1、Sandbox 沙箱
- iOS 为每个应用提供了独立的文件空间,一个应用只能直接访问为本应用分配的文件目录,不可以访问其他目录,每个应用自己独立的访问空间被称为该应用的沙盒。也就是说,一个应用与文件系统的交互绝大部分都被限制在它自己的应用沙盒内。
-
1)在新 App 被安装时,安装器会为应用创建一系列角色不同的容器(container)。

-
2)iOS 中同一个应用在不同的手机中分配的路径可能是不同的,所以我们无法通过硬编码指定完整路径名来找到对应文件。Foundation 框架提供了一组专门的接口来获取应用沙箱不同位置的目录路径。
// 获取用户主路径
NSString *NSHomeDirectory(void);
// 获取临时文件路径
NSString *NSTemporaryDirectory(void);
// 获取满足条件的路径列表
NSArray<NSString *> *NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains(NSSearchPathDirectory directory, NSSearchPathDomainMask domainMask, BOOL expandTilde);
- 该函数返回一组路径的数组,如果仅是查找用户的目录,这个数组只包含一个元素,如果第二个参数包含多个值,该数组会包含多个元素。当为 iOS 编写程序时,第二个参数应是 NSUserDomainMask,并且得到一个包含单个路径的数组作为返回。在 iOS 中后两个参数是不变的。
directory :指定查找的目录范围。
NSSearchPathDirectory | 说明
---------------------------------|-------------------------------------
ApplicationDirectory | /Applications
LibraryDirectory | /Library
DocumentDirectory | /Documents
ApplicationSupportDirectory | /Library/Application Support
UserDirectory | /Users
CachesDirectory | /Library/Caches
domainMask :指定查找的文件系统域,可以是多值。
NSSearchPathDomainMask | 说明
---------------------------------|-------------------------------------
UserDomainMask | 用户域,指向当前用户的 home 目录(~)
LocalDomainMask | 本地域,指向对所有用户可用的当前机器范围
NetworkDomainMask | 网络域,指向 /Network
SystemDomainMask | 系统域,指向 /System
expandTilde :指定是否展开路径中的代字符(~)。
2、NSBundle 路径
- 在 iOS 中提到的 NSBundle 是文件系统中的一个特殊位置,它存放的是应用可执行文件及相关资源文件。这个位置的所有文件在系统运行时只具有可读或者可执行的权限,不能进行修改。
- 应用程序 bundle 中主要有以下几种类型的文件:
- Info.plist:用来配置应用的基本参数信息。包括版本号,指向的可执行文件名、包名等。
- 可执行文件:每个应用程序必须要有一个可执行文件。
- 资源文件:是可执行文件以外的数据文件,常用的如图像、图标、音频文件、视图文件、配置文件等。
- 应用程序 bundle 的配置信息都存在 Info.plist 文件中。它里面各项都以 key-value 的形式进行描述,包括了应用程序唯一标识名、版本号、可执行文件名等信息。
-
2.1 bundle 配置信息主要参数:
key | 友好显示名 | value
---------------------------|-------------------------------|------------------------------------------------------
CFBundleDisplayName | Bundle display name | 程序的应用名,安装后显示在桌面上的那个名称,可以进行本地化设置
CFBundleExecutable | Executable file | 应用可执行程序的名称
CFBundleIdentifier | Bundle identifier | 应用程序的唯一标识
CFBundleVersion | Bundle version | 应用编译版本号
CFBundleShortVersionString | Bundle version string, short | 应用 release 发布版版本号
