蓝桥杯之带分数
最近在蓝桥杯中遇到很多的题,类似于将1-9的数字 全部排列出来,满足一个条件,比如这个带分数的题。就需要用1-9所有的数。
这里就运用深度搜索来做。在一个数组中,将全部的1-9这九个数字全部排列出来。
代码如下:
public class Main {
static int[] a = new int[10];//1-9这9个数字是否访问过的状态数组
static int[] b = new int[10];//需要排列的数组
public static void main(String[] args) {
dfs(1);
}
static void dfs(int i) {
if (i > 9) {
for (int k = 1; k <= 9; k++) {
System.out.print(b[k]);
}
System.out.println();
return;//满足条件后输出
} else {
for (int j = 1; j <= 9; j++) {
if (a[j] == 0) {//判断是否某某数字已经出现过
a[j] = 1;//将该数字的状态置为1
b[i] = j;//将该位置i置为数字j
dfs(i + 1);//跳向下一个数字
b[i] = 0;// 回溯
a[j] = 0;// 回溯
}
}
}
return;
}
}
一维深搜:
public class Main {
static int n1;
static int[] arr;
static int n2;
static int Count = 0;
static int[] brr;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
n1 = scan.nextInt();
arr = new int[n1];
n2 = scan.nextInt();
brr=new int[n2+1];
for (int i = 0; i < n1; i++) {
arr[i] = scan.nextInt();
}
dfs(0,1);
System.out.println(Count);
}
//
static void dfs(int i,int count) {
//一维遍历深搜
//退出递归条件
if(i<=n1){//之所以要==n1,会将arr元素组中最后一个元素遍历装进了brr中。不然会少掉这种。
if(count==n2+1){//如果当前brr中元素为3个。这里的加一的原因是数组是从1开始的,0没有用
//这个地方是为了呼应后面判断大小arr[j]>brr[count-1]。
//装第一个元素的时候,可以直接装进去,因为brr[0]为0可以直接装进进去
Count++;//并且里面肯定装的是 递增元素,因为是判断必须比brr结果数组前一个大的数,才能够放进数组
return;
}
}else{
return;
}
for(int j=i;j<n1;j++){//从当前进来这个位置开始遍历,因为上一次传入的是j+1,题意是按从前到后的顺序找升序。
if(arr[j]>brr[count-1]){//判断当前遍历的数与brr结果数组中的最后一个值进行比较大小。如果大,就存入brr。
brr[count]=arr[j];
dfs(j+1,count+1);//因为已经遍历到了当前的j位置所以下一次从j+1开始遍历
brr[count]=0;//回溯
}
}
return;
}
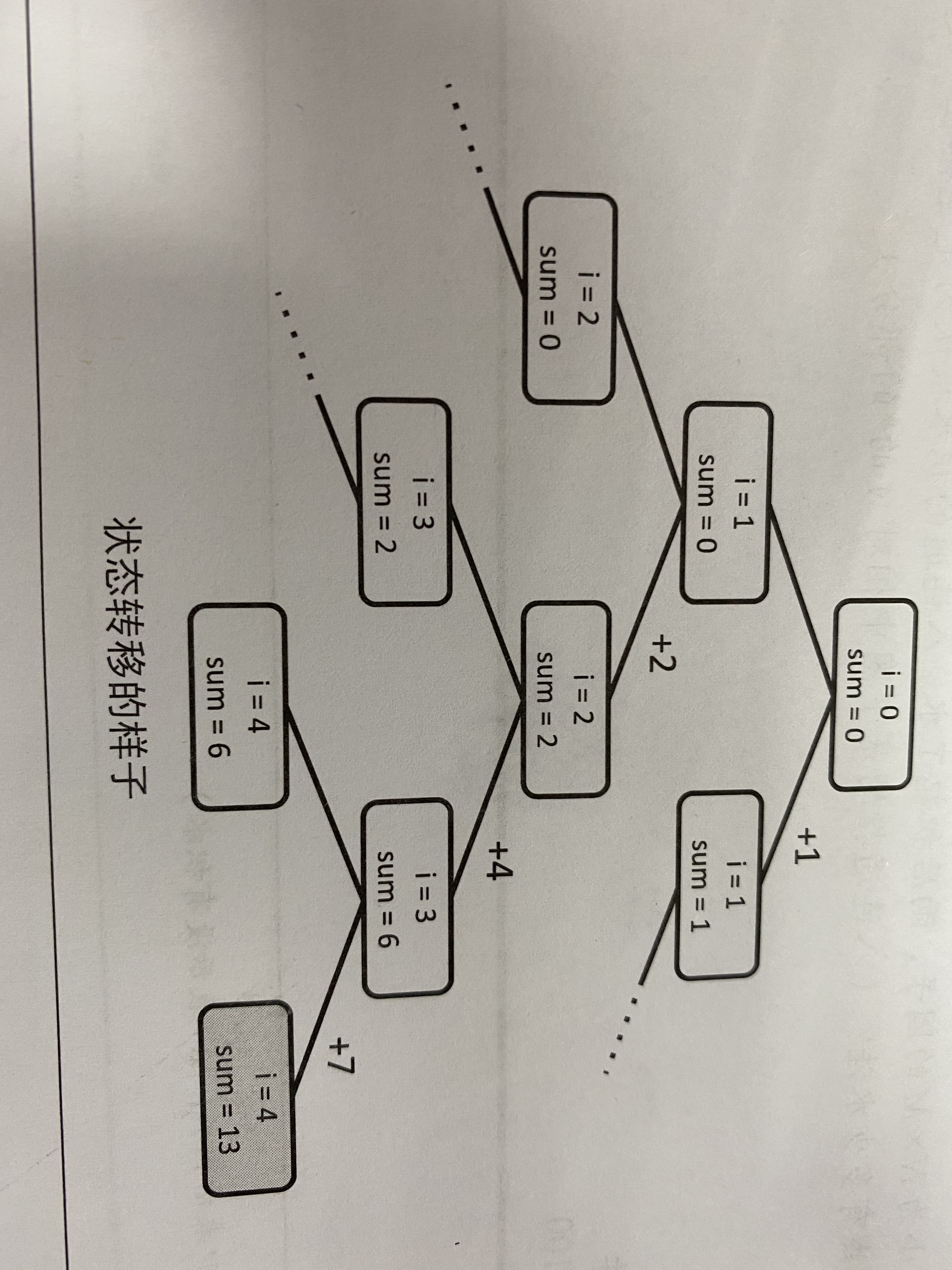
问题:从给定整数a1、a2 ... an中,判断是否可以从中选出若干数,使它们的和恰好为k。
输入:
n=4;
a[{1,2,4,7};
k=13;
输出:yes
代码:
public class Main {
static int MAX_N;
static int[] a;
static int n,k;
public static void main(String[] args) {
a=new int[]{1,2,4,7};
k=14;
n=4;
if(dfs(0,0)==true)
System.out.println("yes");
else
System.out.println("no");
}
static boolean dfs(int i,int sum){//i代表遍历的指针。
if(i==n)//当遍历完了所有的值。
return sum==k;
if(dfs(i+1,sum))//遍历下一个,不加当前的值。
return true;
if(dfs(i+1,sum+a[i]))//遍历下一个,加上当前的值。
return true;
return false;//未遍历到,return false;一直返回false;
}
}