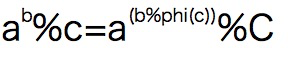链接:https://www.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/142/A 来源:牛客网 题目描述 A ternary string is a sequence of digits, where each digit is either 0, 1, or 2. Chiaki has a ternary string s which can self-reproduce. Every second, a digit 0 is inserted after every 1 in the string, and then a digit 1 is inserted after every 2 in the string, and finally the first character will disappear. For example, ``212'' will become ``11021'' after one second, and become ``01002110'' after another second. Chiaki would like to know the number of seconds needed until the string become an empty string. As the answer could be very large, she only needs the answer modulo (109 + 7). 输入描述: There are multiple test cases. The first line of input is an integer T indicates the number of test cases. For each test case: The first line contains a ternary string s (1 ≤ |s| ≤ 105). It is guaranteed that the sum of all |s| does not exceed 2 x 106. 输出描述: For each test case, output an integer denoting the answer. If the string never becomes empty, output -1 instead. 示例1 输入 复制 3 000 012 22 输出 复制 3 93 45
欧拉降幂且记录;
(1)如果在消除一个 0 前经过了 n 秒,那么消掉这个 0 需要 n + 1 秒。
(2)如果在消除一个 1 前经过了 n 秒,那么消掉这个 1 与其产生的所有数需要 (n + 1) * 2 秒。
(3)如果在消除一个 2 前经过了 n 秒,那么消掉这个 2 与其产生的所有数需要 (2 ^ (n + 1) - 1) * 3 秒。
#include<cstdio> #include<algorithm> #include<cmath> #include<cstdlib> #include<ctime> #include<vector> #include<map> #include<string.h> using namespace std; #define ll long long map<ll,ll>mp; char s[100000]; ll phi(ll x) { if(mp[x]) return mp[x]; ll temp=x; ll ans=x; if(x==1) return mp[1]=1; for(ll i=2;i*i<=x;i++){ if(x%i==0){ ans=ans/i*(i-1); while(x%i==0) x/=i; } } if(x>1) ans=ans/x*(x-1); return mp[temp]=ans; } ll qsm(ll a,ll b,ll c) { ll ret = 1; for (;b;b >>= 1,(a *= a)%=c) if (b & 1) (ret *= a)%=c; return ret; } ll solve(ll x,ll mod) { if(x==0||mod==1) return 0; if(s[x]=='0'){ return (1LL+solve(x-1,mod)+mod)%mod; }else if(s[x]=='1'){ return (2*(solve(x-1,mod)+1)+mod)%mod; }else{ ll ph=phi(mod); ll t=(solve(x-1,ph))%ph; return (qsm(2,t,mod)*6%mod-3+mod*3)%mod; } } int main() { int n; scanf("%d",&n); while(n--) { scanf("%s",s+1); printf("%lld\n",solve(strlen(s+1),1e9+7)); } return 0; }