数据显示两种:1、显示于屏幕之上;2、重定向到文件中去;
1、了解输入和输出
我们接触了两种输出方式:1、在屏幕上;2、重定向到某个文件;而在文件中,我们会需要在显示器上显示一部分,而存储文件中存储一部分。以下并介绍一些常见的输入输出方式
1.1、标准文件描述符
文件描述符(file descriptor)表示每个文件对象;
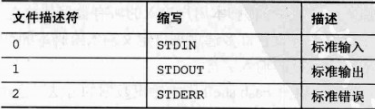
1、STDIN 标准输入
对于Linux而言,键盘输入就是标准输入。使用符号 < 实现标准输入重定向;
cat < testfile #testfile文件交个cat来运行
2、STDOUT 标准输出
将文件内容输出到终端接口。也就是显示器和文本
ls -l > test2 cat test2
>> 符号,可以向文本追加内容
who >> test2
cat test2
错误输出是无法输出到文本中的,所以正确的输出结果和错误的输出结果是由区别的;
ls -al badfel > test3 ls: cannot access badfile: No such file or directory cat test3
3、STDERR 错误输出
错误输出就可以使用这个字符来进行重定向
1.2、重定向错误
1、仅重定向错误
2 代表错误输出
ls -al badfile 2> test4 cat test4
此时,错误的内容才会被定义到test4文件中去;
混合正常输出和错误输出:
ls -al test badtest test2 2> test5
这样的话,只有badtest显示的错误内容会被重定向到test5文件中去;
2、重定向错误和数据
为了解决上面的问题,我们一般如下:
ls -al test test2 test3 badtest 2> test6 1> test7 cat test6 cat test7
除此以外,还可以将输出的正确或者错误的内容定向到一个文件中:
ls -al test test2 test3 badtest &> test7 cat test7
2、在脚本中重定向输出
脚本重定向输出有两种方法:1、临时重定向每行;2、在脚本中永久重定向所有命令;
2.1、临时重定向
故意生成错误信息, >&2
echo "This is an error message" >&2
例如:
#!/bin/bash # testing STDERR messages echo "This is an error" >&2 echo "This is normal ouput"
./test8 2> test9 cat test9 #此时,你去查看test9的内容,This is an error就会被重定向进来
这种方式来生成错误信息是非常好的。
2.2、永久重定向
通过exec命令通知shell脚本再脚本执行期间重定向特定的文件描述符;
#!/bin/bash # redirecting all output to a file exec 1>testout #将下面的echo的内容都重新定位到testout文件中 echo "This is a test of redirecting all output" echo "from a script to another file." echo "without having to redirect every individual line"
./test10 cat testout
还可以在脚本中间重定向STDOUT:
#!/bin/bash # redirecting output to different locations exec 2>testerror echo "This is the start of the script" echo "now reidirecting all output to another location" exec 1>testout echo "This output should go to the testout file" echo "but this should go to the testerror file" >&2
./test11 cat testout cat testerror
问题:如果只想将部分脚本的输出重定向到另外一个位置(如错误认知),这个性能就时分方便,但是在使用的时候,重定向STDOUT或STDERR之后,就无法轻松的将它们重定向到原来的位置了;这个问题,我们之后再解决;
3、在脚本中重定向输入
exec也可以帮助重定向输入: exec 0< testfile
脚本中使用:
#!/bin/bash # redirection file input exec 0< testfile count=1 while read line do echo "Line #$count: $line" count=$[ $count + 1 ] done
read命令读取用户输入信息,而这里则是将testfile的文件做为输入信息,来运行;
4、创建自己的重定向
文件描述符其实是由9个,0 1 2 只是我们最常用的。其他6个时刻以自己的定义然后使用的;
4.1、创建输出文件描述符
可以自己定重定向的编号;
#!/bin/bash # using an alternative file descriptor exec 3>test13out echo "This hsould display on the monitor" echo "and this should be stored in the file" >&3 echo "Then this should be back on the monitor"
./test13 cat test13out
4.2、重定向文件描述符
3>&1 将原本指定的3的标识符,转换为1
#!/bin/bash # storing STDOUT,then coming back to it exec 3>&1 exec 1>test14out echo "This should store in the output file" echo "along with this line." exec 1>&3 echo "Now things should be back to normal"
这是一种临时重定向脚本文件输出然后将输出设置回普通设置的常见方法;
4.3、创建输入文件描述符
可以使用重定向输出文件描述符的方式冲抵昂想输入文件描述符。在重定向到文件之前,将STDIN文件描述符位置保存到另一个文件描述符,然后再完成了文件读取操作后,可以将STDIN恢复为原来的位置;
#!/bin/bash # redirecting input file descriptors exec 6<&0 #将6变为标准输入0 exec 0< testfile count=1 while read line do echo "Line #$count: $line" count=$[ $count + 1 ] done exec 0<&6 #在将标准输入0变为6 read -p "Are you done now? " answer case $answer in Y|y) echo "Goodbye";; N|n) echo "Sorry, this is th end.";; esac
./test15
4.4、创建读取/写入文件描述符
可以使用同一个文件描述符从一个文件中读取数据,同时向这个文件中写入数据;
#!/bin/bash # testing input/output file descrptor exec 3<> testfile read line <&3 echo "Read: $line" echo "This is a test line" >&3
cat testfile This is the first line. This is the second line. This is the third line. ./test16 Read: This is the first line cat testfile This is the first line. This is a test line This is the third line.
