间歇性混吃等死,持续性踌躇满志系列-------------第13天
1、查看线程的运行状态

1 package code0327; 2 3 class Demo01 implements Runnable { 4 public synchronized void waitForASecond() throws InterruptedException { 5 wait(500); //使当前线程等待0.5秒或其他线程调用notify()或notifyAll()方法 6 } 7 8 public synchronized void waitForYears() throws InterruptedException { 9 //使当前线程永久等待,直到其他线程调用notify()或notifyAll()方法 10 wait(); 11 } 12 13 public synchronized void notifyNow() throws InterruptedException { 14 //唤醒由调用wait()方法进入等待状态的线程 15 notify(); 16 } 17 18 public void run() { 19 try { 20 //在线程中运行waitForASecond()方法 21 waitForASecond(); 22 //在线程中运行waitForYears()方法 23 waitForYears(); 24 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 25 e.printStackTrace(); 26 } 27 } 28 } 29 30 class Test { 31 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException{ 32 //创建state对象 33 Demo01 state = new Demo01(); 34 //利用state对象创建Thread对象 35 Thread thread = new Thread(state); 36 //输出线程状态 37 System.out.println("新建线程:"+thread.getState()); 38 //调用thread对象的start()方法,启动新线程 39 thread.start(); 40 //输出线程状态 41 System.out.println("启动线程:"+thread.getState()); 42 //当前线程休眠0.1秒,使新线程运行waiForASecond()方法 43 Thread.sleep(100); 44 //输出线程状态 45 System.out.println("计时等待:"+thread.getState()); 46 //当前线程休眠1秒,使新线程运行waiForYears()方法 47 Thread.sleep(1000); 48 //输出线程状态 49 System.out.println("等待线程:"+thread.getState()); 50 //调用state的notifyNow()方法 51 state.notifyNow(); 52 //输出线程状态 53 System.out.println("唤醒线程:"+thread.getState()); 54 //当前线程休眠1秒,使新线程结束 55 Thread.sleep(1000); 56 //输出线程状态 57 System.out.println("终止线程:"+thread.getState()); 58 } 59 }
运行结果图

2、查看JVM的线程名

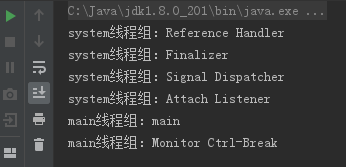
1 package code0327; 2 3 import java.util.ArrayList; 4 import java.util.List; 5 6 public class ThreadList { 7 //获得根线程组 8 private static ThreadGroup getRootThreadGroups() { 9 //获得当前线程组 10 ThreadGroup rootGroup = Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup(); 11 while (true){ 12 //如果getParent()方法的返回值非空则不是根线程组 13 if(rootGroup.getParent()!=null){ 14 //获得父线程组 15 rootGroup = rootGroup.getParent(); 16 }else { 17 //如果到达根线程组则退出循环 18 break; 19 } 20 } 21 //返回根线程组 22 return rootGroup; 23 } 24 //获得线程组中所有的线程名 25 public static List<String> getThreads(ThreadGroup group){ 26 //创建保存线程名的列表 27 List<String> threadList = new ArrayList<String>(); 28 //根据活动线程数创建线程数组 29 Thread[] threads = new Thread[group.activeCount()]; 30 //复制线程到线程数组 31 int count = group.enumerate(threads,false); 32 //遍历线程数组将线程名及其所在组保存到列表中 33 for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { 34 threadList.add(group.getName()+"线程组:"+threads[i].getName()); 35 } 36 return threadList; 37 } 38 //获得线程组中子线程组 39 public static List<String> getThreadGroups(ThreadGroup group){ 40 //获得给定线程组中线程名 41 List<String> threadList = getThreads(group); 42 //创建线程组数组 43 ThreadGroup[] groups = new ThreadGroup[group.activeCount()]; 44 //复制子线程组到线程组数据 45 int count = group.enumerate(groups,false); 46 //遍历所有子线程组 47 for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { 48 //利用getThreads()方法获得线程组名李彪 49 threadList.addAll(getThreads(groups[i])); 50 } 51 //返回所有线程名 52 return threadList; 53 } 54 55 public static void main(String[] args) { 56 for(String string:getThreadGroups(getRootThreadGroups())){ 57 //遍历输出列表中的字符串 58 System.out.println(string); 59 } 60 } 61 }
运行结果图
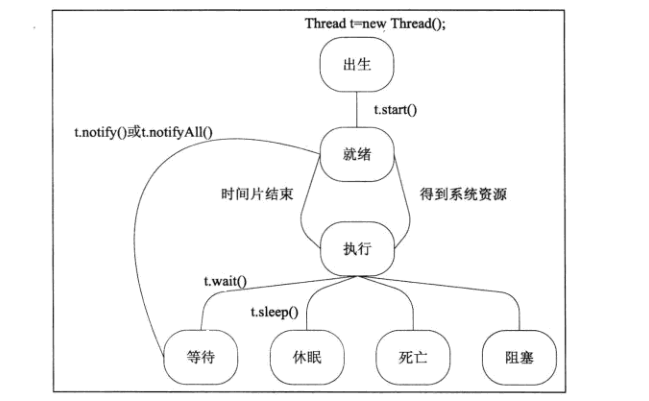
3、线程的生命周期

