1 reactor网络服务模型
(1) handle
(2)同步事件分离器
(3)dispatcher
(4)事件处理器
2 reactor的两个线程组,其中一个是负责监听客户端连接事件,另一个负责将具体的事件处理接入netty的channelHandle责任链,进行数据入站出站。
3 责任链处理,在netty的服务启动时默认初始化3个channelHandle,HeadHandle和TailHandle是一个空的handle,只作为头尾标记,除了这两个头尾以外ServerBootstrapAcceptorHandle作为数据入站处理器被添加进来。这个ServerBootstrapAcceptoHandle是挂接在服务端的NIOServerSocketChannel的pipeline中的,用来监听客户端的连接。
4 两个线程组进行事件交接的连接点就在ServerBootstrapAcceptor,一旦有新的客户端连接上来以后,就会由ServerBootstrapAcceptor执行channelRead方法,将初始化保存的“数据入站出站责任链”,挂接到新连接上来的channel对象中。
5 这样数据发送端与数据接收端的消息传递就可以经过挂接上的channelHandle来处理了。
6 处理流入数据是从HeadChannelHandle开始的,处理流出数据是从TailChannelHandle开始的,在AbstractChannelHandlerContext类中保存了两个成员变量:
abstract class AbstractChannelHandlerContext extends DefaultAttributeMap implements ChannelHandlerContext { volatile AbstractChannelHandlerContext next; volatile AbstractChannelHandlerContext prev; private final boolean inbound; private final boolean outbound; private final AbstractChannel channel; private final DefaultChannelPipeline pipeline; private final String name; private boolean removed;
在数据做流向动作时进行判断。
7 这里很重要,数据入站处理和数据流出处理(数据流入从head链表头开始处理,而数据流出是从链表尾开始,注册channelhandle链表节点是千万不能弄错顺序):
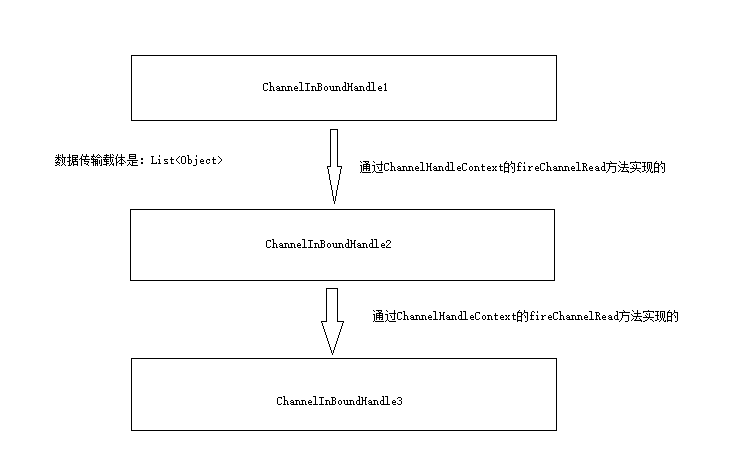
首先数据入站处理,我们拿解码器举例子,ReplayingDecoder或者ByteToMessageDecoder都可以,只是不同级别的实现。我们发现数据流转是通过ChannelHandleContext的fireChannelRead方法实现的,ChannelHandleContext本身是多个节点的链表实现的,而且上下文中的数据传递依赖于一个List<Object>,每次数据处理完成以后,将list传入ChannelHandleContext的fireChannelRead方法,寻找下一个链表节点进行数据处理:
8 ctx.channel().writeAndFlush(res);和ctx.writeAndFlush(res);是不同的:
ctx.channel().writeAndFlush(res);会从tailChannelHandle开始处理。
ctx.writeAndFlush(res);则是从下一个ChannelHandle开始处理
具体代码测试和结果如下:
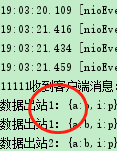
static final AtomicInteger a = new AtomicInteger(0); static ChannelInboundHandler channelInboundHandler = new SimpleChannelInboundHandler<String>() { @Override protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, String msg) throws Exception { System.out.println("11111收到客户端消息:" + msg); String res = msg + "你好"; ctx.channel().writeAndFlush(res); } }; static ChannelOutboundHandler channelOutboundHandler1 = new MessageToMessageEncoder<String>() { @Override protected void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, String msg, List<Object> out) throws Exception { if (a.get() == 0) { a.getAndIncrement(); System.out.println("数据出站1:" + msg); ctx.channel().writeAndFlush(msg);//如果使用channel中的writeAndFlush,相当于使用了tailChannelHandle的writeAndFlush要完整走完所有出站ChannelHandle } else { System.out.println("数据出站1:" + msg); ctx.writeAndFlush(msg); } } }; static ChannelOutboundHandler channelOutboundHandler2 = new MessageToMessageEncoder<String>() { @Override protected void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, String msg, List<Object> out) throws Exception { System.out.println("数据出站2:" + msg); ctx.writeAndFlush(msg); } }; public static void main(String[] args) { EventLoopGroup parent = new NioEventLoopGroup(1); EventLoopGroup children = new NioEventLoopGroup(2); final EventLoopGroup handle = new NioEventLoopGroup(); ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap(); serverBootstrap.group(parent, children) .channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) .handler(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG)) .childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { @Override protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception { ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline(); pipeline.addLast(new ClientMonitorHandlerAdapter());//数据流入处理1 pipeline.addLast(new CustomDataFrameDecoder());//数据流入处理2 pipeline.addLast(new CustomDataFrameToStrDecoder());//数据流入处理3 pipeline.addLast(handle, channelInboundHandler);//数据流入处理4 pipeline.addLast(new CustomDataFrameEncoder());//数据流出处理3 pipeline.addLast(handle, channelOutboundHandler2);//数据流出处理2 pipeline.addLast(handle, channelOutboundHandler1);//数据流出处理1 } }); ChannelFuture channelFuture = null; try { channelFuture = serverBootstrap.bind(9099).sync(); channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { channelFuture.channel().close(); parent.shutdownGracefully(); children.shutdownGracefully(); }
运行的测试结果如下: