There is a kind of balanced binary search tree named red-black tree in the data structure. It has the following 5 properties:
(1) Every node is either red or black.
(2) The root is black.
(3) Every leaf (NULL) is black.
(4) If a node is red, then both its children are black.
(5) For each node, all simple paths from the node to descendant leaves contain the same number of black nodes.
For example, the tree in Figure 1 is a red-black tree, while the ones in Figure 2 and 3 are not.
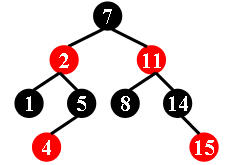
Figure 1
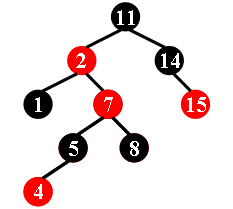
Figure 2
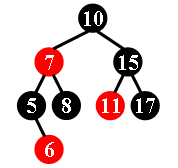
Figure 3
For each given binary search tree, you are supposed to tell if it is a legal red-black tree.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains several test cases. The first line gives a positive integer K (≤30) which is the total number of cases. For each case, the first line gives a positive integer N (≤30), the total number of nodes in the binary tree. The second line gives the preorder traversal sequence of the tree. While all the keys in a tree are positive integers, we use negative signs to represent red nodes. All the numbers in a line are separated by a space. The sample input cases correspond to the trees shown in Figure 1, 2 and 3.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print in a line "Yes" if the given tree is a red-black tree, or "No" if not.
Sample Input:
3
9
7 -2 1 5 -4 -11 8 14 -15
9
11 -2 1 -7 5 -4 8 14 -15
8
10 -7 5 -6 8 15 -11 17
Sample Output:
Yes
No
No
#include<iostream> //偏难
#include<vector>
#include<math.h>
using namespace std;
struct node{
int val;
node* left;
node* right;
node(int v):val(v), left(NULL), right(NULL){
}
};
vector<int> a, pre;
int cnt=0, flag=0;
node* buildtree(node* t, int b, int e){
if(b>e) return NULL;
t=new node(a[b]);
int i=b+1;
while(i<=e&&abs(a[i])<abs(a[b])) i++;
t->left=buildtree(t->left, b+1, i-1);
t->right=buildtree(t->right, i, e);
return t;
}
bool isRBTree(node* root, int num){
if(!root)
if(num!=cnt)
return false;
else
return true;
if(root->val>0) num++;
else{
if(root->right&&root->right->val<0) return false;
if(root->left&&root->left->val<0) return false;
}
return isBTree(root->left, num)&&isBTree(root->right, num);
}
int main(){
int k, n;
cin>>k;
for(int i=0; i<k; i++){
cin>>n;
a.clear();
a.resize(n);
cnt=0;
for(int j=0; j<n; j++)
cin>>a[j];
node* root=NULL;
root=buildtree(root, 0, n-1);
node* temp=root;
while(temp){
cnt=(temp->val>0?cnt+1:cnt);
temp=temp->left;
}
if(isRBTree(root, 0)&&root->val>0)
cout<<"Yes"<<endl;
else
cout<<"No"<<endl;
}
return 0;
}