Description
下图转自“英式没品笑话百科”的新浪微博 —— 所以无论有没有遇到难题,其实都不用担心。
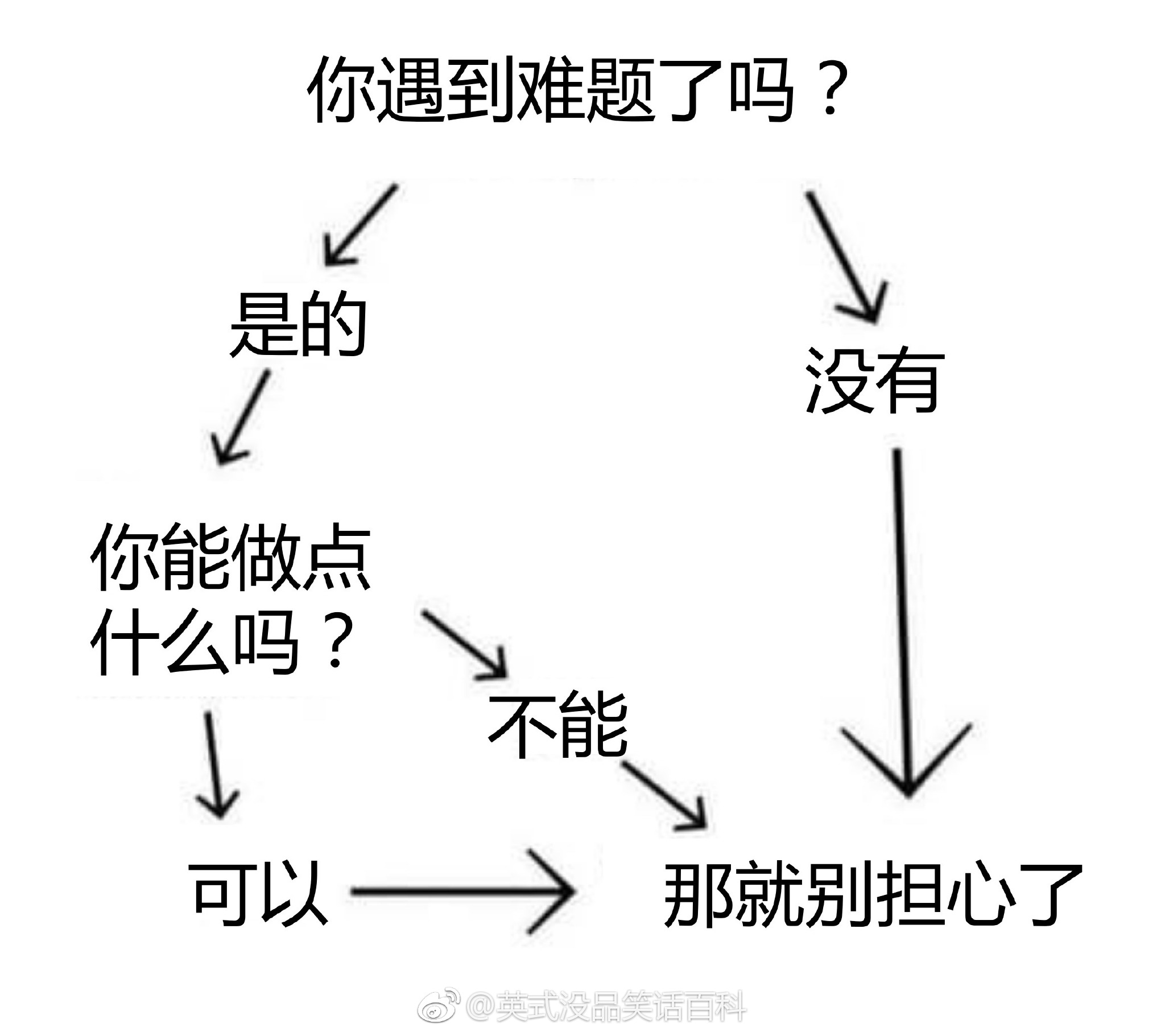
博主将这种逻辑推演称为“逻辑自洽”,即从某个命题出发的所有推理路径都会将结论引导到同一个最终命题(开玩笑的,千万别以为这是真正的逻辑自洽的定义……)。现给定一个更为复杂的逻辑推理图,本题就请你检查从一个给定命题到另一个命题的推理是否是“逻辑自洽”的,以及存在多少种不同的推理路径。例如上图,从“你遇到难题了吗?”到“那就别担心了”就是一种“逻辑自洽”的推理,一共有 (3) 条不同的推理路径。
Input
输入首先在一行中给出两个正整数 (N)和 (M),分别为命题个数和推理个数。这里我们假设命题从 (1) 到 (N) 编号。
接下来 (M) 行,每行给出一对命题之间的推理关系,即两个命题的编号 (S1,S2),表示可以从 (S1) 推出$ S2$。题目保证任意两命题之间只存在最多一种推理关系,且任一命题不能循环自证(即从该命题出发推出该命题自己)。
最后一行给出待检验的两个命题的编号 (A,B)。
Output
在一行中首先输出从 (A) 到 (B) 有多少种不同的推理路径,然后输出 (Yes) 如果推理是“逻辑自洽”的,或 (No) 如果不是。
题目保证输出数据不超过 (10^9。)
Sample Input 1
7 8
7 6
7 4
6 5
4 1
5 2
5 3
2 1
3 1
7 1
Sample Output 1
3 Yes
Sample Input 2
7 8
7 6
7 4
6 5
4 1
5 2
5 3
6 1
3 1
7 1
Sample Output 2
3 No
Solution
这题正解有两个,记忆化搜索和拓扑排序。
我用的是拓扑排序。
统计有源有向无环简单图的路径数,是拓扑排序的经典应用了。关键在于如何判断是不是所有从起点出发的路径都会汇集到终点。一个简单的方法就是看一下当终点出队列时,看下队列里是否还有点,如果有,说明到这些点的路径都不会经过终点。
Code
#include<cmath>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=500;
const int maxm=maxn*maxn/2;
int n,m,tot,S,T;
int pre[maxm+8],now[maxn+8],son[maxm+8];
int deg[maxn+8],f[maxn+8],st[maxn+8];
int vis[maxn+8],r_deg[maxn+8];
int read()
{
int x=0,f=1;char ch=getchar();
for (;ch<'0'||ch>'9';ch=getchar()) if (ch=='-') f=-1;
for (;ch>='0'&&ch<='9';ch=getchar()) x=x*10+ch-'0';
return x*f;
}
void add(int u,int v)
{
pre[++tot]=now[u];
now[u]=tot;
son[tot]=v;
deg[v]++;
r_deg[u]=1;
}
void dfs(int x)
{
vis[x]=1;
if (x==T) return;
for (int p=now[x];p;p=pre[p])
{
int child=son[p];
if (vis[child]) continue;
dfs(child);
}
}
int main()
{
n=read(),m=read();
for (int i=1;i<=m;i++)
{
int u=read(),v=read();
add(u,v);
}
S=read(),T=read();
dfs(S);
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++)
if (!vis[i])
for (int p=now[i];p;p=pre[p])
{
int child=son[p];
deg[child]--;
}
int head=1,tail=0;
st[++tail]=S;
f[S]=1;
bool flag=1;
while(head<=tail)
{
int x=st[head++];
if (x==T) break;
if (r_deg[x]==0) flag=0;
for (int p=now[x];p;p=pre[p])
{
int child=son[p];
f[child]+=f[x];
deg[child]--;
if (!deg[child])
{
st[++tail]=child;
}
}
}
if (head<=tail) flag=0;
printf("%d ",f[T]);
flag?puts("Yes"):puts("No");
return 0;
}