4.5、关闭文件描述符
如果创建新的输入或输出文件描述符,shell将在脚本退出时自动关闭它们。但是有时需要脚本结束前手动关闭文件描述符; 使用 &- 来实现,例如: exec 3&-
#!/bin/bash #testing closing file descriptors exec 3> test17file echo "This is a test line of data" >& 3 exec 3>&- echo "This won't work" >&3
关闭文件提示符以后就不能再向它写入任何数据了。否则shell就会报错。
关闭文件描述符时还需要注意另一件事情,如果稍后脚本中打开同一个输出文件,shell将使用新文件替换现有的文件。这意味着如果您输出任何数据,它将覆盖现有文件。
#!/bin/bash # testing closing file descriptors exec 3> test17file echo "This is a test line of data " >&3 exec 3>&- cat test17file exec 3> test17file echo "This'll be bad" >&3
5、列出开放文件描述符
lsof命令:列出整个Linux系统上所有的开放文件描述符。
-p 指定进程PID,还有-d 指定要显示的文件描述符编号;
$$ 变量,shell将变量设置为当前PID。-a 选项可以连接其他两个选项的结果;
/usr/sbin/lsof -a -p $$ -d 0,1,2
lsof默认输出包括几个信息列,如表:
COMMAND 进程中的命令名称的前9个字符
PID 进程的进程ID
USER 拥有进程的用户的登录名
FD 文件描述符编号和访问类型(r读,w写,u读/写)
TYPE 文件类型(CHR-字符,BLK-块,DIR-目录,REG-常规文件)
DEVICE 设备编号(主要和次要)
SIZE 如果可用,则为文件大小
NODE 本地文件的节点编号
NAME 文件的名称
#!/bin/bash # testing lsof with file descriptors exec 3> test18file1 exec 6> test18file2 exec 7< testfile

6、禁止命令输出
有时候我们不希望显示任何脚本输出;
ls -al > /dev/null
ls -al badfile test16 badfile 2> 、dev/null
7、使用临时文件
/tmp目录处理不需要永久保存的文件。需要删除的文件就会移动到该目录下面来;
创建临时文件有一个特殊的命令 mktemp 。
7.1、创建本地临时文件
默认情况下mktemp就是在本地创建临时文件。
mktemp testing.XXXXXX #指定模板;
ls -al testing*
mktemp testing.XXXXXX
testing.1DRLuV
可以看出,mktemp命令输出是它所创建的文件的名称。在脚本中使用mktemp命令时,需要使用一个变量保存该文件名,以便稍后在脚本中引用。
#!/bin/bash # creating and using a temp file tempfile=`mktemp test19.XXXXXX` exec 3>$tempfile echo "This script writes to temp file $tempfile" echo "This is the first line" >&3 echo "This is the second line." >&3 echo "This is the last line." >&3
exec 3>&- echo "Done creating temp file. The contents are:" cat $tempfile rm -f $tempfile 2> /dev/null
7.2、在/tmp中创建临时文件
-t 选项强迫mktemp在系统的临时文件夹中创建文件。
mktemp -t test.XXXXXX /tmp/test.xG3374 ls -al /tmp/test*
返回的是完整路径名。这样就可以在任何目录引用临时文件。
#!/bin/bash # creating a temp file in /tmp tempfile=`mktemp -t tmp.XXXXXX` echo "This is a test file." > $tempfile echo "This is the second line of the test." >> $tempfile echo "The temp file is located at: $tempfile" cat $tempfile rm -f $tempfile
7.3、创建临时目录
-d 选项然mktemp命令穿件一个临时目录而不是一个文件。
#!/bin/bash # using a temporary directory tempdir=`mktemp -d dir.XXXXXX` cd $tempdir tempfile1=`mktemp temp.XXXXX` tempfile2=`mktemp temp.XXXXX` exec 7> $tempfile1 exec 8> $tempfile2 echo "Sending data to directory $temdir" echo "This is a test line of data for $tempfile1" >&7 echo "This is a test line of data for $tempfile2" >&8
8、记录消息
又是后很有必要将输出同时发送到监视器和日志文件。这种情况下不需要使用两次重定向。只用使用tee命令即可;
tee命令就像管道的T型接口,将STDIN的数据同时发送到两个目的地。一个是STDOUT,一个是tee指定的文件名。
用法:tee filename
date | tee testfile cat testfile
who | tee testfile #对于再次输入的文件会被覆盖
cat testfile
#!/bin/bash # using the tee command for logging tempfile=test22file echo "This is the start of the test" | tee $tempfile echo "This is the second line of the test" | tee -a $tempfile echo "This is the end of the test" | tee -a $tempfile
-a 参数则会是添加数据,而不是覆盖数据了;