Thread.sleep(100); 31 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 32 e.printStackTrace(); 33 } 34 synchronized(s1){ 35 s1.append("G"); 36 System.out.println(s1.toString()+" "+s2.toString()); 37 } 38 } 39 } 40 }).start(); 41 } 42 }
Lock接口解决线程安全问题,ReentrantLock
1 public class test02 { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 Runnable myRun = new MyRun(); 4 new Thread(myRun).start(); 5 new Thread(myRun).start(); 6 new Thread(myRun).start(); 7 } 8 9 static class MyRun implements Runnable{ 10 private Integer num = 20; 11 private ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(); 12 public void run() { 13 while (true){ 14 try{ 15 //调用lock() 16 lock.lock(); 17 if (num > 0){ 18 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"["+num+"]"); 19 num --; 20 } 21 }finally { 22 //解锁 23 lock.unlock(); 24 } 25 } 26 } 27 } 28 }
Lock与synchronized异同
同:都是为了解决线程安全问题
异:synchronized,在执行完相应的同步代码后会自动释放锁
Lock,在执行到需要同步的代码时需要手动的调用lock()和unlock()方法加锁和解锁;Lock只有代码块锁没有方法锁;使用Lock,JVM会用较少的时间调度线程,性能更好;区别于synchronized的隐式锁,Lock是显式锁;Lock有更好的扩展性,提供更多子类。
线程通信(只能用在同步代码块或同步方法里即有synchronized修饰,调用者是锁,这三个方法是定义在Object类里的即任意对象都有这三个方法)
wait();使当前线程进入阻塞态,并释放同步锁给其他线程。
notify();唤醒被wait的一个线程,如果有多个wait的线程则唤醒优先级高的那个线程。
notifyAll();唤醒所有被wait的线程。
1 public class test02 { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 Runnable myRun = new MyRun(); 4 new Thread(myRun).start(); 5 new Thread(myRun).start(); 6 new Thread(myRun).start(); 7 } 8 9 static class MyRun implements Runnable{ 10 private Integer num = 20; 11 private ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(); 12 public void run() { 13 while (true){ 14 synchronized(this){ 15 notify(); //this.notify(); 调用者是锁,与锁保持一致 16 if (num > 0){ 17 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"["+num+"]"); 18 num --; 19 } 20 try { 21 wait(); //this.wait(); 调用者是锁,与锁保持一致 22 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 23 e.printStackTrace(); 24 } 25 } 26 } 27 } 28 } 29 }
sleep()与wait()的异同:
同:都会使线程进入阻塞态。
异:sleep()是定义在Thread类里的方法,wait()是定义在Object类里的方法
sleep()可以随时调用,wait()只能在同步代码块或同步方法中调用
在同步代码块或同步方法中sleep()不会释放同步锁,wait()会释放同步锁。
生产者消费者模式
1 public class test02 { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 SyncStack stack = new SyncStack(); 4 Runnable p=new Producer(stack); 5 Runnable c = new Consumer(stack); 6 Thread p1 = new Thread(p); 7 Thread c1 = new Thread(c); 8 9 p1.start(); 10 c1.start(); 11 12 } 13 } 14 15 class SyncStack{ //支持多线程同步操作的堆栈的实现 16 private int index = 0; 17 private char []data = new char[6]; 18 public synchronized void push(char c){ 19 if(index == data.length){ 20 try{ 21 this.wait(); 22 }catch(InterruptedException e){} 23 } 24 this.notify(); 25 data[index] = c; 26 index++; 27 } 28 public synchronized char pop(){ 29 if(index ==0){ 30 try{ 31 this.wait(); 32 }catch(InterruptedException e){} 33 } 34 this.notify(); 35 index--; 36 return data[index]; 37 } 38 } 39 40 41 class Producer implements Runnable{ 42 SyncStack stack; 43 public Producer(SyncStack s){ 44 stack = s; 45 } 46 public void run(){ 47 for(int i=0; i<20; i++){ 48 char c =(char)(Math.random()*26+'A'); 49 stack.push(c); 50 System.out.println("produced:"+c); 51 try{ 52 Thread.sleep((int)(Math.random()*1000)); 53 }catch(InterruptedException e){ 54 } 55 } 56 } 57 } 58 59 60 class Consumer implements Runnable{ 61 SyncStack stack; 62 public Consumer(SyncStack s){ 63 stack = s; 64 } 65 public void run(){ 66 for(int i=0;i<20;i++){ 67 char c = stack.pop(); 68 System.out.println("消费:"+c); 69 try{ 70 Thread.sleep((int)(Math.random()*1000)); 71 }catch(InterruptedException e){ 72 } 73 } 74 } 75 }
JDK5提供了创建线程的新方法
1、实现Callable接口,其中的call()方法类似Runnable接口里的run()方法,call()方法可以返回值、抛异常、支持泛型。