- 当创建一个应用时,系统存储了应用相关联的所有数据(其中包括图片、本地化字符串、图标等),将这些内容放入一个称为应用包(application bundle)的包中。在应用中添加一个资源时很方便的:仅需将文件拖到 Xcode 的左边窗格中。当出现对话框时,通常选择复制资源文件到你的项目目录中,这样你的项目都是自包含的。
- command-line tool 是没有 bundle 的,所以用 NSBundle 的时候一直是 null,如果要使用 bundle 获取项目中的资源,必须要使用 application。
- Bundle 常见问题
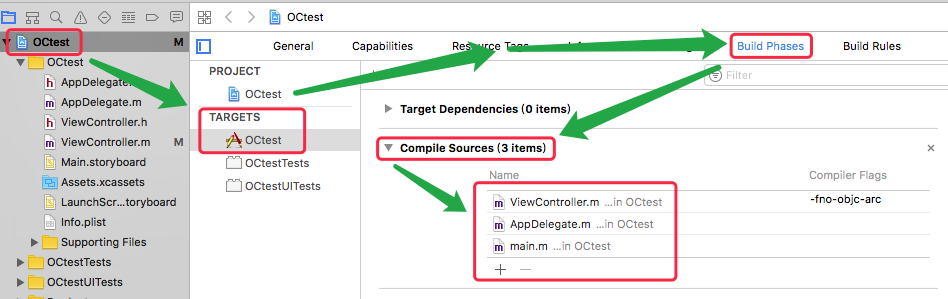
- 项目里面的某个 .m 文件无法使用
- 检查 TARGETS => Build Phases => Compile Sources 里是否包含此 .m 文件。
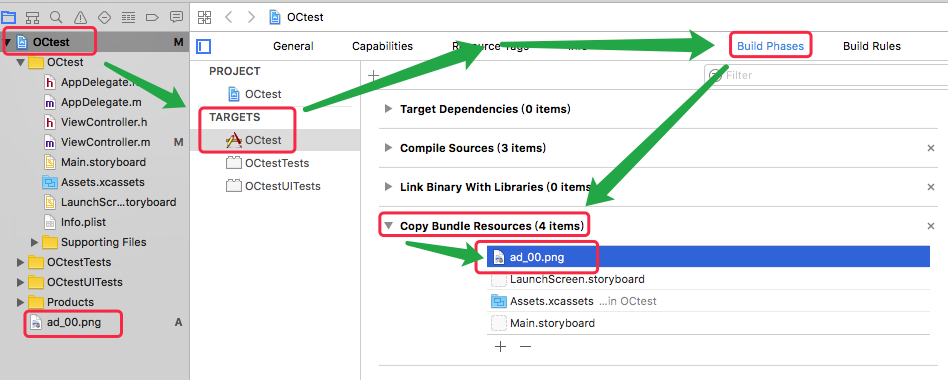
- 项目里面的某个资源文件(比如 plist、音频等)无法使用
- 检查 TARGETS => Build Phases => Copy Bundle Resources 里是否包含此资源文件。
-
2.2 获取 NSBundle 资源
// 获得 Bundle 信息
/*
通常指向 xxx.app/ 这个根目录
*/
NSBundle *mainBundle = [NSBundle mainBundle];
// 获取 Bundle 文件路径
NSString *bundlePath = [NSBundle mainBundle].bundlePath;
NSString *resourcePath = [NSBundle mainBundle].resourcePath;
// 获取 Bundle URL 路径
NSURL *bundleUrl = [NSBundle mainBundle].bundleURL;
NSURL *resourceURL = [NSBundle mainBundle].resourceURL;
// 获得 Bundle 目录下的文件路径
NSString *filePath1 = [[NSBundle mainBundle] pathForResource:@"test" ofType:@"txt"];
// 获得 bundle 下子目录 subdirectory 下的文件路径
NSString *filePath2 = [[NSBundle mainBundle] pathForResource:@"test" ofType:@"txt" inDirectory:@"testFolder"];
// 获得 Bundle 目录下的 URL 路径
NSURL *fileUrl1 = [[NSBundle mainBundle] URLForResource:@"test" withExtension:@"txt"];
// 获得 bundle 下子目录 subdirectory 下的 URL 路径
NSURL *fileUrl2 = [[NSBundle mainBundle] URLForResource:@"test" withExtension:@"txt" subdirectory:@"testFolder"];
// 获取应用程序唯一标识包名
NSString *indentifier = [NSBundle mainBundle].bundleIdentifier;
// 获取应用程序 Info.plist 配置项词典对象实例
NSDictionary *info = [NSBundle mainBundle].infoDictionary;
// 获取某一特定字段的内容
NSString *bundleID = [[NSBundle mainBundle] objectForInfoDictionaryKey:@"CFBundleName"];
3、NSURL 路径
- 在文件系统中,文件和目录都是使用完整文件路径来唯一标识的。我们可以使用 NSString 和 NSURL 两种对象来描述文件路径。官方建议使用 NSURL 。
- NSURL 是用来表示 URL 地址的类,通过 URL 我们可以定位一个远程 web 服务器上的资源位置,也可以定位硬盘上的一个本地文件的路径。对于 web 资源,往往结合 NSURLSession、NSURLConnection、NSURLDownload 等使用,对于本地资源,一般结合 NSFileManager、NSFileHandle、NSBundle 使用。
- NSURLComponents 只支持 iOS7.0 及以上的 API 类,它可以实现对 URL 各个部分的读写。NSURLComponents 对 URL 各个部分的内容都有两种格式的属性来表示:
原生格式 | URL-Encoded
-----------------|-------------------------
scheme | -
host | percentEncodedHost
port | -
path | percentEncodedPath
query | percentEncodedQuery
