主要属性
private final long totalMemory;//最大缓存空间 , 由配置文件指定
private final int poolableSize;//每个池的缓存空间大小
private final ReentrantLock lock; //重入锁
private final Deque<ByteBuffer> free; //空闲的ByteBuffer
private final Deque<Condition> waiters; //等待分配空间的线程
/** Total available memory is the sum of nonPooledAvailableMemory and the number of byte buffers in free * poolableSize. */
private long nonPooledAvailableMemory; //ByteBuffer之外的缓冲区,设计为了适应突然的大数据量
//构造方法
public BufferPool(long memory, int poolableSize, Metrics metrics, Time time, String metricGrpName) {
this.poolableSize = poolableSize; //指定的 poolableSize
this.lock = new ReentrantLock();//初始化 ReentrantLock 锁
this.free = new ArrayDeque<>(); //初始化一个 空(empty)的Array队列,存储内存
this.waiters = new ArrayDeque<>(); //初始化一个空(empty)的array队列,存储等待线程
this.totalMemory = memory;//总的内存
this.nonPooledAvailableMemory = memory;//默认的池外内存,就是总的内存
//下面是一些数据统计,不做分析
this.metrics = metrics;
this.time = time;
this.waitTime = this.metrics.sensor(WAIT_TIME_SENSOR_NAME);
MetricName rateMetricName = metrics.metricName("bufferpool-wait-ratio",
metricGrpName,
"The fraction of time an appender waits for space allocation.");
MetricName totalMetricName = metrics.metricName("bufferpool-wait-time-total",
metricGrpName,
"The total time an appender waits for space allocation.");
this.waitTime.add(new Meter(TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS, rateMetricName, totalMetricName));
}
allocate 方法
org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.internals.BufferPool#allocate
/**
* Allocate a buffer of the given size. This method blocks if there is not enough memory and the buffer pool
* is configured with blocking mode.
分配指定空间的缓存, 如果缓冲区中没有足够的空闲空间,那么会阻塞线程,
直到超时或得到足够空间
*
* @param size The buffer size to allocate in bytes ,要获取的指定大小空间
* @param maxTimeToBlockMs The maximum time in milliseconds to block for buffer memory to be available , 最大等待时长
* @return The buffer
* @throws InterruptedException If the thread is interrupted while blocked
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if size is larger than the total memory controlled by the pool (and hence we would block
* forever)
*/
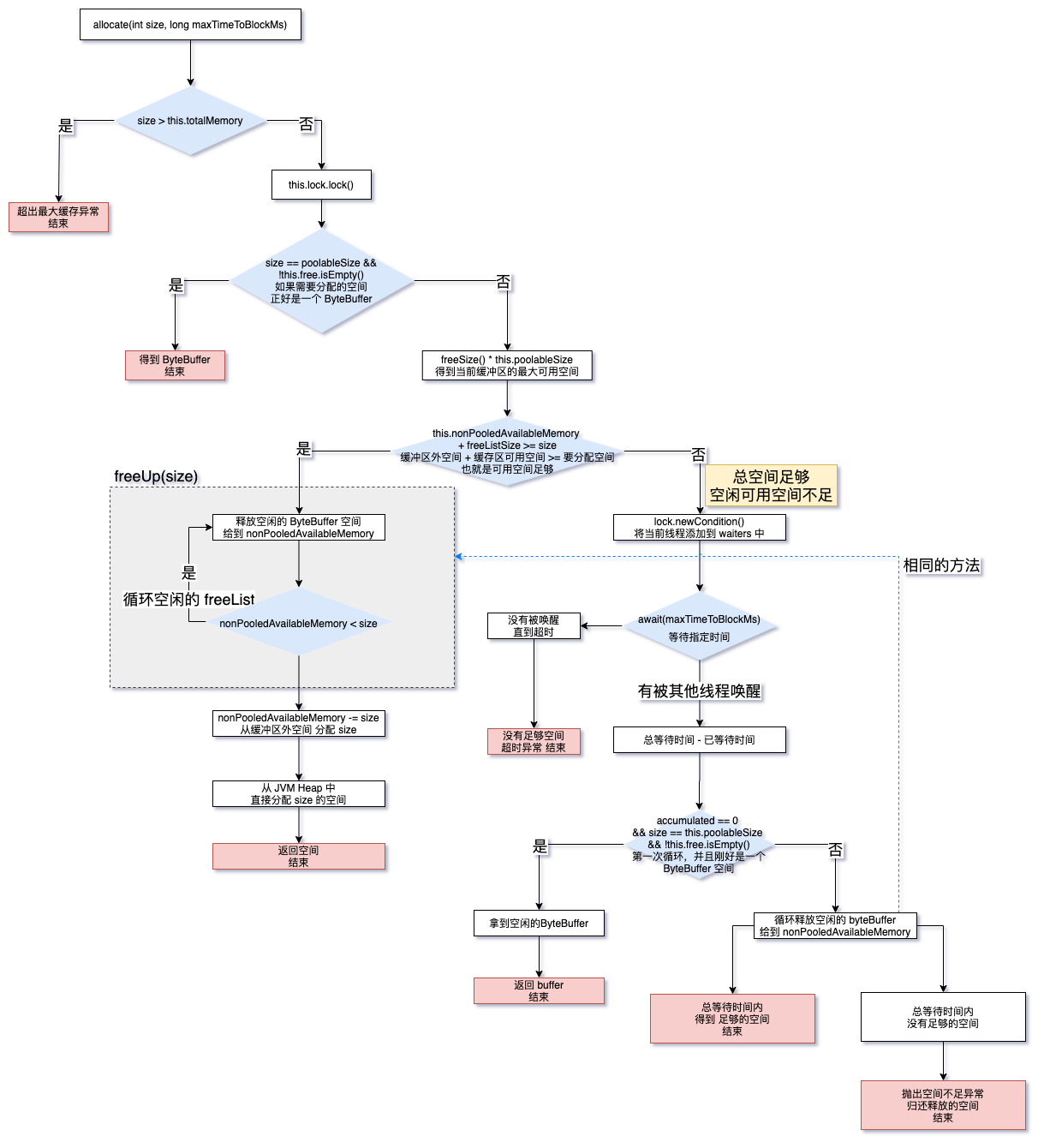
public ByteBuffer allocate(int size, long maxTimeToBlockMs) throws InterruptedException {
//大于总缓冲区空间,抛出异常
if (size > this.totalMemory)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Attempt to allocate " + size
+ " bytes, but there is a hard limit of "
+ this.totalMemory
+ " on memory allocations.");
ByteBuffer buffer = null;
//会有线程争抢,所以需要锁
this.lock.lock();
try {
// check if we have a free buffer of the right size pooled
// 如果有空间大小正合适的空闲buffer, 走到获取并返回
if (size == poolableSize && !this.free.isEmpty())
return this.free.pollFirst();
// now check if the request is immediately satisfiable with the
// memory on hand or if we need to block
// 判断是否有足够的空闲的内存
int freeListSize = freeSize() * this.poolableSize;
if (this.nonPooledAvailableMemory + freeListSize >= size) {
// we have enough unallocated or pooled memory to immediately
// 有足够的,未分配的空闲内存
// satisfy the request, but need to allocate the buffer
// 需要整理到一个buffer外空间中,从JVM Heap 中分配内存
freeUp(size); // 循环释放 空闲的 buffer
this.nonPooledAvailableMemory -= size;
} else {
// we are out of memory and will have to block
// 没有足够空闲的 内存或 buffer
int accumulated = 0; //累计已经释放的内存
//阻塞自己,等待别的线程释放内存
Condition moreMemory = this.lock.newCondition();
try {
long remainingTimeToBlockNs = TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.toNanos(maxTimeToBlockMs);
//把自己添加到等待队列中
this.waiters.addLast(moreMemory);
// loop over and over until we have a buffer or have reserved
// 循环 直到有足够空闲,或超时
// enough memory to allocate one
while (accumulated < size) { // 已释放内存 < 要获取的内存 (释放的还不够)
//计时
long startWaitNs = time.nanoseconds();
long timeNs;
boolean waitingTimeElapsed;
try {
waitingTimeElapsed = !moreMemory.await(remainingTimeToBlockNs, TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS);
} finally {
//还没到最大时长,被唤醒了。更新下已经等待的时长
long endWaitNs = time.nanoseconds();
timeNs = Math.max(0L, endWaitNs - startWaitNs);
recordWaitTime(timeNs);
}
if (waitingTimeElapsed) {
//等待超时了 , 不等了。抛出异常,结束
throw new TimeoutException("Failed to allocate memory within the configured max blocking time " + maxTimeToBlockMs + " ms.");
}
remainingTimeToBlockNs -= timeNs;
// check if we can satisfy this request from the free list,
// otherwise allocate memory
// 是否有释放的刚好足够的空间,否则的话,还得再调整空间
if (accumulated == 0 && size == this.poolableSize && !this.free.isEmpty()) {
// just grab a buffer from the free list
// 有,直接取一个byteBuffer ,返回 , 结束
buffer = this.free.pollFirst();
accumulated = size;
} else {
// we'll need to allocate memory, but we may only get
// part of what we need on this iteration
// 没有足够空闲的,需要调整分配空间 , 如果分配多了,那么只需要得到 足够size的空间
// 例如: 需要 50 ,释放出来了 80 ,那么只取 其中的 50 。
freeUp(size - accumulated);
int got = (int) Math.min(size - accumulated, this.nonPooledAvailableMemory);
this.nonPooledAvailableMemory -= got;
accumulated += got;
}
}
// Don't reclaim memory on throwable since nothing was thrown
accumulated = 0;
} finally {
// When this loop was not able to successfully terminate don't loose available memory
// 在循环的过程中,有异常了。 那么已经释放出来的空间,再还回去。
this.nonPooledAvailableMemory += accumulated;
//把自己从等待队列中移除 , 并结束
this.waiters.remove(moreMemory);
}
}
} finally {
// signal any additional waiters if there is more memory left
// over for them
// 后续处理 , 这里不管分配空间是成功还是失败,都会执行
try {
//三个条件
// this.nonPooledAvailableMemory == 0 && this.free.isEmpty() : 池外内存为0 ,并且空闲的byteBuffer 没有了。
// 取反,就是 nonPooledAvailableMemory > 0 || this.free.isNotEmpty() : 池外有内存,或 有空闲的 ByteBuffer
// !this.waiters.isEmpty() : 等待队列里有线程正在等待
if (!(this.nonPooledAvailableMemory == 0 && this.free.isEmpty()) && !this.waiters.isEmpty())
//唤醒队列里正在等待的线程
this.waiters.peekFirst().signal();
} finally {
// Another finally... otherwise find bugs complains
// 最后的最后,一定得解锁。否则就是BUG了
lock.unlock();
}
}
//到这里,说明空间足够,并且有足够空闲的了。可以执行真正的分配空间了。
if (buffer == null)
//没有正好的 buffer,从缓冲区外(JVM Heap)中直接分配内存
return safeAllocateByteBuffer(size);
else
// 有正好的 buffer,返回buffer
return buffer;
}
/**
* Allocate a buffer. If buffer allocation fails (e.g. because of OOM) then return the size count back to
* available memory and signal the next waiter if it exists.
*/
private ByteBuffer safeAllocateByteBuffer(int size) {
boolean error = true;
try {
//分配空间
ByteBuffer buffer = allocateByteBuffer(size);
error = false;
//返回buffer
return buffer;
} finally {
if (error) {
//分配失败了, 加锁,操作内存pool
this.lock.lock();
try {
//归还空间给 池外内存
this.nonPooledAvailableMemory += size;
if (!this.waiters.isEmpty())
//有其他在等待的线程的话,唤醒其他线程
this.waiters.peekFirst().signal();
} finally {
// 加锁不忘解锁
this.lock.unlock();
}
}
}
}
// Protected for testing.
protected ByteBuffer allocateByteBuffer(int size) {
// 从JVM Heap 中分配空间,并得到持有空间的ByteBuffer对象
return ByteBuffer.allocate(size);
}
/**
* Attempt to ensure we have at least the requested number of bytes of memory for allocation by deallocating pooled
* buffers (if needed)
*/
private void freeUp(int size) {
while (!this.free.isEmpty() && this.nonPooledAvailableMemory < size)
//循环把 free 里的 byteBuffer 全捞出来,给 nonPooledAvailableMemory
this.nonPooledAvailableMemory += this.free.pollLast().capacity();
}
deallocate
org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.internals.BufferPool#deallocate(ByteBuffer, int)
/**
* Return buffers to the pool. If they are of the poolable size add them to the free list, otherwise just mark the
* memory as free.
* 归还 buffer 到 pool 里,即 buffer放回到 free 队列中。
* 其他的直接标记为 空闲内存就可以了
* @param buffer The buffer to return
* @param size The size of the buffer to mark as deallocated, note that this may be smaller than buffer.capacity
* since the buffer may re-allocate itself during in-place compression
*/
public void deallocate(ByteBuffer buffer, int size) {
//照例先加锁
lock.lock();
try {
if (size == this.poolableSize && size == buffer.capacity()) {
//如果是完整的buffer,放回到队列里
buffer.clear();
this.free.add(buffer);
} else {
//不是完整的buffer,标记为空闲内存就可以了。
this.nonPooledAvailableMemory += size;
}
//如果有内存的线程,唤醒线程
Condition moreMem = this.waiters.peekFirst();
if (moreMem != null)
moreMem.signal();
} finally {
//解锁
lock.unlock();
}
}
主要逻辑:
- 如果 size == poolableSize , 就放到 free 中
- 如果 size != poolableSize , 归还到 nonPooledAvailableMemory 中. buffer 对象没有引用。等待GC释放
- 有等待线程的话,唤醒线程
free 分析
free 的生产和归还
free 对象的使用有点绕,在初始化时,是一个空的Array队列。 allocate() 方法是从 free 中取 buffer 或 释放 buffer , deallocate() 是归还 buffer 到 free 中。
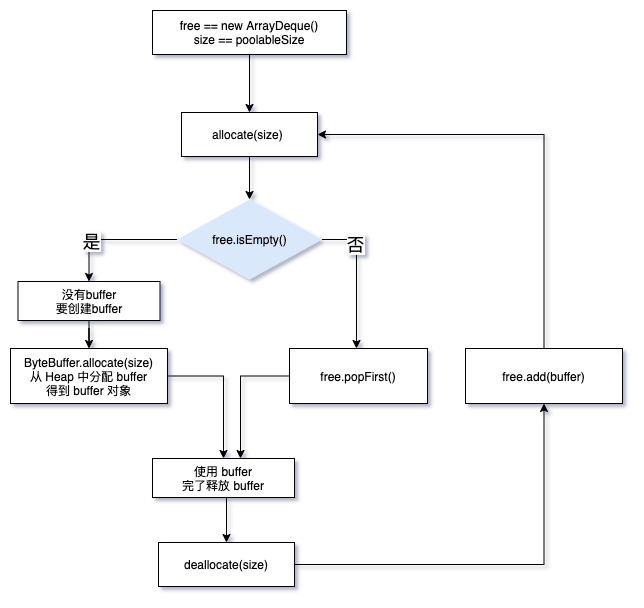
- 当 free 空时,从 allocate() 中生产 buffer 对象
- deallocate() 方法将 buffer 放到 free 中
free 为什么是双向队列
- 获取 buffer 是从一头取
- freeUp() 方法释放 buffer 是从另一头
理论上 allocate() 方法是单线程访问。怕是以防万一吧,一边获取一边释放。
free的最大化使用
// RecordAccumulator 的 this.batchSize == BufferPool.poolableSize
int size = Math.max(this.batchSize, AbstractRecords.estimateSizeInBytesUpperBound(maxUsableMagic, compression, key, value, headers));
buffer = bufferPool.allocate(size, maxTimeToBlock);
在传入的参数中,在 size 和 poolableSize 中 , 取最大值。
- <= poolableSize的,可以直接使用一个ByteBuffer。
-
poolableSize 的,就需要开新的内存了。
所以,对于内存来说,poolableSize的大小设置很重要。尽可能的重复利用 缓存 byteBuffer
经验之谈的话,大概取 80% 左右的比例。最大有 100 的数据,那么poolableSize 设置为 80 。当然还要具体情况具体分析。
总结
- 共享变量的使用:
- Lock 锁
- 先进先出(FIFO)
- 队列
如果文章有帮助到您,请点个赞,您的反馈会让我感到文章是有价值的