1.结构
单链表和向量实现难度低,维护容易却查找效率低,AVL树、红黑树等高级数据结构效率高但较为复杂,难以维护。
SkipList的实现较红黑树简单得多,而且同时保证了查询和维护等操作平均仅需O(logn)时间。
不难看出,跳表的结构大致可以被描述为:带索引的有序的链表
底层的链表存储了所有数据,而上层的链表则作为索引存在。
普通单链表节点的指针域中仅有一个next指向后继元素,双向链表中增加了一个前驱。
而在跳表中,一个节点中可以有4个指针,分别指向前驱、后继、上邻、下邻。
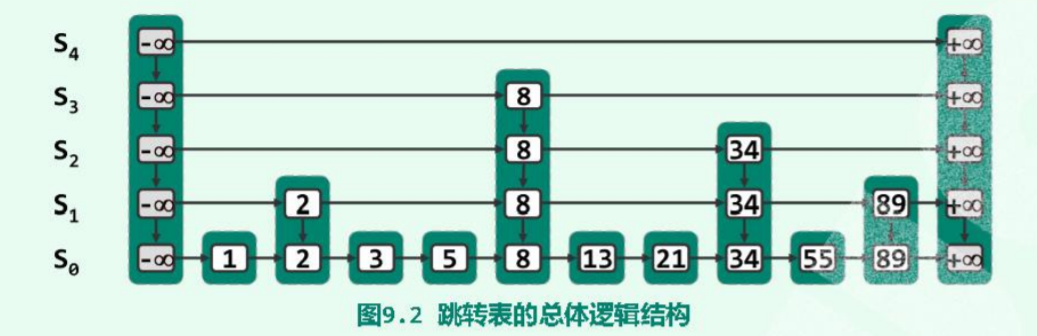
2.SkipListNode
根据跳表的定义很容易设计出这样一个类
key:关键码
value:数据域
pre,next,up,down:分别指向前后上下的节点
public class SkipListNode<T> { public int key; public T value; /** 前驱、后继 */ public SkipListNode<T> pre, next; /** 上邻、下邻 */ public SkipListNode<T> up, down; public static final int HEAD_KEY = Integer.MIN_VALUE; public static final int TAIL_KEY = Integer.MAX_VALUE; public SkipListNode(int k, T v) { key = k; value = v; } public int getKey() { return key; } public void setKey(int key) { this.key = key; } public T getValue() { return value; } public void setValue(T value) { this.value = value; } @Override public boolean equals(Object object) { if (this == object) { return true; } if (object == null) { return false; } if (!(object instanceof SkipListNode<?>)) { return false; } SkipListNode<T> skipListNode; try { skipListNode = (SkipListNode<T>) object; } catch (ClassCastException ex) { return false; } return (skipListNode.getKey() == key) && (skipListNode.getValue() == value); } @Override public String toString() { return "key-value:" + key + "," + value; } }
3.SkipList
包含了几个重要的操作:查找(get),插入(put),删除(remove),加层(addEmptyLevel)
查找(get)
最重要的方法,其他的几个方法都是以查找为基础的。
实际进行查找操作的方法是findNode。
查找的过程很清晰,从顶层的头节点开始顺序查找,一旦遇到下一个关键码大于目标关键码(确定了目标在下层的区间),则转入下层查找。
目标关键码在跳表中不一定存在,则此时findNode返回的将是小于且距离目标关键码的值最近的节点。
/** * 如果传入的key值在跳跃表中不存在,则findNode返回跳跃表中key值小于key,并且key值相差最小的底层节点 * 所以不能用此方法来代替get * @param key key * @return key值相差最小的底层节点 */ public SkipListNode<T> findNode(int key) { SkipListNode<T> p = head; while (true) { while (p.next.key != SkipListNode.TAIL_KEY && p.next.key <= key) { p = p.next; } //转入下层 if (p.down != null) { p = p.down; } else { break; } } return p; }
因为存在查找失败的情况,所以要给findNode加一层判断,当findNode返回的节点确实等于目标关键码而非最近小于时,才将该节点返回。
public SkipListNode<T> get(int key) { SkipListNode<T> p = findNode(key); if (p.key == key) { return p; } return null; }
加层(addEmptyLevel)
这个没什么好说的,将各个变量初始化,listLevel++
public void addEmptyLevel() { SkipListNode<T> p1 = new SkipListNode<T>(SkipListNode.HEAD_KEY, null); SkipListNode<T> p2 = new SkipListNode<T>(SkipListNode.TAIL_KEY, null); p1.next = p2; p1.down = head; p2.pre = p1; p2.down = tail; head.up = p1; tail.up = p2; head = p1; tail = p2; listLevel++; }
插入(put)
实际的插入操作是由insertNode方法完成的。
单纯的插入操作其实很简单,insertNode要求传入待插入节点的前驱。
/** * 单层插入 * @param p 前驱 * @param q 待插入的节点 */ private void insertNode(SkipListNode<T> p, SkipListNode<T> q) { q.next = p.next; q.pre = p; p.next.pre = q; p.next = q; }
首先在跳表中findNode,由上可知,findNode的返回值分两种情况:第一种,当key已存在,关键码不能重复,所以终止插入操作;第二种,当key不存在,此时findNode返回最近小于key的节点,正好将这个节点作为待插入节点的前驱,调用insertNode方法即可。
插入操作进行到这里已经完成了,但插入新节点后,还涉及到比较复杂的升层问题。
首先考虑SkipList的空间复杂度,SkipList是基于有序链表实现的,不难看出,为了加快查找速度,SkipList为有序链表建立了索引,即以空间换时间,牺牲了一定的空间效率换取了更高的查找效率,这算得上是比较常用的手段。但是,SkipList的层数并非越多越好,索引也不是越密集越好,如果没有一定的策略,在浪费了空间的同时,时间的效率也无法得到保证。
网上主流的随机策略是升层的概率逐层递减为1/2,根据数学归纳法计算数学期望,总体的消耗量将仅为O(n)。
(证明见《数据结构与算法分析(C++语言版)第3版》 邓俊辉 P254)
在jdk实现的ConcurrentSkipListMap中,随机策略有所不同。
/** * 插入 * put方法有一些需要注意的步骤: * 1.如果put的key值在跳跃表中存在,则进行修改操作; * 2.如果put的key值在跳跃表中不存在,则需要进行新增节点的操作,并且需要由random随机数决定新加入的节点的高度(最大level); * 3.当新添加的节点高度达到跳跃表的最大level,需要添加一个空白层(除了-oo和+oo没有别的节点) * @param key key * @param value value */ public void put(int key, T value) { SkipListNode<T> p = findNode(key); //如果已经存在,则终止插入操作 if (p.key == key) { p.value = value; return; } SkipListNode<T> q = new SkipListNode<>(key, value); insertNode(p, q); //随机决定是否升层 int currentLevel = 0; while (random.nextDouble() > PROBABILITY) { if (currentLevel >= listLevel) { addEmptyLevel(); } while (p.up == null) { System.out.println(p); p = p.pre; } p = p.up; SkipListNode<T> z = new SkipListNode<>(key, null); insertNode(p, z); z.down = q; q.up = z; //把指针移到上一层 q = z; currentLevel++; } size++; }