fragment | percentEncodedFragment
user | percentEncodedUser
password | percentEncodedPassword
-
1)NSURL 结构:
protocol://hostname[:port]/path/[;parameters][?query]#fragment // 带方括号[]的为可选项
protocol :协议
hostname :主机名
port :端口
path :路径
parameters :参数
query :查询
fragment :信息片段
http:// 超文本传输协议
https:// 超文本传输安全协议
ftp:// 文件传输协议
file:// 本地文件 URL
data:// 数据 URL
-
2)URL 的创建
// 由字符串创建
// 简单字符串直接创建
NSURL *url1 = [NSURL URLWithString:@"https://swiftinaction.com/example"];
NSString *complexString = @"https://swiftinaction.com/中文字符串/example";
NSString *convertString = [complexString stringByAddingPercentEncodingWithAllowedCharacters:
[NSCharacterSet characterSetWithCharactersInString:@"`#%^{}"[]|\<> "]];
// 由复杂字符串/中文创建时,需要对字符串进行编码转换
NSURL *url2 = [NSURL URLWithString:convertString];
// 由基础 URL 和基于基础 URL 的一个相对路径字符串创建
NSURL *baseUrl = [NSURL URLWithString:@"https://swiftinaction.com"];
NSURL *fullUrl = [NSURL URLWithString:@"/example" relativeToURL:baseUrl];
// 生成绝对路径
NSURL *url3 = [fullUrl absoluteURL];
// 由文件路径创建
// 自动判断 URL 路径为文件,还是目录,为目录时自动在路径末尾加 “/”
NSURL *url4 = [NSURL fileURLWithPath:@"/Users/JHQ0228/Desktop/test"];
// 指定 URL 路径为一个目录,自动在路径末尾加 “/”
NSURL *url5 = [NSURL fileURLWithPath:@"/Users/JHQ0228/Desktop/test" isDirectory: YES];
-
3)URL 的获取
NSURL *url1 = [NSURL URLWithString:@"http://JHQ:password@swiftinaction.com:8080/sayHello/toChinese.png; date=20160223?name=JHQ#atMorning"];
// 获取 URL 的 绝对路径字符串
NSString *absoluteString = [url1 absoluteString];
// 获取 URL 的 协议类型
NSString *scheneString = [url1 scheme];
// 获取 URL 的 主机名
NSString *hostString = [url1 host];
// 获取 URL 的 端口
NSNumber *portString = [url1 port];
// 获取 URL 的 路径名
NSString *pathString = [url1 path];
// 获取 URL 的 参数
NSString *parametersString = [url1 parameterString];
// 获取 URL 的 查询语句
NSString *queryString = [url1 query];
// 获取 URL 的 信息片段语句
NSString *fragmentString = [url1 fragment];
// 获取 URL 的 路径组成部分
NSArray *pathComponents = [url1 pathComponents];
// 获取 URL 的 相对路径
NSString *relativePath = [url1 relativePath];
// 获取 URL 的 路径最后一个组成部分
NSString *lastPathComponent = [url1 lastPathComponent];
// 获取 URL 的 路径扩展名
NSString *pathExtension = [url1 pathExtension];
// 获取 URL 的 用户名
NSString *user = [url1 user];
// 获取 URL 的 密码
NSString *password = [url1 password];
-
4)URL 的判断
NSURL *fileUrl = [[NSBundle mainBundle] URLForResource:@"testFile" withExtension:@"txt"];
// 检查文件的可达性
/*
只能用来判断文件系统内部资源的可达性,对于 web URl 等其他类型全返回 false
*/
BOOL bl1 = [fileUrl checkResourceIsReachableAndReturnError:nil];
// 判断是否为文件 URl
BOOL bl2 = [fileUrl isFileURL];
-
5)URL 的路径拼接
NSURL *url = [NSURL URLWithString:@"http://swiftinaction.com/sayHello"];
// 追加路径到当前路径末尾
// 只追加路径,不在路径末尾添加 “/”
NSURL *appendUrl1 = [url URLByAppendingPathComponent:@"toJhq"];
// isDirectory 为 true 时在路径末尾添加 “/”
NSURL *appendUrl2 = [url URLByAppendingPathComponent:@"toJhq" isDirectory: YES];
// 追加路径后缀到当前路径末尾
/*
当路径以 “/” 结尾时,后缀会添加到末尾的 “/” 之前
*/
NSURL *appendUrl3 = [url URLByAppendingPathExtension:@"png"];
// 删除路径末尾的最后一个路径
NSURL *deleteUrl1 = [appendUrl1 URLByDeletingLastPathComponent];
// 删除路径末尾的后缀
NSURL *deleteUrl2 = [appendUrl3 URLByDeletingPathExtension];
-
6)NSURLComponents
// NSURLComponents 的创建
NSURLComponents *componentsUrl = [NSURLComponents componentsWithString:@"http://swiftinaction.com/sayHello"];
// NSURLComponents 的设置
componentsUrl.scheme = @"https";
componentsUrl.host = @"swiftinaction.com.cn";
componentsUrl.port = @8080;
componentsUrl.path = @"/sayHello/toChinese/你好";
componentsUrl.query = @"name=JHQ";
componentsUrl.fragment = @"atMorning";
componentsUrl.user = @"JHQ";
componentsUrl.password = @"123456789";
// NSURLComponents 的转换
// 将 NSURLComponents 转为 NSURL
NSURL *nsUrl = [componentsUrl URL];
NSString *componentsUrlString1 = [componentsUrl path];
// 转换为内容数据的十六进制编码字符串
NSString *componentsUrlString2 = [componentsUrl percentEncodedPath];
4、数据持久化方法
- 在 iOS 开发过程中,不管是做什么应用,都会碰到数据保存的问题。将数据保存到本地,能够让程序的运行更加流畅,不会出现让人厌恶的菊花形状,使得用户体验更好。下面介绍一下数据保存的方式:
-
1、NSKeyedArchiver
- 采用归档的形式来保存数据,数据对象需要遵守 NSCoding 协议,对象对应的类必须提供 encodeWithCoder: 和 initWithCoder: 方法。缺点:只能一次性归档保存以及一次性解压。所以只能针对小量数据,对数据操作比较笨拙,如果想改动数据的某一小部分,需要解压或归档整个数据。
-
2、NSUserDefaults
- 用来保存应用程序设置和属性、用户保存的数据。用户再次打开程序或开机后这些数据仍然存在。NSUserDefaults 可以存储的数据类型包括:NSData、NSString、NSNumber、NSDate、NSArray、NSDictionary。缺点:如果要存储其他类型,需要转换为前面的类型,才能用 NSUserDefaults 存储。
-
3、Write to file
- 永久保存在磁盘中。第一步:获得文件即将保存的路径:第二步:生成在该路径下的文件:第三步:往文件中写入数据:最后:从文件中读出数据。
-
4、SQLite
- 采用 SQLite 数据库来存储数据。SQLite 作为一中小型数据库,应用 iOS 中,跟前三种保存方式相比,相对比较复杂一些。


