计蒜客:后缀数组专题题解
这几天写后缀系列的东西简直写得石乐志,各种奇怪的问题。
不过也是涨姿势了,学到了点新东西。
首先,我不会后缀数组的倍增构造方法,这个东西现想太容易挂,背代码也不是很容易吧。所以接下来的题目我会尽可能用后缀自动机去求解。对于非得用后缀数组height做的题目,我会介绍一种新的,用后缀自动机构建后缀数组的方法。
好了,我们开始:
习题:密码安全度:

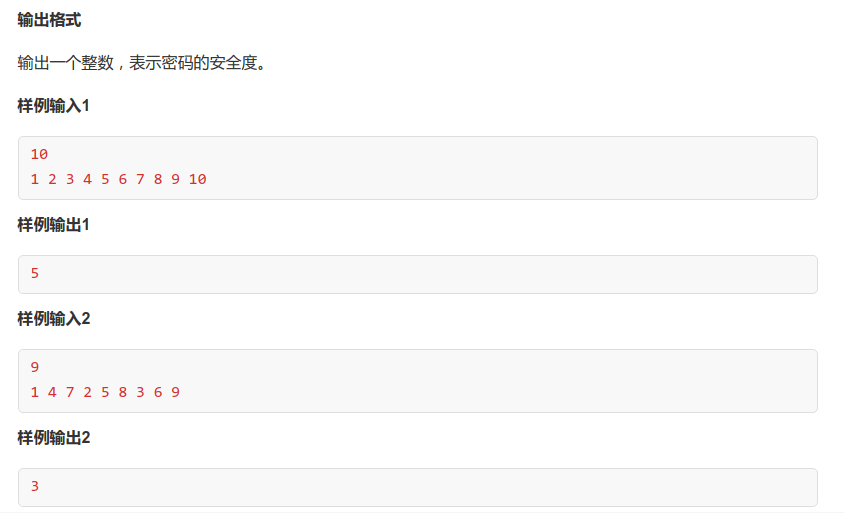
两个子串对应的差相等,显然差分。然后我们对这个差分序列建立SAM,对于每一个节点,拓扑排序跑出maxr,minr,然后用min(len,maxr-minr-1)更新答案(为什么-1?因为他让你源序列中不重复,如果不-1的话在原序列中会包含一个重复元素,例如2,5,8,10,13,更新的ans应该是2的说)。
最后答案+1输出即可。
代码:

1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<cstdio> 3 #include<cstring> 4 #include<algorithm> 5 #include<map> 6 #include<queue> 7 #define debug cout 8 using namespace std; 9 const int maxn=4e5+1e2; 10 const int inf=0x3f3f3f3f; 11 12 struct Node { 13 map<int,Node*> ch; 14 Node* fa; 15 int len,deg,mir,mxr; 16 Node() { 17 mir = inf , mxr = -inf; 18 } 19 }ns[maxn],*root,*last; 20 21 int in[maxn>>1]; 22 int n,m,cnt,ans; 23 24 inline Node* NewNode(int ll) { 25 ns[++cnt].len = ll; 26 return ns+cnt; 27 } 28 29 inline void extend(int x,int rr) { 30 Node* p = last; 31 Node* np = NewNode(p->len+1); 32 np->mir = np->mxr = rr; 33 while( p && p->ch.find(x) == p->ch.end() ) 34 p->ch[x] = np, 35 p = p->fa; 36 if( !p ) 37 np->fa = root; 38 else { 39 Node* q = p->ch[x]; 40 if( q->len == p->len + 1 ) 41 np->fa = q; 42 else { 43 Node* nq = NewNode(p->len+1); 44 nq->fa = q->fa; 45 nq->ch = q->ch; 46 np->fa = q->fa = nq; 47 while( p && p->ch[x] == q ) 48 p->ch[x] = nq, 49 p = p->fa; 50 } 51 } 52 last = np; 53 } 54 55 inline void topo() { 56 ans = -1; 57 for(int i=1;i<=cnt;i++) 58 if( ns[i].fa ) 59 ++ns[i].fa->deg; 60 queue<Node*> q; 61 for(int i=1;i<=cnt;i++) 62 if( !ns[i].deg ) 63 q.push(ns+i); 64 while( q.size() ) { 65 const Node* pos = q.front(); q.pop(); 66 if( pos == root ) 67 break; 68 ans = max( ans , min( pos->len , pos->mxr - pos->mir - 1 ) ); 69 pos->fa->mxr = max( pos->fa->mxr , pos->mxr ); 70 pos->fa->mir = min( pos->fa->mir , pos->mir ); 71 if( !--pos->fa->deg ) 72 q.push(pos->fa); 73 } 74 } 75 76 int main() { 77 scanf("%d",&n); 78 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) 79 scanf("%d",in+i); 80 81 last = root = NewNode(0); 82 for(int i=2;i<=n;i++) 83 extend(in[i]-in[i-1],i-1); 84 topo(); 85 86 printf("%d ",ans+1); 87 88 return 0; 89 }
习题:蒜头君传纸条:


出现至少k次的连续序列,我们构造后缀自动机,然后拓扑排序统计其right集合的大小(right集合大小就是相同子串数QAQ)。如果right集合比k大,则用当前节点的长度更新答案。
代码:

1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<cstdio> 3 #include<cstring> 4 #include<algorithm> 5 #include<map> 6 #include<queue> 7 #define debug cout 8 using namespace std; 9 const int maxn=4e5+1e2; 10 11 struct Node { 12 map<int,Node*> ch; 13 Node* fa; 14 int len,deg,sum; 15 }ns[maxn],*root,*last; 16 17 int in[maxn>>1],n,m,cnt,ans; 18 19 inline Node* NewNode(int ll) { 20 ns[++cnt].len = ll; 21 return ns+cnt; 22 } 23 inline void extend(int x) { 24 Node* p = last; 25 Node* np = NewNode(p->len+1); 26 np->sum = 1; 27 while( p && p->ch.find(x) == p->ch.end() ) 28 p->ch[x] = np, 29 p = p->fa; 30 if( !p ) 31 np->fa = root; 32 else { 33 Node* q = p->ch[x]; 34 if( q->len == p->len + 1 ) 35 np->fa = q; 36 else { 37 Node* nq = NewNode(p->len+1); 38 nq->fa = q->fa; 39 nq->ch = q->ch; 40 q->fa = np->fa = nq; 41 while( p && p->ch[x] == q ) 42 p->ch[x] = nq, 43 p = p->fa; 44 } 45 } 46 last = np; 47 } 48 49 inline void topo() { 50 for(int i=1;i<=cnt;i++) 51 if( ns[i].fa ) 52 ++ns[i].fa->deg; 53 queue<Node*> q; 54 for(int i=1;i<=cnt;i++) 55 if( !ns[i].deg ) 56 q.push(ns+i); 57 while( q.size() ) { 58 const Node* pos = q.front(); q.pop(); 59 if( pos == root ) 60 break; 61 if( pos->sum >= m ) 62 ans = max( ans , pos->len ); 63 pos->fa->sum += pos->sum; 64 if( !--pos->fa->deg ) 65 q.push(pos->fa); 66 } 67 } 68 69 int main() { 70 scanf("%d%d",&n,&m); 71 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) 72 scanf("%d",in+i); 73 74 last = root = NewNode(0); 75 76 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) 77 extend(in[i]); 78 topo(); 79 80 81 printf("%d ",ans); 82 83 return 0; 84 }
习题:蒜头君传纸条进阶版:


这对于SAM我这种选手是一道坑题!
首先用SAM做,很容易想到正常求kth子串,然后右端点就是匹配到位置的right的最小值。然而SAM每次求kth子串是线性的,所以所以这样做是n方暴力!我交上去T了一次才知道。
正解非得用sa,及其height数组。
怎么做呢?对于对于从大到小排好序的每一个后缀,其贡献的不同的子串数为n-(sa[i]-1)-heightp[i-1]。(注意我的数组全都是从1开始用的),然后我们对于这个数组跑前缀和,二分一下,就能知道第k个子串出现的字典序最小的位置。
注意:字典序最小的位置不一定是最靠前的位置,例如对于aaaaa,我们查询第1个子串,找到的字典序最小的位置是5,然后就很愉悦地WA了。
正确的做法是先跑出当前答案串的长度len,在维护height[i]>=len的情况下向右边扫,同时用这一段用sa的min值更新区间左答案。
扫的过程可以二分+rmq,然后再rmq查询最小值。由于数据水,我直接暴力更新AC了。
我说过我拒接倍增构建后缀数组,那我怎么做的呢?先反向构建后缀自动机,这样跑出来的fail树就是后缀树了,然后再对fail树进行dfs构建出后缀数组。
为什么这样是正确的?我也不是很明白。自行脑补一下大概是对的吧。
代码:

1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<cstdio> 3 #include<cstring> 4 #include<algorithm> 5 #define lli long long int 6 #define debug cout 7 using namespace std; 8 const int maxn=2e5+1e2; 9 10 char in[maxn]; 11 int fa[maxn],ch[maxn][26],tc[maxn][26],len[maxn],rig[maxn],root,last,cnt; 12 int stk[maxn],top; 13 int sa[maxn],rnk[maxn],height[maxn],sal; 14 lli sum[maxn],l,r,v; 15 int m,li; 16 17 inline int NewNode(int ll) { 18 len[++cnt] = ll; 19 return cnt; 20 } 21 inline void extend(int x,int pos) { 22 int p = last; 23 int np = NewNode(len[p]+1); 24 rig[np] = pos; 25 while( p && !ch[p][x] ) 26 ch[p][x] = np, 27 p = fa[p]; 28 if( !p ) 29 fa[np] = root; 30 else { 31 int q = ch[p][x]; 32 if( len[q] == len[p] + 1 ) 33 fa[np] = q; 34 else { 35 int nq = NewNode(len[p]+1); 36 memcpy(ch[nq],ch[q],sizeof(ch[q])); 37 fa[nq] = fa[q]; 38 fa[q] = fa[np] = nq; 39 while( p && ch[p][x] == q ) 40 ch[p][x] = nq, 41 p = fa[p]; 42 } 43 } 44 last = np; 45 } 46 47 inline void pre(int pos) { 48 for(int i=0;i<26;i++) 49 if( ch[pos][i] && len[ch[pos][i]] == len[pos] + 1 ) { 50 const int &x = ch[pos][i]; 51 stk[++top] = i; 52 tc[fa[x]][stk[len[x]-len[fa[x]]]] = x; 53 pre(x); 54 stk[top--] = '�'; 55 } 56 } 57 inline void dfs(int pos) { 58 if( rig[pos] ) 59 sa[++sal] = rig[pos]; 60 for(int i=0;i<26;i++) 61 if( tc[pos][i] ) 62 dfs(tc[pos][i]); 63 } 64 65 inline void calh() { 66 for(int i=1;i<=li;i++) 67 rnk[sa[i]] = i; 68 int k = 0; 69 for(int i=1;i<=li;i++) { 70 const int p1 = i , p2 = sa[rnk[i]-1]; 71 if(k) 72 k--; 73 while( p1+k<=li && p2+k<=li && in[p1+k] == in[p2+k] ) 74 ++k; 75 height[rnk[i]-1] = k; 76 } 77 } 78 79 int main() { 80 scanf("%s",in+1); 81 li = strlen(in+1); 82 83 last = root = NewNode(0); 84 for(int i=li;i;i--) 85 extend(in[i]-'a',i); 86 pre(root), 87 dfs(root); 88 89 calh(); 90 91 for(int i=1;i<=li;i++) 92 sum[i] = sum[i-1] + li - ( sa[i] - 1 ) - height[i-1]; 93 94 scanf("%d",&m); 95 96 while(m--) { 97 scanf("%lld",&v); 98 v = ( v ^ l ^ r ) + 1; 99 if( v > sum[li] ) 100 l = r = 0; 101 else { 102 int pos = lower_bound(sum+1,sum+1+li,v) - sum; 103 l = sa[pos] ; 104 int len = height[pos-1] + v - sum[pos-1]; 105 for(int i=pos+1;i<=li&&height[i-1]>=len;i++) 106 l = min( l , (lli)sa[i] ); 107 r = l + len - 1; 108 } 109 printf("%lld %lld ",l,r); 110 } 111 return 0; 112 }
习题:密码安全性进阶版:


出现两次的不重复子串个数,SAM卖萌题?直接用min(len,mixr-minr)-fa->len+1更新ans即可。
代码:

1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<cstdio> 3 #include<cstring> 4 #include<algorithm> 5 #include<queue> 6 #define debug cout 7 using namespace std; 8 const int maxn=2e3+1e2; 9 const int inf=0x3f3f3f3f; 10 11 char in[maxn]; 12 int cnt,li; 13 long long ans; 14 15 struct Node { 16 Node *fa,*ch[26]; 17 int len,deg,mir,mxr; 18 Node() { 19 mir = inf , mxr = -inf; 20 } 21 }ns[maxn],*last,*root; 22 23 Node* NewNode(int ll) { 24 ns[++cnt].len = ll; 25 return ns+cnt; 26 } 27 28 inline void extend(int x,int pos) { 29 Node* p = last; 30 Node* np = NewNode(p->len+1); 31 np->mir = np->mxr = pos; 32 while( p && !p->ch[x] ) 33 p->ch[x] = np, 34 p = p->fa; 35 if( !p ) 36 np->fa = root; 37 else { 38 Node* q = p->ch[x]; 39 if( q->len == p->len + 1 ) 40 np->fa = q; 41 else { 42 Node* nq = NewNode(p->len+1); 43 memcpy(nq->ch,q->ch,sizeof(q->ch)); 44 nq->fa = q->fa; 45 q->fa = np->fa = nq; 46 while( p && p->ch[x] == q ) 47 p->ch[x] = nq, 48 p = p->fa; 49 } 50 } 51 last = np; 52 } 53 54 inline void topo() { 55 for(int i=1;i<=cnt;i++) 56 if( ns[i].fa ) 57 ++ns[i].fa->deg; 58 queue<Node*> q; 59 for(int i=1;i<=cnt;i++) 60 if( !ns[i].deg ) 61 q.push(ns+i); 62 while( q.size() ) { 63 const Node* pos = q.front(); q.pop(); 64 if( pos == root ) 65 break; 66 if( min( pos->len , pos->mxr - pos->mir) > pos->fa->len ) { 67 ans += min( pos->len , pos->mxr - pos->mir) - pos->fa->len; 68 } 69 pos->fa->mir = min( pos->fa->mir , pos->mir ); 70 pos->fa->mxr = max( pos->fa->mxr , pos->mxr ); 71 if( !--pos->fa->deg ) 72 q.push(pos->fa); 73 } 74 } 75 76 int main() { 77 scanf("%s",in+1); 78 li = strlen(in+1); 79 80 last = root = NewNode(0); 81 for(int i=1;i<=li;i++) 82 extend(in[i]-'a',i); 83 84 topo(); 85 printf("%lld ",ans); 86 87 return 0; 88 }
习题:抄袭检测:

两个串的最长公共子串,怎么说呢?SAM裸题。对于一个串建立SAM,另一个串匹配。匹配失败时走parent边,不断用匹配长度更新答案即可。
代码:

1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<cstdio> 3 #include<cstring> 4 #include<algorithm> 5 using namespace std; 6 const int maxn=2e5+1e2; 7 8 char in[maxn>>1]; 9 int n,cnt,li,ans; 10 11 struct Node { 12 Node *fa,*ch[26]; 13 int len; 14 }ns[maxn],*root,*last; 15 16 inline Node* NewNode(int ll) { 17 ns[++cnt].len = ll; 18 return ns+cnt; 19 } 20 inline void extend(int x) { 21 Node* p = last; 22 Node* np = NewNode(p->len+1); 23 while( p && !p->ch[x] ) 24 p->ch[x] = np, 25 p = p->fa; 26 if( !p ) 27 np->fa = root; 28 else { 29 Node* q = p->ch[x]; 30 if( q->len == p->len + 1 ) 31 np->fa = q; 32 else { 33 Node* nq = NewNode(p->len+1); 34 memcpy(nq->ch,q->ch,sizeof(q->ch)); 35 nq->fa = q->fa; 36 q->fa = np->fa = nq; 37 while( p && p->ch[x] == q ) 38 p->ch[x] = nq, 39 p = p->fa; 40 } 41 } 42 last = np; 43 } 44 45 inline void getans() { 46 int len = 0; 47 Node* now = root; 48 for(int i=1;i<=li;i++) { 49 const int t = in[i] - 'a'; 50 if( now->ch[t] ) { 51 ++len; 52 now = now->ch[t]; 53 } 54 else { 55 while( now && !now->ch[t] ) 56 now = now->fa; 57 if( !now ) { 58 len = 0; 59 now = root; 60 } 61 else { 62 len = now->len + 1; 63 now = now->ch[t]; 64 } 65 } 66 ans = max( ans , len ); 67 } 68 } 69 70 int main() { 71 scanf("%s",in+1); 72 li = strlen(in+1); 73 74 last = root = NewNode(0); 75 for(int i=1;i<=li;i++) 76 extend(in[i]-'a'); 77 78 scanf("%s",in+1); 79 li = strlen(in+1); 80 81 getans(); 82 83 printf("%d ",ans); 84 85 return 0; 86 }
习题:抄袭检测进阶版:


长度不小于k的公共子串个数。
如果重复的串只计算一遍,那是SAM水题。然而,这样连样例都过不了。(这样跑样例会输出6,别问我怎么知道的)
重复的串只计算一遍,那么,我们对于一个子串,考虑把他在两个串中出现次数相乘。
对于第一个串中的出现次数,直接建立自动机然后拓扑排序r的大小即可。
对于在第二个串中的出现次数,就比较麻烦了:
我们还是在自动机上匹配,在匹配到每个节点时,显然当前匹配的长度不会大于节点的len(自己动脑子想想,完美匹配也就能相等罢了,怎么会大于)。
所以,我们用当前匹配的长度减去max(k,当前节点的min长度(即now->fa->len+1)),就是这种状态下能在当前节点匹配的子串的个数。
然后再乘以当前节点的right集合的大小,就是这些子串的出现次数总和。
别忘了统计对于当前节点父亲所代表的串的匹配,这个方法是在在父亲节点打标记,然后再拓扑排序转移标记,对于每个节点,答案加上标记次数乘right大小即可。
估计你也看不明白,自己脑补一下好了……
对了,在拓扑排序时,别忘了判断当前节点是否有父亲,否则你会收获一个段错误!
代码:

1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<cstdio> 3 #include<cstring> 4 #include<algorithm> 5 #include<queue> 6 #define lli long long int 7 #define debug cout 8 using namespace std; 9 const int maxn=2e5+1e2; 10 11 char in[maxn>>1]; 12 int k,cnt,li; 13 lli ans; 14 15 struct Node { 16 Node *fa,*ch[26]; 17 int len,deg; 18 lli lazy,sizr; 19 }ns[maxn],*root,*last; 20 21 inline Node* NewNode(int ll) { 22 ns[++cnt].len = ll; 23 return ns+cnt; 24 } 25 26 inline void extend(int x) { 27 Node* p = last; 28 Node* np = NewNode(p->len+1); 29 np->sizr = 1; 30 while( p && !p->ch[x] ) 31 p->ch[x] = np, 32 p = p->fa; 33 if( !p ) 34 np->fa = root; 35 else { 36 Node* q = p->ch[x]; 37 if( q->len == p->len + 1 ) 38 np->fa = q; 39 else { 40 Node* nq = NewNode(p->len+1); 41 memcpy(nq->ch,q->ch,sizeof(q->ch)); 42 nq->fa = q->fa; 43 q->fa = np->fa = nq; 44 while( p && p->ch[x] == q ) 45 p->ch[x] = nq, 46 p = p->fa; 47 } 48 } 49 last = np; 50 } 51 52 inline void pre() { 53 for(int i=1;i<=cnt;i++) 54 if( ns[i].fa ) 55 ++ns[i].fa->deg; 56 queue<Node*> q; 57 for(int i=1;i<=cnt;i++) 58 if( !ns[i].deg ) 59 q.push(ns+i); 60 while( q.size() ) { 61 const Node* pos = q.front(); q.pop(); 62 if( pos == root ) 63 break; 64 pos->fa->sizr += pos->sizr; 65 if( !--pos->fa->deg ) 66 q.push(pos->fa); 67 } 68 } 69 70 inline void getans() { 71 int len = 0; 72 Node* now = root; 73 for(int i=1;i<=li;i++) { 74 int t = in[i] - 'a'; 75 if( now->ch[t] ) { 76 ++len; 77 now = now->ch[t]; 78 } 79 else { 80 while( now && !now->ch[t] ) 81 now = now->fa; 82 if( !now ) { 83 now = root; 84 len = 0; 85 } 86 else { 87 len = now->len + 1; 88 now = now->ch[t]; 89 } 90 } 91 if( now == root ) // remember this or you will get a segmentation fault 92 continue; 93 // len can't more than pos->len! 94 if( len >= max( k , now->fa->len + 1 ) ) 95 ans += now->sizr * ( len - max( k , now->fa->len + 1 ) + 1 ); 96 if( len >= now->fa->len ) 97 ++now->fa->lazy; 98 } 99 } 100 101 inline void topo() { 102 for(int i=1;i<=cnt;i++) 103 ns[i].deg = 0; 104 for(int i=1;i<=cnt;i++) 105 if( ns[i].fa ) 106 ++ns[i].fa->deg; 107 queue<Node*> q; 108 for(int i=1;i<=cnt;i++) 109 if( !ns[i].deg ) 110 q.push(ns+i); 111 while( q.size() ) { 112 const Node* pos = q.front(); q.pop(); 113 if( pos == root ) 114 break; 115 if( pos->len >= max( k , pos->fa->len + 1 ) ) 116 ans += pos->sizr * pos->lazy * ( pos->len - max( k , pos->fa->len + 1 ) + 1 ); 117 pos->fa->lazy += pos->lazy; 118 if( !--pos->fa->deg ) 119 q.push(pos->fa); 120 } 121 } 122 123 int main() { 124 scanf("%d",&k); 125 scanf("%s",in+1); 126 li = strlen(in+1); 127 128 last = root = NewNode(0); 129 for(int i=1;i<=li;i++) 130 extend(in[i]-'a'); 131 132 scanf("%s",in+1); 133 li = strlen(in+1); 134 135 pre(); 136 getans(); 137 topo(); 138 139 printf("%lld ",ans); 140 141 return 0; 142 }
习题:常见密码统计:


至少半数密码的子串,这个用SAM也不是那么好搞了。
所以,我们需要:广义SAM。
所谓广义SAM,就是把一堆串塞进一个SAM里。每次加入一个串时把last重置为root。
对于一个字符,如果last有直系的这个字符节点,则直接转移,如果没有或不是直系,就新建节点。
然后我们在每个节点上维护一个bitset,记录这个节点包含在那些串中。拓扑排序转移,如果bitset的大小满足要求,则用节点长度更新答案。
怎么输出?把自动机记录着前面的串dfs一遍就好了QAQ。
注意:这题的半数不包含整好一半!比如说有58个串,则在29个串中出现的子串是不行的!WA了一遍才知道,有毒吧!
代码:

1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<cstdio> 3 #include<cstring> 4 #include<algorithm> 5 #include<bitset> 6 #include<queue> 7 #define debug cout 8 using namespace std; 9 const int maxn=2e5+1e2; 10 11 char in[maxn>>1],out[maxn]; 12 int nn,li,ol,cnt,ans; 13 unsigned cc; 14 15 struct Node { 16 Node *fa,*ch[26]; 17 int len,deg; 18 bitset<105> bs; 19 }ns[maxn],*last,*root; 20 21 inline Node* NewNode(int ll) { 22 ns[++cnt].len = ll; 23 return ns+cnt; 24 } 25 26 inline void extend(int x) { 27 Node* p = last; 28 Node* np = NewNode(p->len+1); 29 while( p && !p->ch[x] ) 30 p->ch[x] = np, 31 p = p->fa; 32 if( !p ) 33 np->fa = root; 34 else { 35 Node* q = p->ch[x]; 36 if( q->len == p->len + 1 ) 37 np->fa = q; 38 else { 39 Node* nq = NewNode(p->len+1); 40 memcpy(nq->ch,q->ch,sizeof(q->ch)); 41 nq->fa = q->fa; 42 q->fa = np->fa = nq; 43 while( p && p->ch[x] == q ) 44 p->ch[x] = nq, 45 p = p->fa; 46 } 47 } 48 last = np; 49 } 50 51 inline void EX_extend(int x,int id) { 52 if( last->ch[x] ) { 53 Node *p = last , *q = last->ch[x]; 54 if( q->len == p->len + 1 ) 55 last = q; 56 else { 57 Node* npq = NewNode(p->len+1); 58 memcpy(npq->ch,q->ch,sizeof(q->ch)); 59 npq->fa = q->fa; 60 q->fa = npq; 61 while( p && p->ch[x] == q ) 62 p->ch[x] = npq, 63 p = p->fa; 64 last = npq; 65 } 66 } 67 else 68 extend(x); 69 last->bs[id] = 1; 70 } 71 72 inline void topo() { 73 for(int i=1;i<=cnt;i++) 74 if( ns[i].fa ) 75 ++ns[i].fa->deg; 76 queue<Node*> q; 77 for(int i=1;i<=cnt;i++) 78 if( !ns[i].deg ) 79 q.push(ns+i); 80 while( q.size() ) { 81 const Node* pos = q.front(); q.pop(); 82 if( pos == root ) 83 break; 84 if( pos->bs.count() > cc ) 85 ans = max( ans , pos->len ); 86 pos->fa->bs |= pos->bs; 87 if( !--pos->fa->deg ) 88 q.push(pos->fa); 89 } 90 } 91 92 inline void dfs(Node* pos) { 93 if( pos->len > ans ) 94 return; 95 if( pos->len == ans && pos->bs.count() > cc ) { 96 puts(out); 97 return; 98 } 99 for(int i=0;i<26;i++) 100 if( pos->ch[i] && pos->ch[i]->len == pos->len + 1 ) { 101 out[ol++] = 'a' + i; 102 dfs(pos->ch[i]); 103 out[--ol] = '�'; 104 } 105 } 106 107 int main() { 108 scanf("%d",&nn); 109 cc = nn >> 1; 110 111 root = NewNode(0); 112 for(int i=1;i<=nn;i++) { 113 scanf("%s",in+1); 114 li = strlen(in+1); 115 last = root; 116 for(int j=1;j<=li;j++) 117 EX_extend(in[j]-'a',i); 118 } 119 120 topo(); 121 if( ans ) 122 dfs(root); 123 else 124 puts("?"); 125 126 return 0; 127 }
习题:通用密码统计:


所有串或反转后的串的子串。
由于反转两次相当于没有反转,所以我们对于第一个串建立SAM,然后把后面的串正反同id分别在SAM上匹配即可。
具体实现同n个串的最长公共子串,无非就是维护个数组,与len取min,向父亲节点转移什么的。
代码:

1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<cstdio> 3 #include<cstring> 4 #include<algorithm> 5 #include<queue> 6 #define debug cout 7 using namespace std; 8 const int maxn=4e3+1e2; 9 10 char in[maxn>>1]; 11 int n,len,cnt,ans; 12 13 struct Node { 14 Node *fa,*ch[26]; 15 int len,deg,f[110]; 16 }ns[maxn],*last,*root; 17 18 inline Node* NewNode(int ll) { 19 ns[++cnt].len = ll; 20 return ns+cnt; 21 } 22 23 inline void extend(int x) { 24 Node* p = last; 25 Node* np = NewNode(p->len+1); 26 while( p && !p->ch[x] ) 27 p->ch[x] = np, 28 p = p->fa; 29 if( !p ) 30 np->fa = root; 31 else { 32 Node* q = p->ch[x]; 33 if( q->len == p->len + 1 ) 34 np->fa = q; 35 else { 36 Node* nq = NewNode(p->len+1); 37 memcpy(nq->ch,q->ch,sizeof(q->ch)); 38 nq->fa = q->fa; 39 q->fa = np->fa = nq; 40 while( p && p->ch[x] == q ) 41 p->ch[x] = nq, 42 p = p->fa; 43 } 44 } 45 last = np; 46 } 47 48 inline void pir(char* sou,int l,int id) { 49 Node* now = root; 50 int len = 0; 51 for(int i=1;i<=l;i++) { 52 const int t = sou[i] - 'a'; 53 if( now->ch[t] ) { 54 ++len, 55 now = now->ch[t]; 56 } 57 else { 58 while( now && !now->ch[t] ) 59 now = now->fa; 60 if( !now ) 61 now = root , len = 0; 62 else 63 len = now->len + 1, 64 now = now->ch[t]; 65 } 66 now->f[id] = max( now->f[id] , len ); 67 } 68 } 69 70 inline void topo() { 71 for(int i=1;i<=cnt;i++) 72 if( ns[i].fa ) 73 ++ns[i].fa->deg; 74 queue<Node*> q; 75 for(int i=1;i<=cnt;i++) 76 if( !ns[i].deg ) 77 q.push(ns+i); 78 while( q.size() ) { 79 const Node* pos = q.front(); q.pop(); 80 if( pos == root ) 81 break; 82 int mxl = pos->len; 83 for(int i=1;i<n;i++) 84 mxl = min( mxl , pos->f[i] ); 85 ans = max( ans , mxl ); 86 for(int i=1;i<n;i++) 87 pos->fa->f[i] = max( pos->fa->f[i] , pos->f[i] ); 88 if( !--pos->fa->deg ) 89 q.push(pos->fa); 90 } 91 } 92 93 int main() { 94 scanf("%d",&n); 95 scanf("%s",in+1); 96 len = strlen(in+1); 97 if( n == 1 ) { 98 printf("%d ",len); 99 return 0; 100 } 101 102 last = root = NewNode(0); 103 for(int i=1;i<=len;i++) 104 extend(in[i]-'a'); 105 106 for(int i=1;i<n;i++) { 107 scanf("%s",in+1); 108 len = strlen(in+1); 109 pir(in,len,i); 110 reverse(in+1,in+1+len); // right ] ? 111 pir(in,len,i); 112 } 113 114 topo(); 115 116 printf("%d ",ans); 117 118 return 0; 119 }