1 package code0327; 2 3 import javax.swing.*; 4 import java.awt.*; 5 import java.util.Random; 6 7 public class SleepMethodTest extends JFrame { 8 private Thread t; 9 //定义颜色数组 10 private static Color[] color = {Color.BLACK, Color.YELLOW, Color.RED, Color.PINK, Color.LIGHT_GRAY}; 11 //创建随机对象 12 private static final Random rand = new Random(); 13 14 //获取随机颜色值的方法 15 private static Color getC() { 16 return color[rand.nextInt(color.length)]; 17 } 18 19 public SleepMethodTest() { 20 //创建匿名线程对象 21 t = new Thread(new Runnable() { 22 //定义初始坐标 23 int x = 350; 24 int y = 450; 25 26 //覆盖线程接口方法 27 public void run() { 28 //无限循环 29 while (true) { 30 try { 31 //线程休眠0.1秒 32 t.sleep(100); 33 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 34 e.printStackTrace(); 35 } 36 //获取组件绘图上下文对象 37 Graphics graphics = getGraphics(); 38 //设置绘图颜色 39 graphics.setColor(getC()); 40 //绘制直线并递增垂直坐标 41 graphics.drawLine(x, y, 100, y++); 42 if (y >= 80) { 43 y = 50; 44 } 45 } 46 } 47 }); 48 //启动线程 49 t.start(); 50 } 51 52 public static void main(String[] args) { 53 init(new SleepMethodTest(),500,500); 54 } 55 //初始化程序界面方法 56 public static void init(JFrame frame,int width,int height){ 57 frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); 58 frame.setSize(width,height); 59 frame.setVisible(true); 60 } 61 }
运行结果图
4、static关键字
一旦用了static关键字,那么这样的内容不再属于对象自己,而是属于类的,所有凡是本类的对象,都共享同一份。

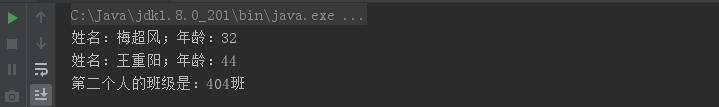
1 package cn.intcast.demo13; 2 3 public class Student { 4 private String name; //姓名 5 private int age; //年龄 6 static String room; //static修饰的所在教室 7 8 public Student() { 9 } 10 11 public String getName() { 12 return name; 13 } 14 15 public void setName(String name) { 16 this.name = name; 17 } 18 19 public int getAge() { 20 return age; 21 } 22 23 public void setAge(int age) { 24 this.age = age; 25 } 26 27 public Student(String name, int age) { 28 this.name = name; 29 this.age = age; 30 } 31 }

1 package cn.intcast.demo13; 2 3 public class Code01Static { 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 Student one = new Student("梅超风",32); 6 System.out.println("姓名:"+one.getName()+";年龄:"+one.getAge()); 7 Student two = new Student("黄老邪",64); 8 two.setName("王重阳"); 9 two.setAge(44); 10 System.out.println("姓名:"+two.getName()+";年龄:"+two.getAge()); 11 one.room = "404班"; 12 System.out.println("第二个人的班级是:"+two.room); 13 } 14 }
运行结果图
5、若static修饰成员方法,那么该方法就是静态方法。静态方法不属于对象,而是属于类的。
如果没有static关键字,那么必须先创建对象,然后通过对象才能使用。对于静态方法来说,可以通过对象名进行调用,也可以直接通过类名称来调用。


1 package cn.intcast.demo13; 2 3 public class MyClass { 4 public void method(){ 5 System.out.println("这是普通的成员方法"); 6 } 7 public static void methodStatic(){ 8 System.out.println("这是静态方法"); 9 } 10 }

1 package cn.intcast.demo13; 2 3 public class CodeStatic { 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 //首先创建对象 6 MyClass obj = new MyClass(); 7 //然后才能使用没有static关键字的内容 8 obj.method(); 9 //对于静态方法来说,可以通过对象名进行调用,也可以直接通过类名称来调用。 10 obj.methodStatic(); //正确,不推荐,这种写法在编译之后也会被javac翻译成为"类名称.静态方法名" 11 MyClass.methodStatic(); //正确,推荐 12 13 } 14 }
运行结果图

6、静态static的内存图
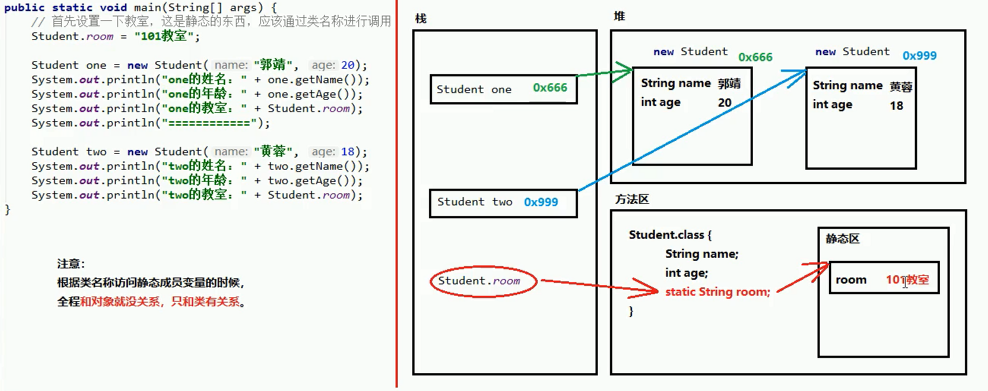
7、静态代码块
格式:
public class 类名称{
static{
//静态代码块
}
}
特点:当第一次用到本类时,静态代码块执行唯一一次。
静态内容总是优先于非静态。所以静态代码块比构造方法先执行。
典型用途:用来一次性的对静态成员变量进行赋值