删除(remove)
删除操作本质上和普通链表的删除没有什么区别,唯一的不同是要注意其他层的节点要一并删除。
/** * 首先查找到包含key值的节点,将节点从链表中移除,接着如果有更高level的节点,则重复这个操作即可。 * @param key key * @return T(删除的数据) */ public T remove(int key) { SkipListNode<T> p = get(key); if (p == null) { return null; } T oldV = p.value; SkipListNode<T> q; while (p != null) { q = p.next; q.pre = p.pre; p.pre.next = q; p = p.up; } return oldV; }
全部代码

public class SkipList<T> { private SkipListNode<T> head, tail; private int size; private int listLevel; private final Random random; private static final double PROBABILITY = 0.5; public SkipList() { head = new SkipListNode<T>(SkipListNode.HEAD_KEY, null); tail = new SkipListNode<>(SkipListNode.TAIL_KEY, null); head.next = tail; tail.pre = head; size = 0; listLevel = 0; random = new Random(); } /** * 根据key查找 * @param key key * @return SkipListNode<T> */ public SkipListNode<T> get(int key) { SkipListNode<T> p = findNode(key); if (p.key == key) { return p; } return null; } /** * 首先查找到包含key值的节点,将节点从链表中移除,接着如果有更高level的节点,则repeat这个操作即可。 * @param key key * @return T(删除的数据) */ public T remove(int key) { SkipListNode<T> p = get(key); if (p == null) { return null; } T oldV = p.value; SkipListNode<T> q; while (p != null) { q = p.next; q.pre = p.pre; p.pre.next = q; p = p.up; } return oldV; } /** * 插入 * put方法有一些需要注意的步骤: * 1.如果put的key值在跳跃表中存在,则进行修改操作; * 2.如果put的key值在跳跃表中不存在,则需要进行新增节点的操作,并且需要由random随机数决定新加入的节点的高度(最大level); * 3.当新添加的节点高度达到跳跃表的最大level,需要添加一个空白层(除了-oo和+oo没有别的节点) * @param key key * @param value value */ public void put(int key, T value) { SkipListNode<T> p = findNode(key); //如果已经存在,则终止插入操作 if (p.key == key) { p.value = value; return; } SkipListNode<T> q = new SkipListNode<>(key, value); insertNode(p, q); //随机决定是否升层 int currentLevel = 0; while (random.nextDouble() > PROBABILITY) { if (currentLevel >= listLevel) { addEmptyLevel(); } while (p.up == null) { System.out.println(p); p = p.pre; } p = p.up; SkipListNode<T> z = new SkipListNode<>(key, null); insertNode(p, z); z.down = q; q.up = z; //把指针移到上一层 q = z; currentLevel++; } size++; } /** * 如果传入的key值在跳跃表中不存在,则findNode返回跳跃表中key值小于key,并且key值相差最小的底层节点; * 所以不能用此方法来代替get * @param key key * @return key值相差最小的底层节点 */ public SkipListNode<T> findNode(int key) { SkipListNode<T> p = head; while (true) { while (p.next.key != SkipListNode.TAIL_KEY && p.next.key <= key) { p = p.next; } //转入下层 if (p.down != null) { p = p.down; } else { break; } } return p; } public boolean isEmpty() { return size == 0; } public int size() { return size; } /** * 添加新的一层 */ public void addEmptyLevel() { SkipListNode<T> p1 = new SkipListNode<T>(SkipListNode.HEAD_KEY, null); SkipListNode<T> p2 = new SkipListNode<T>(SkipListNode.TAIL_KEY, null); p1.next = p2; p1.down = head; p2.pre = p1; p2.down = tail; head.up = p1; tail.up = p2; head = p1; tail = p2; listLevel++; } /** * 单层插入 * @param p 前驱 * @param q 待插入的节点 */ private void insertNode(SkipListNode<T> p, SkipListNode<T> q) { q.next = p.next; q.pre = p; p.next.pre = q; p.next = q; } public int getLevel() { return listLevel; } }
4.java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentSkipListMap
ConcurrentSkipListMap是线程安全的有序的哈希表,适用于高并发的场景。
ConcurrentSkipListMap和TreeMap,它们虽然都是有序的哈希表。但是,第一,它们的线程安全机制不同,TreeMap是非线程安全的,而ConcurrentSkipListMap是线程安全的。第二,ConcurrentSkipListMap是通过跳表实现的,而TreeMap是通过红黑树实现的。