1 public class test02 { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 4 Callable call = new MyCall(); 5 FutureTask future = new FutureTask(call); 6 //FutureTask继承了Runnable可以作为Thread()的参数 7 Thread thread = new Thread(future); 8 thread.start(); 9 10 try { 11 //FutureTask中的get()获取call()的返回值 12 Integer sum = (Integer) future.get(); 13 System.out.println(sum); 14 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 15 e.printStackTrace(); 16 } catch (ExecutionException e) { 17 e.printStackTrace(); 18 } 19 } 20 } 21 22 //实现Callable接口 23 class MyCall implements Callable { 24 25 private Integer sum = 0; 26 //执行call()方法,相当于Runnable中的run()方法不同的是call()方法可以返回值和抛异常,不需要返回值时可return null 27 public Object call() throws Exception { 28 for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { 29 if (i % 2 == 0){ 30 sum+=i; 31 } 32 } 33 return sum; 34 } 35 }
2、线程池创建并管理线程

1 public class test02 { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 //Executors是线程池的工具类,创建10条线程的线程池 4 ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10); 5 6 /* 7 可以强转成实现类设置核心池的大小、最大线程数、没有线程任务后的存活时间 8 ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = (ThreadPoolExecutor)executorService; 9 threadPoolExecutor.setCorePoolSize(20); 10 threadPoolExecutor.setMaximumPoolSize(15); 11 threadPoolExecutor.setKeepAliveTime(1000,TimeUnit.HOURS); 12 */ 13 14 //ExecutorService接口的execute()适用于Runnable定义的线程方法,submit()适用于Callable定义的线程方法,shutdown()关闭线程池 15 executorService.execute(new MyRun()); 16 FutureTask future = new FutureTask(new MyCall()); 17 executorService.submit(future); 18 executorService.shutdown(); 19 20 try { 21 int sum = (Integer) future.get(); 22 System.out.println(sum); 23 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 24 e.printStackTrace(); 25 } catch (ExecutionException e) { 26 e.printStackTrace(); 27 } 28 29 } 30 } 31 32 //实现Callable接口 33 class MyCall implements Callable { 34 35 private Integer sum = 0; 36 //执行call()方法,相当于Runnable中的run()方法不同的是call()方法可以返回值和抛异常,不需要返回值时可return null 37 public Object call() throws Exception { 38 for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) { 39 if (i % 2 == 0){ 40 sum+=i; 41 } 42 } 43 return sum; 44 } 45 } 46 47 class MyRun implements Runnable { 48 49 private Integer sum = 0; 50 51 public void run() { 52 for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) { 53 if (i % 2 != 0){ 54 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"["+i+"]"); 55 } 56 } 57 } 58 }
Executors.newScheduledThreadPool()
1 public class test02 { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 ScheduledExecutorService scheduledThreadPool_01 = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(5); 4 5 //schedule(Runnable command,long delay, TimeUnit unit) 延迟3秒执行 6 scheduledThreadPool_01.schedule(new Runnable() { 7 public void run() { 8 System.out.println("delay 3 seconds"); 9 } 10 }, 3, TimeUnit.SECONDS); 11 12 //scheduleAtFixedRate(Runnable command,long initialDelay,long period,TimeUnit unit); 13 //延迟1秒后每3秒执行一次 14 ScheduledExecutorService scheduledThreadPool_02 = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(5); 15 scheduledThreadPool_02.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable() { 16 public void run() { 17 System.out.println("delay 1 seconds, and excute every 3 seconds"); 18 } 19 }, 1, 3, TimeUnit.SECONDS); 20 } 21 }
工具类中的这几个创建线程池的方法是对ThreadPoolExecutor进行了封装,只是各自设置的参数不同而有了各自的特点
1 //ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads,nThreads, 0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()); 2 // 自定义核心线程数量,任务队列空间为Integer.MAX_VALUE,不使用非核心线程 3 Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10); 4 5 //ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE,60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>()); 6 // 只使用非核心线程,不使用核心线程和任务队列 7 Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); 8 9 //ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1,0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()); 10 // 只使用一个核心线程和任务队列 11 Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor(); 12 13 Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(10);
参考:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1MJ411e7SA/