(我永远喜欢floyd)
温馨提示:与SPFA一起食用效果更佳
传送门:https://www.cnblogs.com/Daz-Os0619/p/11388157.html
Floyd
大概思路:
对于某两个点来说,查找他们之间是否连通,若连通,是记录他们间的最短路。
这里的最短路有两个方向:一个是直接到,一个是通过另外一个点到。(十分单纯的最短路了)
不需要多讲上代码!
void floyd() { for (int k = 1; k <= n; ++k) for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) for (int j = 1; j <= n; ++j) dis[i][j] = min(dis[i][j], dis[i][k] + dis[k][j]); }
Dijkstra
大概思路:
(跟SPFA差不多??)
有一个集合P,一开始只有源点S在P中,每次更新都把集合之外路径值最小的一个放入集合中,更新与它相连的点,重复前面的操作直到集合外没有元素。
特殊要求:所有边权要是正的
这时的时间复杂度为O(n*n) (比较危险)
可以采用堆来优化 时间复杂度O(n*logn)
(蒟蒻发言:怎么用堆优化?)
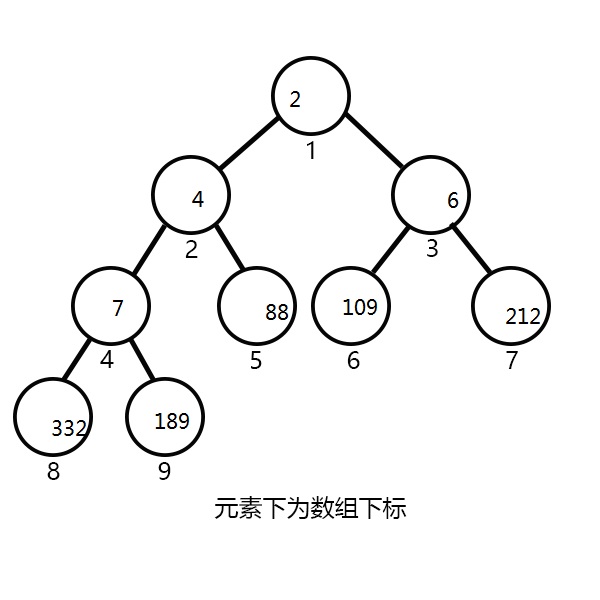
堆
一颗完全二叉树。
这里用到的小根堆是最小值作为堆顶元素,大根堆反之。
大概长下面这样:
利用小根堆优化Dijkstra的理由与用SLF优化SPFA的理由相同,核心思想也相近,但是写法差异很大。
核心思想:因为每一次都会从队首开始遍历,当队首是最小值时,被更新的所以节点的值也会是最小值,这样可以节省很大一部分时间。
(这里就体现优先队列的好处)
下面是核心代码(可以先看注释,后面有图解):
struct edges { int next, to, v; edges() {} edges(int _n, int _t, int _v) : next(_n), to(_t), v(_v) {}//next表示与这条边同起点的上一条边 } e[]; struct heap_node { int v, to; heap_node() {} heap_node(int _v, int _to) : v(_v), to(_to) {} }; inline bool operator < (const heap_node &a, const heap_node &b) { return a.v > b.v; //这里实现的是小根堆,如果要大根堆,把 > 改成 < 即可 } priority_queue <heap_node> h; inline void add_to_heap(const int p) { for (int x = first[p]; x; x = e[x].next)//first表示以first为头的最后一条边 if (dis[e[x].to] == -1)//如果下一条边还没在堆里 h.push(heap_node(e[x].v + dis[p], e[x].to));//加上前一个点的最短路值(跟新),放入堆 } void Dijkstra(int S) { memset(dis, -1, sizeof(dis));//清空(便于将数据放入堆里) while (!h.empty()) h.pop();//清空堆 dis[S] = 0, add_to_heap(S);//现将所有与源点相连的点放入堆中 int p; while (!h.empty()) { //堆空时所有的点都更新完毕(与SPFA相反) if (dis[h.top().to] != -1)//如果与堆顶元素相连的点已经有了最短路值 { h.pop();//弹掉堆顶 (此时堆顶不会被更新了) continue;//一直找到可以被更新的点 } p = h.top().to;//找到与堆顶相连且不在堆里的点 dis[p] = h.top().v;//更新最短路值(只是堆顶的) h.pop();//弹掉 add_to_heap(p);//再更新与它相连的点,并将与它相连的点放入堆 } }
好长的注释啊。。
再画个图解释一下
(这里的样例和SPFA的样例一样)
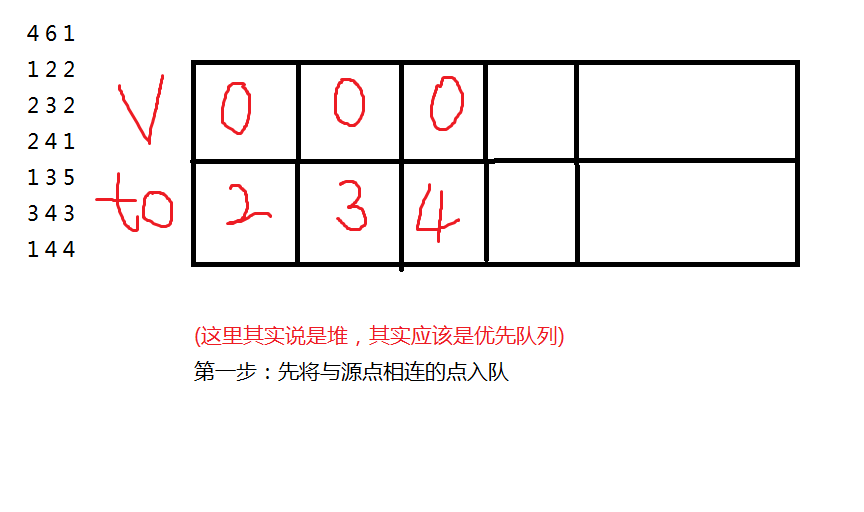
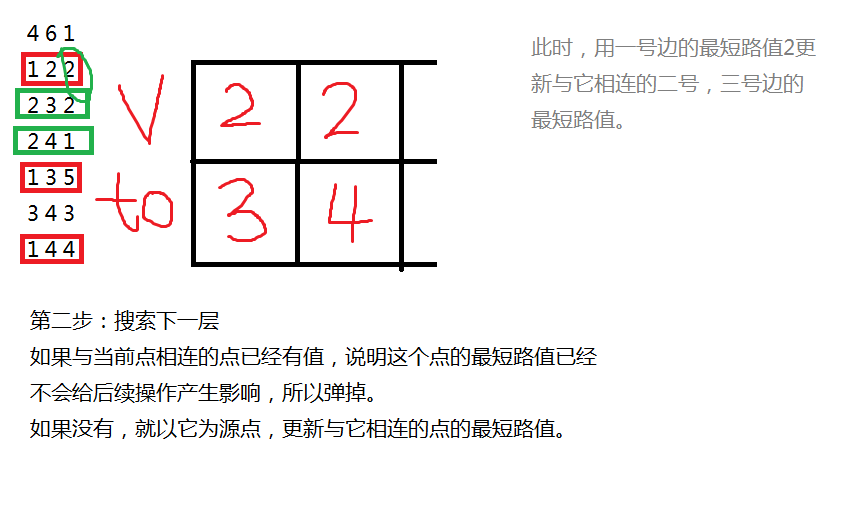

后面就这样一直循环直到队列为空。为空时所有最短路更新完毕。
完整代码:
#include<iostream> #include<vector> #include<queue> #include<cstring> #include<cstdio> using namespace std; struct edge { int next,to,v; edge(){} edge(int a,int b,int c) { next=a; to=b; v=c; } }E[10001]; int first[10001],n,dis[100001]; int S; struct heap { int to,v; heap(){} heap(int a,int b) { to=a; v=b; } }; inline bool operator< (const heap &a,const heap &b) { return a.v>b.v; } priority_queue<heap> h; void add_to_heap(int p) { for(int i=first[p];i;i=E[i].next) { if(dis[E[i].to]==-1) h.push(heap(E[i].to,dis[p]+E[i].v)); } } int tot; void add_edges(int a,int b,int c) { E[++tot]=edge(first[a],b,c); first[a]=tot; } void dijkstra(int S) { while(!h.empty()) h.pop(); memset(dis,-1,sizeof(dis)); dis[S]=0; add_to_heap(S); int p; while(!h.empty()) { if(dis[h.top().to]!=-1) { h.pop(); continue; } p=h.top().to; dis[p]=h.top().v; h.pop(); add_to_heap(p); } } int m; int main() { cin>>n>>m>>S; int A,B,C; for(int i=1;i<=m;i++) { cin>>A>>B>>C; add_edges(A,B,C); } dijkstra(S); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) cout<<dis[i]<<endl; return 0; }
结束!
今天也想放烟花!