判断题:









选择题:












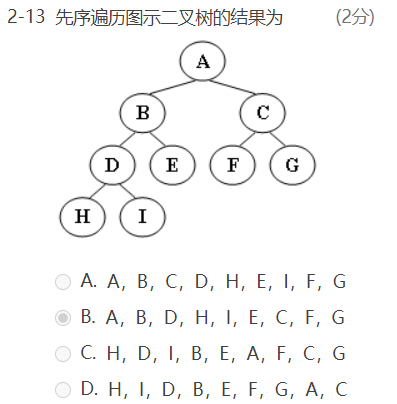

























函数题:
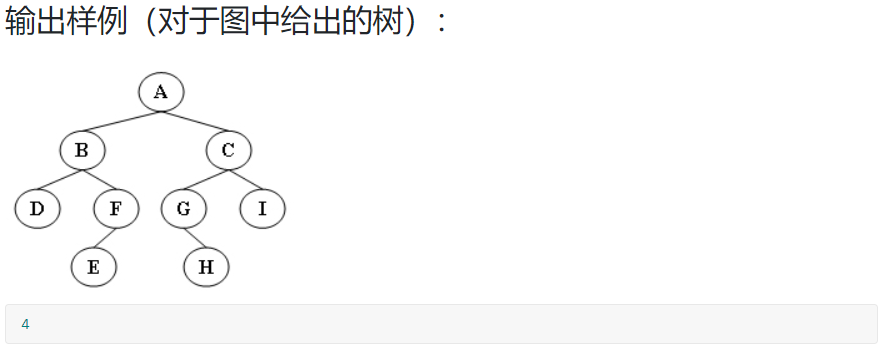
6-1 求二叉树高度:
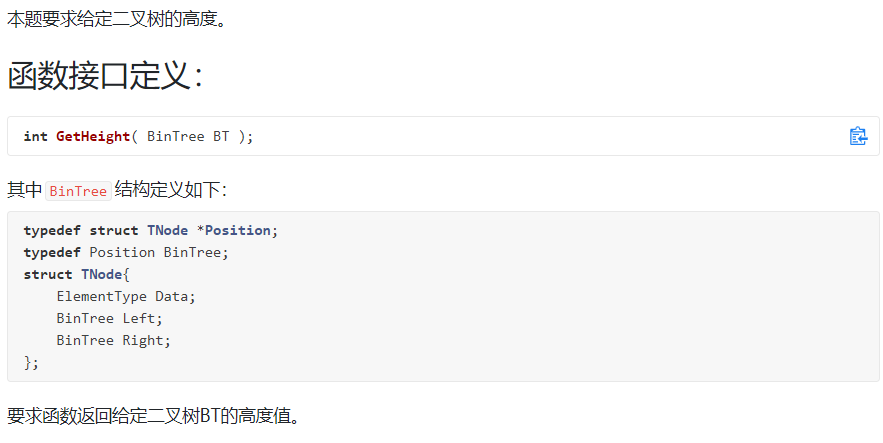
裁判测试程序样例:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef char ElementType;
typedef struct TNode *Position;
typedef Position BinTree;
struct TNode{
ElementType Data;
BinTree Left;
BinTree Right;
};
BinTree CreatBinTree(); /* 实现细节忽略 */
int GetHeight( BinTree BT );
int main()
{
BinTree BT = CreatBinTree();
printf("%d
", GetHeight(BT));
return 0;
}
/* 你的代码将被嵌在这里 */
代码:

