
运行环境:
Win 7
JDK 8 +
Redis 3.0.504
Spring Boot 2.2.2.RELEASE
一、为什么要使用Redis
速度快,完全基于内存,使用C语言实现,网络层使用epoll解决高并发问题,单线程模型避免了不必要的上下文切换及竞争条件;
丰富的数据类型,Redis有8种数据类型,当然常用的主要是 String、Hash、List、Set、 SortSet 这5种类型,他们都是基于键值的方式组织数据。每一种数据类型提供了非常丰富的操作命令,可以满足绝大部分需求,如果有特殊需求还能自己通过 lua 脚本自己创建新的命令(具备原子性);
二、Redis能够做什么?
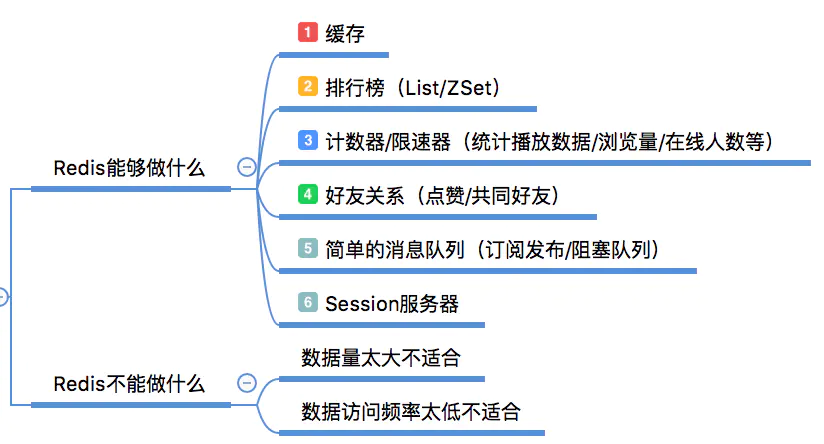
缓存常见的应用场景有哪些呢?
比如常见的电商常见,根据商品 ID 获取商品信息时,店铺信息和商品详情信息就可以缓存在 Redis,直接从 Redis 获取。减少了去数据库查询的次数。减轻数据库压力。
三、运行 springboot-redis 工程案例
git clone 下载工程 springboot-learning-example ,项目地址见 GitHub – https://github.com/zyuQ/springboot-learning-example.git
1. 本地安装 Redis
详情跳转文章 -> Redis 安装
2. springboot-redis 工程项目结构介绍
org.springboot.controller - Controller 层
org.springboot.config - 配置类
org.springboot.pojo - 实体类
org.springboot.utils - 工具类
Application - 应用启动类
application.yml - 应用配置类
四、springboot-redis 工程代码详解
1. 工程项目Maven依赖
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <!-- Redis配置 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> <exclusions> <exclusion> <groupId>org.junit.vintage</groupId> <artifactId>junit-vintage-engine</artifactId> </exclusion> </exclusions> </dependency> </dependencies>
2. application.yml 加入redis相关配置
server: port: 8080 spring: redis: host: 127.0.0.1 port: 6379 jedis: pool: max-idle: 8 # 连接池中的最小空闲连接 min-idle: 0 # 连接池中的最大空闲连接 max-active: 40 # 连接池最大连接数(使用负值表示没有限制) max-wait: -1 # 连接池最大阻塞等待时间(使用负值表示没有限制) timeout: 5000 # 连接超时时间 password: # Redis服务器连接密码
User.java 用户对象:
