The binomial coefficient C(m,n) is defined as
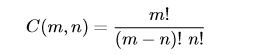
Given four natural numbers p, q, r, and s, compute the the result of dividing C(p,q) by C(r,s).
这是二次项系数,现在给出p,q,r,s,计算C(p,q)除以C(r,s)的结果
Input
Input consists of a sequence of lines. Each line contains four non-negative integer numbers giving values for p, q, r, and s, respectively, separated by a single space. All the numbers will be smaller than 10,000 with p ≥ q and r ≥ s.
输入:包含多组数据,pqrs均小于10000的非负整数。
Output
For each line of input, print a single line containing a real number with 5 digits of precision in the fraction, giving the number as described above. You may assume the result is not greater than 100,000,000.
输出:每行输出除法的结果保留小数点后5位结果,结果保证不超过一亿。
Sample Input
10 5 14 9
93 45 84 59
145 95 143 92
995 487 996 488
2000 1000 1999 999
9998 4999 9996 4998
Sample Output
0.12587
505606.46055
1.28223
0.48996
2.00000
3.99960
思路:指数级的乘法结果太大,运用一些约分的方法防爆。
方法一:
唯一分解定理以前介绍过,大意就是每个数都可以唯一地分解为一堆质数的幂的乘积,如90 = 2 * 3² * 5.其中2和5是一次幂,3是二次幂。
这样我们回到题目数据,显然很多时候我们把分子分母都分解以后会发现能约掉很多质数的幂,这样的话可以采取这样一种策略:用一个数组记录每个质数的幂指数,如果是分子的话就加,是分母的话就减,免去了反复的无用乘除法。当把分子分母们都处理完以后,约分后的分子分母就是答案的分数形式了,此时再求出结果即可。
先把10000以内的素数都记录下来。
然后对每个数据来说,p、s、r-s是分子,q、p-q、r是分母。
接着把这六个数分别代入修改函数,修改素数幂指数数组的值,对于此数组,以90为例,应为every_count={1,2,1,0,0,0,……}。
详见代码,220ms:
1 #include <cstdio> 2 #include <cstring> 3 #include <iostream> 4 #include <iomanip> 5 #include <cmath> 6 using namespace std; 7 8 int p, q, r, s, primes_size/*10000以内素数个数*/; 9 int all_primes[5000];//10000以内素数的按顺序具体记录 10 int every_count[5005];//每个素数幂指数的记录数组 11 bool is_composite[10001];//判定是否为合数 12 13 void modify_count(int a, int d) 14 { 15 for (int i = 0; a > 1 && i < primes_size; i++) 16 while (a % all_primes[i] == 0) 17 { 18 every_count[i] += d;//1与-1的传入使得修改写起来简便 19 a /= all_primes[i]; 20 } 21 } 22 23 void add_factorial(int n, int d) 24 { 25 for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)//n! 26 modify_count(i, d);//修改every_count数组 27 } 28 29 void get_primes() 30 { 31 for (int i = 2; i < 10000; i++) 32 if (!is_composite[i]) 33 { 34 for (int j = i*i; j < 10000; j += i) 35 is_composite[j] = true; 36 all_primes[primes_size++] = i; 37 } 38 } 39 40 int main() 41 { 42 get_primes();//埃氏筛素数 43 44 while (cin >> p >> q >> r >> s) 45 { 46 memset(every_count, 0, sizeof(every_count)); 47 48 //进行6次分解,1与-1的用途见函数内部 49 add_factorial(p, 1); 50 add_factorial(p-q, -1); 51 add_factorial(q, -1); 52 53 add_factorial(r, -1); 54 add_factorial(r-s, 1); 55 add_factorial(s, 1); 56 57 //最后利用素数数组一次性求得答案 58 double ans = 1.0; 59 for (int i = 0; i < primes_size; i++) 60 ans *= pow(all_primes[i], every_count[i]); 61 62 cout << fixed << setprecision(5) << ans << endl; 63 } 64 65 return 0; 66 }
方法二:
也是约分的方式,数学知识降维打击。想必大家都知道上边下边的感叹号是可以约下去一堆的。这里有个知识是,如果你把m!约下去n!,剩下的是n+1~m,数字个数与1~m-n+1相等。也就是可以进行一一对应的double结果乘除。同理约下去(m-n)!也是一样的。
见代码即懂,0ms:
1 #include <cstdio> 2 3 int main() 4 { 5 int p, q, r, s; 6 while (~scanf("%d%d%d%d", &p, &q, &r, &s)) 7 { 8 double ans = 1.0; 9 for (int i = 1, j = p-q+1, x = 1, y = r-s+1; i <= q || x <= s;) 10 { 11 if (i <= q) ans *= (double)(j++)/(i++); 12 13 if (x <= s) ans *= (double)(x++)/(y++); 14 } 15 printf("%.5lf ", ans); 16 } 17 }
最后,虽然方法二严重打击了方法一的信心与自尊心,不过方法一的思想还是很不错的,值得学习。