int GetHeight(BinTree BT)
{
if(BT == NULL)//判断是否为空
return 0;
int l,r;
l=GetHeight(BT->Left);//递归
r=GetHeight(BT->Right);
return l>=r?l+1:r+1;
}
6-2 二叉树的遍历:
裁判测试程序样例:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef char ElementType;
typedef struct TNode *Position;
typedef Position BinTree;
struct TNode{
ElementType Data;
BinTree Left;
BinTree Right;
};
BinTree CreatBinTree(); /* 实现细节忽略 */
void InorderTraversal( BinTree BT );
void PreorderTraversal( BinTree BT );
void PostorderTraversal( BinTree BT );
void LevelorderTraversal( BinTree BT );
int main()
{
BinTree BT = CreatBinTree();
printf("Inorder:"); InorderTraversal(BT); printf("
");
printf("Preorder:"); PreorderTraversal(BT); printf("
");
printf("Postorder:"); PostorderTraversal(BT); printf("
");
printf("Levelorder:"); LevelorderTraversal(BT); printf("
");
return 0;
}
/* 你的代码将被嵌在这里 */

代码:

void InorderTraversal( BinTree BT )//前三个依次递归,只需注意每一次的输出位置即可
{
if(BT)
{
if(BT->Left)
InorderTraversal(BT->Left);
printf(" %c",BT->Data);
if(BT->Right)
InorderTraversal(BT->Right);
}
}
void PreorderTraversal( BinTree BT )
{
if(BT)
{
printf(" %c",BT->Data);
if(BT->Left)
PreorderTraversal(BT->Left);
if(BT->Right)
PreorderTraversal(BT->Right);
}
}
void PostorderTraversal( BinTree BT )
{
if (BT)
{
if (BT->Left)
PostorderTraversal(BT->Left);
if (BT->Right)
PostorderTraversal(BT->Right);
printf(" %c", BT->Data);
}
}
void LevelorderTraversal( BinTree BT )
{
BinTree bt[10001],root;
int h=0,t=0;
if(BT)
{
bt[t++]=BT;
while(h!=t)
{
root=bt[h++];
printf(" %c", root->Data);
if(root->Left)
bt[t++] = root->Left;
if(root->Right)
bt[t++] = root->Right;
}
}
}
6-3 先序输出叶结点:
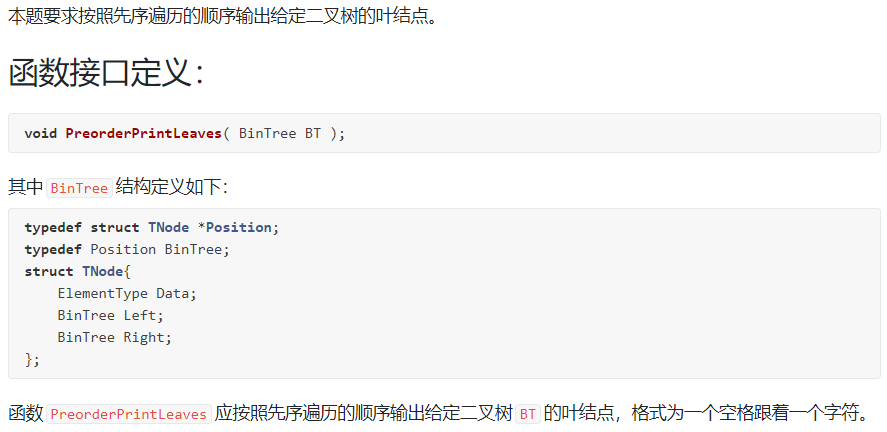
裁判测试程序样例:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef char ElementType;
typedef struct TNode *Position;
typedef Position BinTree;
struct TNode{
ElementType Data;
BinTree Left;
BinTree Right;
};
BinTree CreatBinTree(); /* 实现细节忽略 */
void PreorderPrintLeaves( BinTree BT );
int main()
{
BinTree BT = CreatBinTree();
printf("Leaf nodes are:");
PreorderPrintLeaves(BT);
printf("
");
return 0;
}
/* 你的代码将被嵌在这里 */
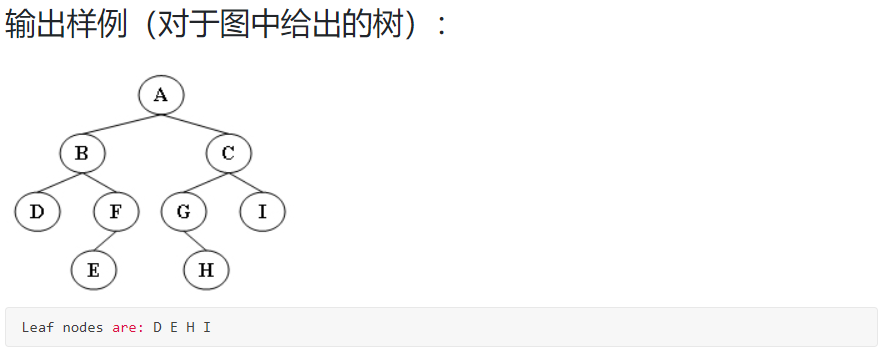
代码:

void PreorderPrintLeaves( BinTree BT )
{
if(BT==NULL)//若为空,只退回当前函数
return ;
PreorderPrintLeaves(BT->Left);//递归调用
PreorderPrintLeaves(BT->Right);
if(BT->Left==NULL&&BT->Right==NULL)
printf(" %c",BT->Data);
//PreorderPrintLeaves(BT->Left);//递归调用
//PreorderPrintLeaves(BT->Right);
}
7-1 根据后序和中序遍历输出先序遍历:

输入样例:
7
2 3 1 5 7 6 4
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
输出样例:
Preorder: 4 1 3 2 6 5 7
代码:

#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef struct BiTNode
{
int Data;
struct BiTNode *lchild;
struct BiTNode *rchild;
}BiTNode, *BiTree;
BiTree PlusTree(int *l, int *r, int n)
{
if(n==0)
return NULL;
else
{
BiTree t=new BiTNode;
t->Data=r[n-1];
int i=0;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
if(r[n-1]==l[i])
break;
}
t->lchild = PlusTree(l, r, i);
t->rchild = PlusTree(l+i+1, r+i, n-i-1);
return t;
}
}
void PreorderTraversal(BiTree BT)
{
if(BT == NULL)
return;
printf(" %d", BT->Data);
PreorderTraversal(BT->lchild);
PreorderTraversal(BT->rchild);
}
int main()
{
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
int a[35],b[35];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
cin>>b[i];
for(int j=0;j<n;j++)
cin>>a[j];
BiTree tree;
tree = PlusTree(a, b, n);
printf("Preorder:");
PreorderTraversal(tree);
printf("
");
return 0;
}
7-2 树的同构:
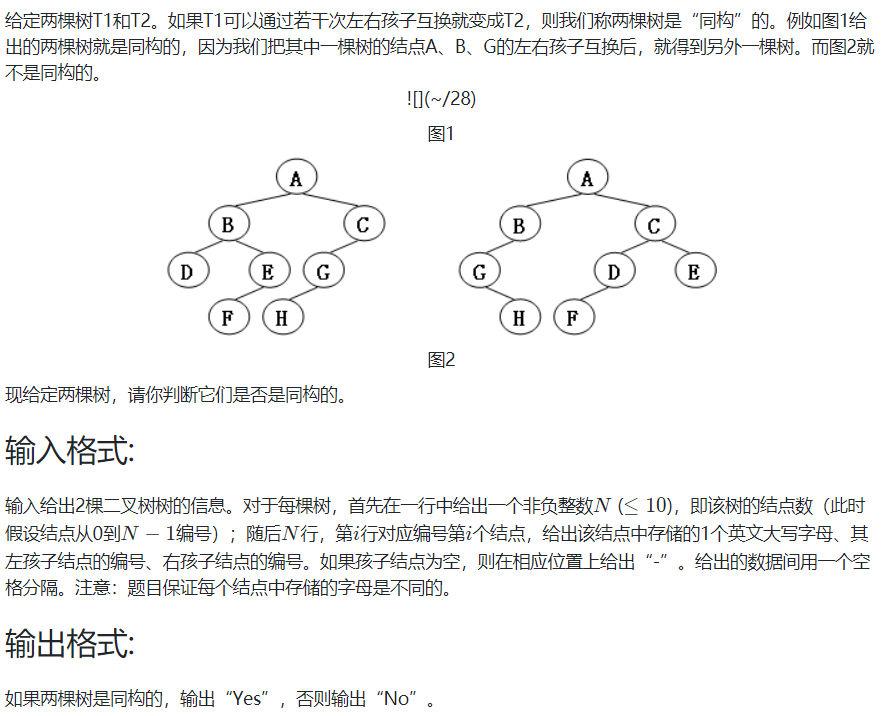
输入样例1:
8
A 1 2
B 3 4
C 5 -
D - -
E 6 -
G 7 -
F - -
H - -
8
G - 4
B 7 6
F - -
A 5 1
H - -
C 0 -
D - -
E 2 -
输出样例:
Yes
输入样例:
8
B 5 7
F - -
A 0 3
C 6 -
H - -
D - -
G 4 -
E 1 -
8
D 6 -
B 5 -
E - -
H - -
C 0 2
G - 3
F - -
A 1 4
输出样例:
No
代码:

#include<cstdio>
typedef int Tree;
struct TNode{
Tree left, right;
char data;
int flag;
}T1[15], T2[15];
int flag[15];
Tree BuildTree( struct TNode T[]){
Tree R=-1, cl, cr;
int n;
scanf("%d
", &n);
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)flag[i]=0;
for(int i=0; i<n; i++){
scanf("%c %c %c
", &T[i].data, &cl, &cr);
if(cl!='-'){
T[i].left=cl - '0';
flag[T[i].left]=1;
}else{
T[i].left=-1;
}
if(cr!='-'){
T[i].right= cr-'0';
flag[T[i].right]=1;
}else{
T[i].right=-1;
}
}
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
if(flag[i]==0){
R=i;
break;
}
return R;
}
int PanDuan(Tree R1, Tree R2){
if(R1==-1 && R2==-1)return 1;
if((R1==-1 && R2!=-1) || (R2==-1 && R1!=-1))return 0;
if(T1[R1].data!=T2[R2].data)return 0;
if(T1[R1].left==-1 && T2[R2].left==-1)
return PanDuan(T1[R1].right, T2[R2].right);
if((T1[R1].left!=-1&&T2[R2].left!=-1)&&(T1[T1[R1].left].data==T2[T2[R2].left].data)){
return(PanDuan(T1[R1].left, T2[R2].left)&&PanDuan(T1[R1].right, T2[R2].right));
}else{
return(PanDuan(T1[R1].right, T2[R2].left)&&PanDuan(T1[R1].left, T2[R2].right));
}
}
int main(){
Tree a, b;
a=BuildTree(T1);
b=BuildTree(T2);
if(PanDuan(a, b)){
printf("Yes");
}else{
printf("No");
}
return 0;
}
7-3 修理牧场:

输入样例:
8
4 5 1 2 1 3 1 1
输出样例:
49
代码:

#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int> > w;
int a[n];
int i=0;
int sum=0; //待求最小值
for(;i<n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
w.push(a[i]);
}
int x;//存取现小顶堆
int y;//存取新小顶堆
while(!w.empty()) //最短的木头二合一
{
x=w.top();
w.pop(); //用完移除
if(w.empty()) //移除x后没有元素了,说明x是木头总长,不再循环
{
break;
}
y=w.top();
w.pop();
x+=y;
sum+=x;
w.push(x); //新木头放入堆中
}
printf("%d",sum);
}
7-4 完全二叉搜索树:

输入样例:
10
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0
输出样例:
6 3 8 1 5 7 9 0 2 4
代码:

#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n, flag;
int a[1001];
int b[1001];
void DFS(int aa)
{
if(aa>n)
return ;
DFS(2*aa);
b[aa]=++flag;
DFS(2*aa+1);
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
}
sort(a+1, a+n+1);
DFS(1);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
if(i==1)
printf("%d",a[b[i]]);
else
printf(" %d",a[b[i]]);
}
}