ConcurrentSkipListMap内部实现的跳表主要有三个方法:doGet(查找),doPut(插入),doRemove(删除)

/** * Gets value for key. Almost the same as findNode, but returns * the found value (to avoid retries during re-reads) * * @param key the key * @return the value, or null if absent */ private V doGet(Object key) { if (key == null) throw new NullPointerException(); Comparator<? super K> cmp = comparator; outer: for (;;) { for (Node<K,V> b = findPredecessor(key, cmp), n = b.next;;) { Object v; int c; if (n == null) break outer; Node<K,V> f = n.next; if (n != b.next) // inconsistent read break; if ((v = n.value) == null) { // n is deleted n.helpDelete(b, f); break; } if (b.value == null || v == n) // b is deleted break; if ((c = cpr(cmp, key, n.key)) == 0) { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") V vv = (V)v; return vv; } if (c < 0) break outer; b = n; n = f; } } return null; } /* ---------------- Insertion -------------- */ /** * Main insertion method. Adds element if not present, or * replaces value if present and onlyIfAbsent is false. * @param key the key * @param value the value that must be associated with key * @param onlyIfAbsent if should not insert if already present * @return the old value, or null if newly inserted */ private V doPut(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) { Node<K,V> z; // added node if (key == null) throw new NullPointerException(); Comparator<? super K> cmp = comparator; outer: for (;;) { for (Node<K,V> b = findPredecessor(key, cmp), n = b.next;;) { if (n != null) { Object v; int c; Node<K,V> f = n.next; if (n != b.next) // inconsistent read break; if ((v = n.value) == null) { // n is deleted n.helpDelete(b, f); break; } if (b.value == null || v == n) // b is deleted break; if ((c = cpr(cmp, key, n.key)) > 0) { b = n; n = f; continue; } if (c == 0) { if (onlyIfAbsent || n.casValue(v, value)) { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") V vv = (V)v; return vv; } break; // restart if lost race to replace value } // else c < 0; fall through } z = new Node<K,V>(key, value, n); if (!b.casNext(n, z)) break; // restart if lost race to append to b break outer; } } int rnd = ThreadLocalRandom.nextSecondarySeed(); if ((rnd & 0x80000001) == 0) { // test highest and lowest bits int level = 1, max; while (((rnd >>>= 1) & 1) != 0) ++level; Index<K,V> idx = null; HeadIndex<K,V> h = head; if (level <= (max = h.level)) { for (int i = 1; i <= level; ++i) idx = new Index<K,V>(z, idx, null); } else { // try to grow by one level level = max + 1; // hold in array and later pick the one to use @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")Index<K,V>[] idxs = (Index<K,V>[])new Index<?,?>[level+1]; for (int i = 1; i <= level; ++i) idxs[i] = idx = new Index<K,V>(z, idx, null); for (;;) { h = head; int oldLevel = h.level; if (level <= oldLevel) // lost race to add level break; HeadIndex<K,V> newh = h; Node<K,V> oldbase = h.node; for (int j = oldLevel+1; j <= level; ++j) newh = new HeadIndex<K,V>(oldbase, newh, idxs[j], j); if (casHead(h, newh)) { h = newh; idx = idxs[level = oldLevel]; break; } } } // find insertion points and splice in splice: for (int insertionLevel = level;;) { int j = h.level; for (Index<K,V> q = h, r = q.right, t = idx;;) { if (q == null || t == null) break splice; if (r != null) { Node<K,V> n = r.node; // compare before deletion check avoids needing recheck int c = cpr(cmp, key, n.key); if (n.value == null) { if (!q.unlink(r)) break; r = q.right; continue; } if (c > 0) { q = r; r = r.right; continue; } } if (j == insertionLevel) { if (!q.link(r, t)) break; // restart if (t.node.value == null) { findNode(key); break splice; } if (--insertionLevel == 0) break splice; } if (--j >= insertionLevel && j < level) t = t.down; q = q.down; r = q.right; } } } return null; } /* ---------------- Deletion -------------- */ /** * Main deletion method. Locates node, nulls value, appends a * deletion marker, unlinks predecessor, removes associated index * nodes, and possibly reduces head index level. * * Index nodes are cleared out simply by calling findPredecessor. * which unlinks indexes to deleted nodes found along path to key, * which will include the indexes to this node. This is done * unconditionally. We can't check beforehand whether there are * index nodes because it might be the case that some or all * indexes hadn't been inserted yet for this node during initial * search for it, and we'd like to ensure lack of garbage * retention, so must call to be sure. * * @param key the key * @param value if non-null, the value that must be * associated with key * @return the node, or null if not found */ final V doRemove(Object key, Object value) { if (key == null) throw new NullPointerException(); Comparator<? super K> cmp = comparator; outer: for (;;) { for (Node<K,V> b = findPredecessor(key, cmp), n = b.next;;) { Object v; int c; if (n == null) break outer; Node<K,V> f = n.next; if (n != b.next) // inconsistent read break; if ((v = n.value) == null) { // n is deleted n.helpDelete(b, f); break; } if (b.value == null || v == n) // b is deleted break; if ((c = cpr(cmp, key, n.key)) < 0) break outer; if (c > 0) { b = n; n = f; continue; } if (value != null && !value.equals(v)) break outer; if (!n.casValue(v, null)) break; if (!n.appendMarker(f) || !b.casNext(n, f)) findNode(key); // retry via findNode else { findPredecessor(key, cmp); // clean index if (head.right == null) tryReduceLevel(); } @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") V vv = (V)v; return vv; } } return null; }
实现方法大致相同,值得注意的是其采用的随机策略。
(rnd & 0x80000001) == 0
0x80000001展开为二进制为10000000000000000000000000000001,即只有最高位和最低位为1
排除了负数(负数最高位为1)和奇数(奇数最低位为1),即只有随机数rnd为正偶数的情况下,才会考虑升层。
而升层的次数等于rnd倒数第二位开始的1的位数。
int rnd = ThreadLocalRandom.nextSecondarySeed(); if ((rnd & 0x80000001) == 0) { // test highest and lowest bits int level = 1, max; while (((rnd >>>= 1) & 1) != 0) ++level; ... }
5.ZSET与SkipList
Redis提供的五种数据结构之一的ZSET(有序集合),其底层由跳表实现(zskiplist)
server.h(Redis由C语言实现)
#define ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL 64 /* Should be enough for 2^64 elements */ #define ZSKIPLIST_P 0.25 /* Skiplist P = 1/4 */ /* ZSETs use a specialized version of Skiplists */ typedef struct zskiplistNode { sds ele; double score; struct zskiplistNode *backward; struct zskiplistLevel { struct zskiplistNode *forward; unsigned long span; } level[]; } zskiplistNode; typedef struct zskiplist { struct zskiplistNode *header, *tail; unsigned long length; int level; } zskiplist; typedef struct zset { dict *dict; zskiplist *zsl; } zset;
zskiplist是限高的,其随机升层的策略如下
/* Returns a random level for the new skiplist node we are going to create. * The return value of this function is between 1 and ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL * (both inclusive), with a powerlaw-alike distribution where higher * levels are less likely to be returned. */ int zslRandomLevel(void) { int level = 1; while ((random()&0xFFFF) < (ZSKIPLIST_P * 0xFFFF)) level += 1; return (level<ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL) ? level : ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL; }
参考资料:《数据结构与算法分析(C++语言版)第3版》 邓俊辉
Java并发集合(二)-ConcurrentSkipListMap分析和使用