package springboot.pojo; import java.io.Serializable; /** * 用户实体类 * 注意:要缓存的Java对象必须实现 Serializable 接口,因为Spring会将对象先序列化再存入Redis */ public class User implements Serializable { /** * 用户编号 */ private Long id; /** * 用户名称 */ private String userName; /** * 用户年龄 */ private int age; /** * 用户描述 */ private String desc; public Long getId() { return id; } public void setId(Long id) { this.id = id; } public String getUserName() { return userName; } public void setUserName(String userName) { this.userName = userName; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public String getDesc() { return desc; } public void setDesc(String desc) { this.desc = desc; } }
Controller 层:
package springboot.controller; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate; import org.springframework.data.redis.core.ValueOperations; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*; import springboot.pojo.User; /** * @Description: * @Author: zyu */ @RestController @RequestMapping("/user") public class HomeController { @Autowired private RedisTemplate redisTemplate; @PostMapping("/save") public String saveUser(User user) { String key = "User_" + user.getId(); ValueOperations operations = redisTemplate.opsForValue(); operations.set(key, user); return "Success"; } @GetMapping("/find/{id}") public User findUserById(@PathVariable("id") Long id) { String key = "User_" + id; ValueOperations operations = redisTemplate.opsForValue(); User user = (User) operations.get(key); return user; } }
运作项目,通过postman工具发送post请求将数据保存至redis缓存中。
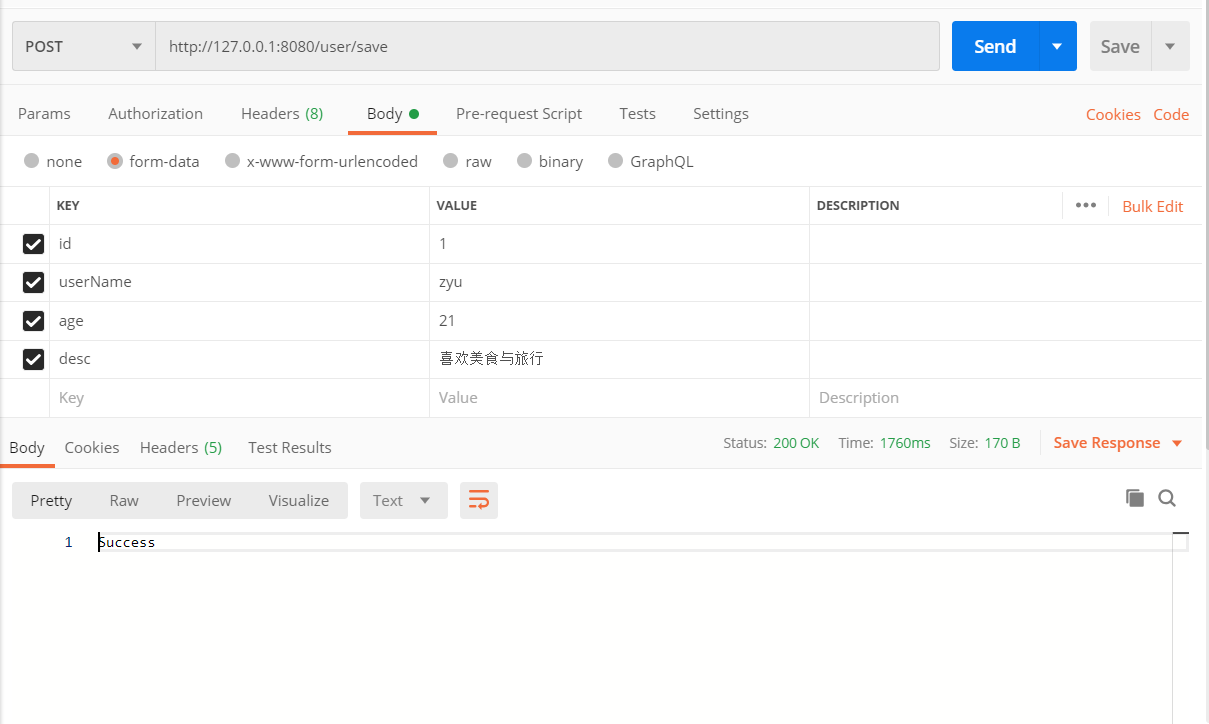
保存成功Success 调用GET 请求访问 http://127.0.0.1:8080/user/find/1
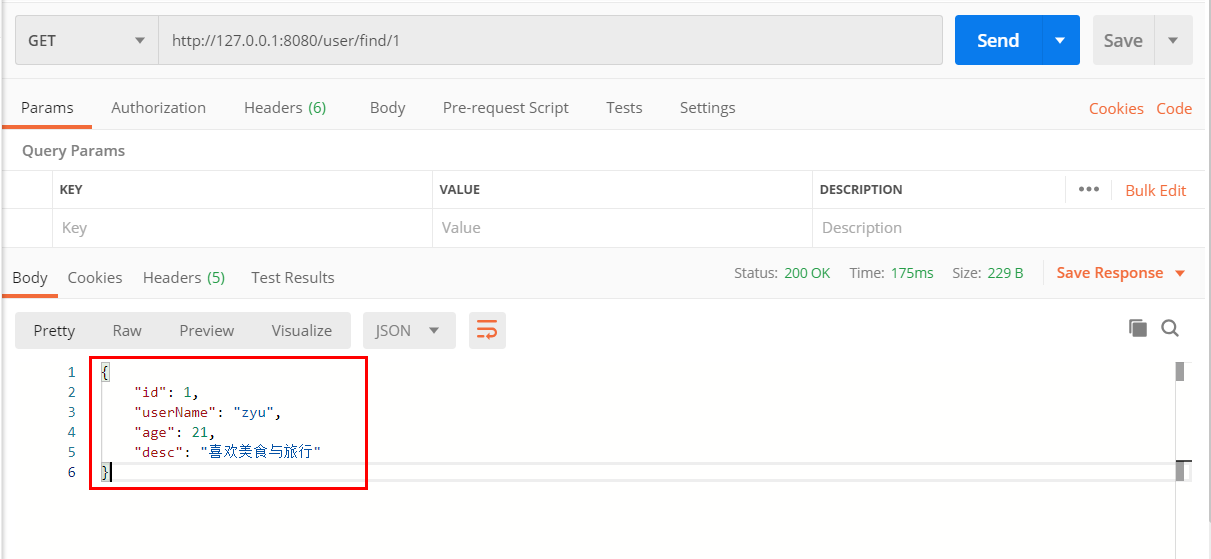
调用成功,说明数据已经保存至redis 缓存中。
但是我们通过Redis管理工具可以看到,对象存储会被序列化
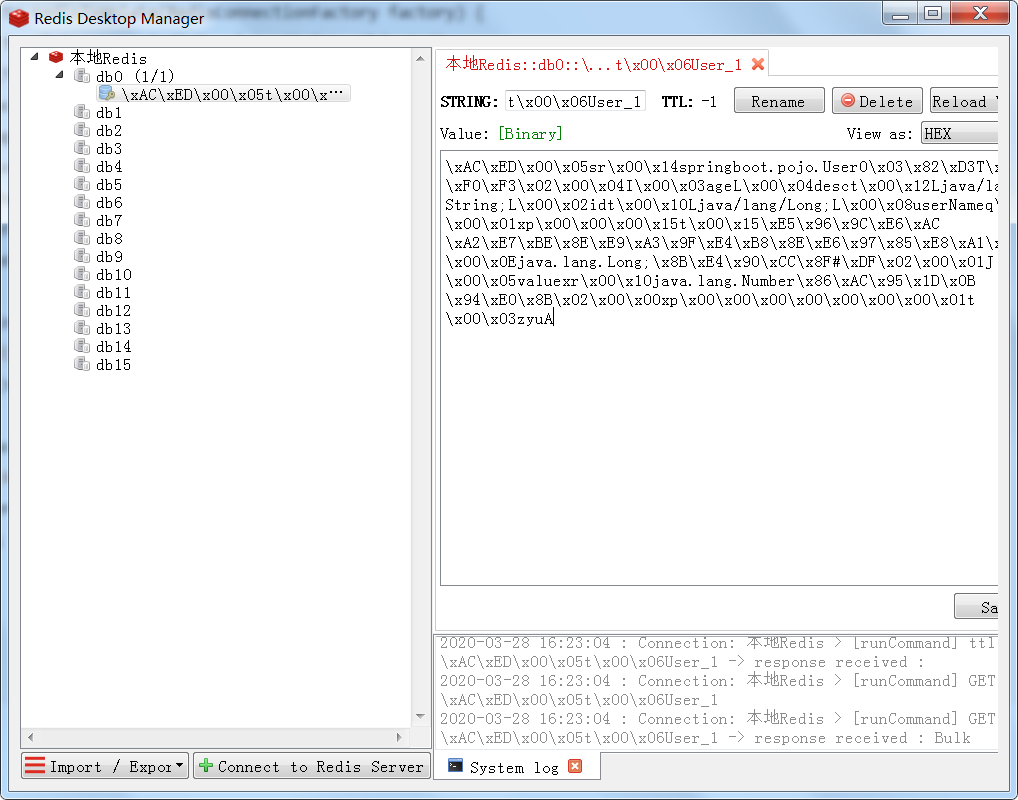
所以我们就重新配置一个RedisTemplate,代码如下:
package springboot.config; import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonAutoDetect; import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.PropertyAccessor; import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory; import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate; import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer; import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer; /** * @Description: * @Author: zyu */ @Configuration public class RedisConfig { @Bean @SuppressWarnings("all") public RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory factory) { RedisTemplate<String, Object> template = new RedisTemplate<String, Object>(); template.setConnectionFactory(factory); Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer jackson2JsonRedisSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(Object.class); ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper(); om.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY); om.enableDefaultTyping(ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL); jackson2JsonRedisSerializer.setObjectMapper(om); StringRedisSerializer stringRedisSerializer = new StringRedisSerializer(); // key采用String的序列化方式 template.setKeySerializer(stringRedisSerializer); // hash的key也采用String的序列化方式 template.setHashKeySerializer(stringRedisSerializer); // value序列化方式采用jackson template.setValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer); // hash的value序列化方式采用jackson template.setHashValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer); template.afterPropertiesSet(); return template; } }
重启项目,调用 /user/save 接口,可以看到存储的数据结构已经变成我们自定义序列化的方式

代码示例
本文示例读者可以通过查看下面仓库中代码: