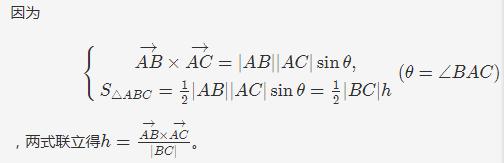凸包和旋转卡壳
(1)极角排序的实现方法
四种方法:http://www.cnblogs.com/devtang/archive/2012/02/01/2334977.html
- 注意输入方式,0、1起始,以及原点的选择(最左下的点 或 输入的第一个点)。
struct point{ int x,y; }a[1019]; int cross(point p0,point p1,point p2) //计算向量叉积 { return (p1.x-p0.x)*(p2.y-p0.y)-(p1.y-p0.y)*(p2.x-p0.x); } double dis(point p1,point p2) //计算点p1p2的距离 { return sqrt((double)(p2.x-p1.x)*(p2.x-p1.x)+(p2.y-p1.y)*(p2.y-p1.y)); } bool cmp(point p1,point p2){ //进行极角排序 int tmp=cross(a[0],p1,p2); if(tmp>0) return true; else if(tmp==0&&dis(a[0],p1)<dis(a[0],p2)) return true; else return false; } //↑↑若角度相同,则距离小的在前面 ... sort(a+1,a+n,cmp); //除去0号点,其余n-1个点进行极角排序

#include <cmath> #include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <string> #include <cstring> #include <vector> #include <algorithm> #include <stack> #include <queue> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; typedef unsigned long long ull; /*【poj2007】【模板】极角排序 */ struct point{ int x,y; }a[1019]; int n; int sta[1019],top; int cross(point p0,point p1,point p2) //计算向量叉积 { return (p1.x-p0.x)*(p2.y-p0.y)-(p1.y-p0.y)*(p2.x-p0.x); } double dis(point p1,point p2) //计算点p1p2的距离 { return sqrt((double)(p2.x-p1.x)*(p2.x-p1.x)+(p2.y-p1.y)*(p2.y-p1.y)); } bool cmp(point p1,point p2){ //进行极角排序 int tmp=cross(a[0],p1,p2); if(tmp>0) return true; else if(tmp==0&&dis(a[0],p1)<dis(a[0],p2)) return true; else return false; //↑↑若角度相同,则距离小的在前面 } void init(){ //输入,并把最左下方的点放在a[0],进行极角排序。 point p0; scanf("%d%d",&a[0].x,&a[0].y); p0.x=a[0].x; p0.y=a[0].y; int k=0; n=1; while(scanf("%d%d",&a[n].x,&a[n].y)!=EOF) n++; /* for(int i=1;i<n;i++){ //一共是0~n-1,n个点 if( (p0.y>a[i].y) || ((p0.y==a[i].y)&&(p0.x>a[i].x)) ) p0.x=a[i].x,p0.y=a[i].y,k=i; //寻找左下角的点 } a[k]=a[0],a[0]=p0; //把原来0位置的点放到k位置(互换位置) */ //↑↑此题中把第一个输入的点作为原点,不需要找左下角的点 sort(a+1,a+n,cmp); //除去0号点,其余n-1个点进行极角排序 } /* void graham(int n){ //极角排序法求凸包 if(n==1) top=0,sta[0]=0; if(n==2) top=1,sta[0]=0,sta[1]=1; if(n>2){ top=1,sta[0]=0,sta[1]=1; for(int i=2;i<n;i++){ while(top>0&&cross(a[sta[top-1]],a[sta[top]],a[i])<=0) top--; top++; sta[top]=i; } } //每加入新的点,判断要出栈的凹点,并将新点入栈 } */ int main(){ init(); for(int i=0;i<n;i++) cout<<"("<<a[i].x<<","<<a[i].y<<")"<<endl; }
(2)极角序 / 水平序 求凸包
推荐阅读:wjyyy 话说我坠爱 jyy了qwq
凸包:周长min的、能包围所有给定点的多边形。
通常有极角序、水平序两种求法,都是先排序之后,维护栈。
极角序是在每次新加节点时删去凹的点:
int sta[1019],top; //用栈实现‘凹’性质的判定 void graham(int n){ //极角排序法求凸包 if(n==1) top=0,sta[0]=0; if(n==2) top=1,sta[0]=0,sta[1]=1; if(n>2){ top=1,sta[0]=0,sta[1]=1; for(int i=2;i<n;i++){ while(top>0&&cross(a[sta[top-1]],a[sta[top]],a[i])<=0) top--; top++; sta[top]=i; } //每加入新的点,判断要出栈的凹点,并将新点入栈 } } ... init(n); graham(n); //输入+极角排序+求凸包 //sta[]中存着凸包相关点的编号,用a[sta[?]]来调用
水平序是正着扫求出下凸壳,再倒着扫求出上凸壳:
ll cmp(const point &a,const point &b) { if(a.x==b.x) return a.y<b.y; return a.x<b.x; } ll cross(point a,point b){ return a.x*b.y-a.y*b.x; } void graham(ll n){ sort(a+1,a+n+1,cmp); //点按照x、y大小排序 for(ll i=1;i<=n;i++){ while(top>=2&&cross(a[i]-sta[top-1],sta[top]-sta[top-1])>=0) top--; sta[++top]=a[i]; } for(ll i=n-1,la=top;i>=1;i--){ while(top>la&&cross(a[i]-sta[top-1],sta[top]-sta[top-1])>=0) top--; sta[++top]=a[i]; } top--; return; }

#include <cmath> #include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <string> #include <cstring> #include <vector> #include <algorithm> #include <stack> #include <queue> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; typedef unsigned long long ull; /*【p2742】模板·凸包 */ struct point{ double x,y; }a[10019]; int sta[10019],top,n; double ans=0.0; double cross(point p0,point p1,point p2) //计算向量叉积 { return (p1.x-p0.x)*(p2.y-p0.y)-(p1.y-p0.y)*(p2.x-p0.x); } double dis(point p1,point p2) //计算点p1p2的距离 { return sqrt((double)(p2.x-p1.x)*(p2.x-p1.x)+(p2.y-p1.y)*(p2.y-p1.y)); } bool cmp(point p1,point p2){ //进行极角排序 double tmp=cross(a[0],p1,p2); if(tmp>0) return true; else if(tmp==0&&dis(a[0],p1)<dis(a[0],p2)) return true; else return false; //↑↑若角度相同,则距离小的在前面 } void init(){ //输入,并把最左下方的点放在a[0],进行极角排序。 point p0; scanf("%lf%lf",&a[0].x,&a[0].y); p0.x=a[0].x; p0.y=a[0].y; int k=0; for(int i=1;i<n;i++){ scanf("%lf%lf",&a[i].x,&a[i].y); if( (p0.y>a[i].y) || ((p0.y==a[i].y)&&(p0.x>a[i].x)) ) p0.x=a[i].x,p0.y=a[i].y,k=i; //寻找左下角的点 } a[k]=a[0],a[0]=p0; //把原来0位置的点放到k位置(互换位置) sort(a+1,a+n,cmp); //除去0号点,其余n-1个点进行极角排序 } void graham(){ //极角排序法求凸包 if(n==1) top=0,sta[0]=0; if(n==2) top=1,sta[0]=0,sta[1]=1; if(n>2){ top=1,sta[0]=0,sta[1]=1; for(int i=2;i<n;i++){ while(top>0&&cross(a[sta[top-1]],a[sta[top]],a[i])<=0) top--; top++; sta[top]=i; } //每加入新的点,判断要出栈的凹点,并将新点入栈 } } int main(){ scanf("%d",&n); init(); graham(); //输入+极角排序+求凸包 for(int i=0;i<top;i++) ans+=dis(a[sta[i]],a[sta[i+1]]); ans+=dis(a[sta[0]],a[sta[top]]); printf("%.2lf ",ans); //凸包总周长 }

#include <cmath> #include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <string> #include <cstring> #include <vector> #include <algorithm> #include <stack> #include <queue> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; typedef unsigned long long ull; /*【poj1113】wall 已知n个点的坐标,建一个环形围墙包住所有点。 使围墙距所有点的距离>=l,求围墙min周长。*/ //经过拐点时是圆弧。走一圈所形成的扇形的内角和是360度,故一个完整的圆。 //故答案为:凸包周长+一个完整的圆周长(2*pi*l)。 const double PI=acos(-1.0); struct point{ int x,y; }a[1019]; int sta[1019],top; int cross(point p0,point p1,point p2) //计算向量叉积 { return (p1.x-p0.x)*(p2.y-p0.y)-(p1.y-p0.y)*(p2.x-p0.x); } double dis(point p1,point p2) //计算点p1p2的距离 { return sqrt((double)(p2.x-p1.x)*(p2.x-p1.x)+(p2.y-p1.y)*(p2.y-p1.y)); } bool cmp(point p1,point p2){ //进行极角排序 int tmp=cross(a[0],p1,p2); if(tmp>0) return true; else if(tmp==0&&dis(a[0],p1)<dis(a[0],p2)) return true; else return false; //↑↑若角度相同,则距离小的在前面 } void init(int n){ //输入,并把最左下方的点放在a[0],进行极角排序。 point p0; scanf("%d%d",&a[0].x,&a[0].y); p0.x=a[0].x; p0.y=a[0].y; int k=0; for(int i=1;i<n;i++){ scanf("%d%d",&a[i].x,&a[i].y); if( (p0.y>a[i].y) || ((p0.y==a[i].y)&&(p0.x>a[i].x)) ) p0.x=a[i].x,p0.y=a[i].y,k=i; //寻找左下角的点 } a[k]=a[0],a[0]=p0; //把原来0位置的点放到k位置(互换位置) sort(a+1,a+n,cmp); //除去0号点,其余n-1个点进行极角排序 } void graham(int n){ //极角排序法求凸包 if(n==1) top=0,sta[0]=0; if(n==2) top=1,sta[0]=0,sta[1]=1; if(n>2){ top=1,sta[0]=0,sta[1]=1; for(int i=2;i<n;i++){ while(top>0&&cross(a[sta[top-1]],a[sta[top]],a[i])<=0) top--; top++; sta[top]=i; } //每加入新的点,判断要出栈的凹点,并将新点入栈 } } int main(){ int N,L; while(scanf("%d%d",&N,&L)!=EOF){ init(N); graham(N); //输入+极角排序+求凸包 double ans=0; ans+=2*PI*L; for(int i=0;i<top;i++) //求凸包总周长 ans+=dis(a[sta[i]],a[sta[i+1]]); ans+=dis(a[sta[0]],a[sta[top]]); printf("%d ",(int)(ans+0.5)); //四舍五入 } }

#include <cmath> #include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <string> #include <cstring> #include <vector> #include <algorithm> #include <stack> #include <queue> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; typedef unsigned long long ull; /*【uva11626】Convex Hull 给你n个点的集合,并且用’N’或’Y’表示该点是否在凸包的边界上, 按逆时针顺序输出凸包,且第一个输出的点必须是x坐标和y坐标最小的. */ //凸包最大点集:各种神奇的排序方法 const int N=100019; struct point{ int x,y; }a[N]; int m; long long cross(point a,point b,point c) { return (c.x-a.x)*(b.y-a.y)-(b.x-a.x)*(c.y-a.y); } long long dis(point a,point b) { return (a.x-b.x)*(a.x-b.x)+(a.y-b.y)*(a.y-b.y); } bool cmp1(point aa,point bb){ long long len=cross(a[0],aa,bb); if(len==0) return dis(a[0],aa)<dis(a[0],bb); return len<0; } bool cmp2(point aa,point bb){ long long len=cross(a[0],aa,bb); if(len==0) return dis(a[0],aa)>dis(a[0],bb); return len<0; } void output(point *p,int n){ for(int i=0;i<n;i++) printf("%d %d ",p[i].x,p[i].y); } void solve(){ int tmp=0; for(int i=1;i<m;i++) //找左下角的点 if(a[i].x<a[tmp].x||a[i].x==a[tmp].x&&a[i].y<a[tmp].y) tmp=i; swap(a[0],a[tmp]); point L[N],U[N]; int l=0,u=0; for(int i=1;i<m;i++) if(a[i].y<=a[0].y) L[l++]=a[i]; else U[u++]=a[i]; sort(L,L+l,cmp1); sort(U,U+u,cmp2); printf("%d ",m); printf("%d %d ",a[0].x,a[0].y); output(L,l); output(U,u); } int main(){ int T,n,x,y; char ch[19]; scanf("%d",&T); while(T--){ scanf("%d",&n); m=0; for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ scanf("%d%d%s",&x,&y,ch); if(ch[0]=='Y') a[m].x=x,a[m++].y=y; } solve(); //按逆时针顺序输出凸包 } }

#include <cmath> #include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <string> #include <cstring> #include <vector> #include <algorithm> #include <stack> #include <queue> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; typedef unsigned long long ull; /*【bzoj2564】集合的面积 */ //题目大意可见:https://www.cnblogs.com/wfj2048/a/7470202.html void reads(ll &x){ x=0;int fx=1;char ch=getchar(); while(ch>'9'||ch<'0'){if(ch=='-')fx=-1;ch=getchar();} while(ch<='9'&&ch>='0'){x=(x<<3)+(x<<1)+ch-'0';ch=getchar();} x=x*fx; //正负号 } const int N=500019; struct point{ ll x,y; point operator + (const point &a) const { return (point){x+a.x,y+a.y}; } point operator - (const point &a) const { return (point){x-a.x,y-a.y}; } }a[N],t1[N],t2[N],sta[N]; ll n,m,top,S; //S存答案,即最终的凸包面积 ll cmp(const point &a,const point &b) { if(a.x==b.x) return a.y<b.y; return a.x<b.x; } ll cross(point a,point b){ return a.x*b.y-a.y*b.x; } void graham(point *a,point *t,ll n){ sort(a+1,a+n+1,cmp); //点按照x、y大小排序 for(ll i=1;i<=n;i++){ while(top>=2&&cross(a[i]-t[top-1],t[top]-t[top-1])>=0) top--; t[++top]=a[i]; } for(ll i=n-1,la=top;i>=1;i--){ while(top>la&&cross(a[i]-t[top-1],t[top]-t[top-1])>=0) top--; t[++top]=a[i]; } top--; return; } int main(){ reads(n),reads(m); for(ll i=1;i<=n;i++) reads(a[i].x),reads(a[i].y); graham(a,t1,n),n=top,top=0; //集合1的凸包 for(ll i=1;i<=m;i++) reads(a[i].x),reads(a[i].y); graham(a,t2,m),m=top,top=0; //集合2的凸包 sta[top=1]=t1[1]+t2[1]; //两凸包第一个点的和肯定会在最终的凸包里 for(ll i=1,j=1;i<=n||j<=m;){ //A凸包到了i点,B凸包到了j点,每次选择i、j更新 point x=t1[(i-1)%n+1]+t2[j%m+1],y=t1[i%n+1]+t2[(j-1)%m+1]; if(cross(x-sta[top],y-sta[top])>=0) sta[++top]=x,j++; //与下同 else sta[++top]=y,i++; //a[i+1]+b[j]比a[i]+b[j+1]更凸,选A凸包更新。 } for(ll i=2;i<top;i++) S+=cross(sta[i]-sta[1],sta[i+1]-sta[1]); cout<<S<<endl; return 0; //叉积求凸包面积 }

#include <cmath> #include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <string> #include <cstring> #include <vector> #include <algorithm> #include <stack> #include <queue> #include <iomanip> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; typedef unsigned long long ull; /*【p3829】信用卡凸包 分析题目可知,答案为‘圆滑处理’圆心围成的凸包+一个圆周的长度。*/ //注意:题目有旋转操作(rotate)、long double的运用细节、结构体的储存、 // sinl&cosl函数的运用、graham函数中sta存储的(编号or坐标值)、凸包周长计算。 const long double Pi=acosl(-1.0); struct Point{ //坐标结构体 long double x,y; Point() { } //坐标转化为()形式表示 Point(long double __x, long double __y) : x(__x), y(__y) { } inline Point operator + (const Point &rhs) const { return Point(x+rhs.x,y+rhs.y); } inline Point operator - (const Point &rhs) const { return Point(x-rhs.x,y-rhs.y); } inline Point rotate(long double theta){ //角度旋转操作 const long double Sin=sinl(theta),Cos=cosl(theta); return Point(x*Cos-y*Sin,x*Sin+y*Cos); } //旋转之后的坐标 }a[50019],O; int sta[50019],top,n,tot=0; long double A,B,R,ans; long double cross(Point p0,Point p1,Point p2) //计算向量叉积 { return (p1.x-p0.x)*(p2.y-p0.y)-(p1.y-p0.y)*(p2.x-p0.x); } long double dis(Point p1,Point p2) //计算点p1p2的距离 { return sqrt((long double)(p2.x-p1.x)*(p2.x-p1.x)+(p2.y-p1.y)*(p2.y-p1.y)); } bool cmp(Point p1,Point p2){ //进行极角排序 long double tmp=cross(a[0],p1,p2); if(tmp>0) return true; else if(tmp==0&&dis(a[0],p1)<dis(a[0],p2)) return true; else return false; } //↑↑若角度相同,则距离小的在前面 void init(){ //把最左下方的点放在a[0],进行极角排序。 Point p0; p0.x=a[0].x; p0.y=a[0].y; int k=0; for(int i=1;i<tot;i++){ if( (p0.y>a[i].y) || ((p0.y==a[i].y)&&(p0.x>a[i].x)) ) p0.x=a[i].x,p0.y=a[i].y,k=i; //寻找左下角的点 } a[k]=a[0],a[0]=p0; //把原来0位置的点放到k位置(互换位置) sort(a+1,a+tot,cmp); } //除去0号点,其余n-1个点进行极角排序 void graham(){ //极角排序法求凸包 if(tot==1) top=0,sta[0]=0; if(tot==2) top=1,sta[0]=0,sta[1]=1; if(tot>2){ top=1,sta[0]=0,sta[1]=1; for(int i=2;i<tot;i++){ while(top>0&&cross(a[sta[top-1]],a[sta[top]],a[i])<=0) top--; top++; sta[top]=i; } //每加入新的点,判断要出栈的凹点,并将新点入栈 } } int main(){ cin>>n>>A>>B>>R; ans=(long double)2*R*Pi; //初始为一个圆周长度 A/=2,B/=2,A-=R,B-=R; //此时A、B为中心与圆心的相距(A,B) for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ static long double x,y,theta; cin>>x>>y>>theta; Point t1=Point(B,A).rotate(theta),t2=Point(B,-A).rotate(theta); O.x=x,O.y=y; a[tot++]=O-t1,a[tot++]=O+t1,a[tot++]=O-t2,a[tot++]=O+t2; //四个圆心的坐标 } init(),graham(); //极角排序求凸包,求凸包总周长 for(int i=0;i<top;i++) ans+=dis(a[sta[i]],a[sta[i+1]]); ans+=dis(a[sta[0]],a[sta[top]]); cout<<fixed<<setprecision(2)<<ans<<endl; }
(3)旋转卡壳的思想与实现

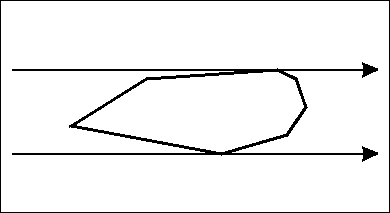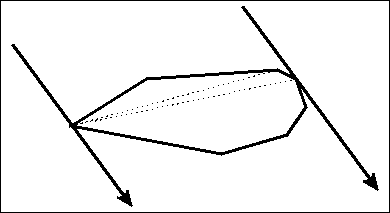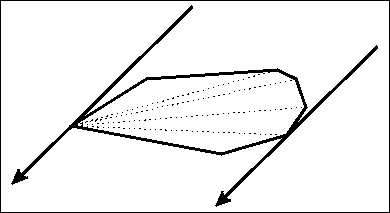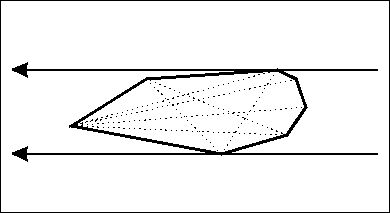
- 凸多边形的切线:一条直线与凸多边形有交点,并且整个凸多边形都在这条直线的一侧。
- 对踵点:过凸多边形上两点作一对平行线,使整个多边形都在这两条线之间,这两个点被称为一对对踵点。
- 凸多边形的直径:即凸多边形上任意两个点之间距离的最大值。直径一定会在对踵点中产生。
Q:为什么直径一定会在对踵点中产生?
如果两个点不是对踵点,那么两个点中一定可以让一个点向另一个点的对踵点方向移动使得距离更大。
点与点之间的距离可以体现为线与线之间的距离,在非对踵点之间构造平行线,一定没有在对踵点构造平行线优。
通常求出每一条边的对踵点。边的对踵点同时是这两个点的对踵点,因此并没有遗漏。
同时,通过边来求,可以很好地运用向量叉积的计算,方便计算,减小误差。

对于最下面这条边来说,对于上面四个顶点,他们分别与这条边构成了四个同底不同高的三角形;
而三角形面积可以用叉积算出来,三角形的面积此时也就反映了点到直线的距离了。
由于面积是单峰的,那么对单独一条边的对踵点,我们可以用三分来求;
对于所有边,我们可以用 two-pointer(双指针)求出。因为对踵点随着枚举边在同旋转方向上移动。
【补充】关于三角形面积
【旋转卡壳求凸多边形直径】

- 代码相关注意事项:双指针的01起点的细节处理、叉乘顺序及符号......
即,如果cross(计算叉积)函数这样写:
long long cross(Point p0,Point p1,Point p2) //计算向量叉积 { return (ll)(p1.x-p0.x)*(p2.y-p0.y)-(ll)(p1.y-p0.y)*(p2.x-p0.x); }
那么,双指针判断程序就要这样写:
while(cross(a[sta[i]],a[sta[j]],a[sta[i+1]]) >cross(a[sta[i]],a[sta[j+1]],a[sta[i+1]])) j=(j+1)%top;
那么,Getmax(旋转卡壳)函数总体整理为:
long long GetMax(){ //旋转卡壳求凸多边形的直径 long long maxx=0; //双指针 + 叉乘比较(面积) if(top==1) return dis(a[sta[0]],a[sta[1]]); //仅有两个点 sta[++top]=sta[0]; int j=2; //把第一个点放到最后 for(int i=0;i<top;i++){ //枚举边 while(cross(a[sta[i]],a[sta[j]],a[sta[i+1]]) >cross(a[sta[i]],a[sta[j+1]],a[sta[i+1]])) j=(j+1)%top; maxx=max(maxx,max(dis(a[sta[i]],a[sta[j]]),dis(a[sta[i+1]],a[sta[j]]))); } return maxx; //凸多边形的直径 }

#include <cmath> #include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <string> #include <cstring> #include <vector> #include <algorithm> #include <stack> #include <queue> #include <iomanip> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; typedef unsigned long long ull; /*【p1452】Beauty Contest 求平面n(≤50000)个点的最远点对。*/ //注意:longlong的运用、01起点的细节处理、叉乘顺序及符号、双指针求旋转卡壳 struct Point{ //坐标结构体 long long x,y; Point() { } //坐标转化为()形式表示 Point(long long __x, long long __y) : x(__x), y(__y) { } inline Point operator + (const Point &rhs) const { return Point(x+rhs.x,y+rhs.y); } inline Point operator - (const Point &rhs) const { return Point(x-rhs.x,y-rhs.y); } }a[50019]; int sta[50019],top,n; long long cross(Point p0,Point p1,Point p2) //计算向量叉积 { return (ll)(p1.x-p0.x)*(p2.y-p0.y)-(ll)(p1.y-p0.y)*(p2.x-p0.x); } long long dis(Point p1,Point p2) //计算点p1p2的距离 { return (ll)(p2.x-p1.x)*(p2.x-p1.x)+(ll)(p2.y-p1.y)*(p2.y-p1.y); } bool cmp(Point p1,Point p2){ //进行极角排序 long long tmp=cross(a[0],p1,p2); if(tmp>0) return true; else if(tmp==0&&dis(a[0],p1)<dis(a[0],p2)) return true; else return false; } //↑↑若角度相同,则距离小的在前面 void init(){ //把最左下方的点放在a[0],进行极角排序。 Point p0; p0.x=a[0].x; p0.y=a[0].y; int k=0; for(int i=1;i<n;i++){ if( (p0.y>a[i].y) || ((p0.y==a[i].y)&&(p0.x>a[i].x)) ) p0.x=a[i].x,p0.y=a[i].y,k=i; //寻找左下角的点 } a[k]=a[0],a[0]=p0; //把原来0位置的点放到k位置(互换位置) sort(a+1,a+n,cmp); } //除去0号点,其余n-1个点进行极角排序 void graham(){ //极角排序法求凸包 if(n==1) top=0,sta[0]=0; if(n==2) top=1,sta[0]=0,sta[1]=1; if(n>2){ top=1,sta[0]=0,sta[1]=1; for(int i=2;i<n;i++){ while(top>0&&cross(a[sta[top-1]],a[sta[top]],a[i])<=0) top--; top++; sta[top]=i; } //每加入新的点,判断要出栈的凹点,并将新点入栈 } //for(int i=0;i<=top;i++) cout<<a[sta[i]].x<<" "<<a[sta[i]].y<<endl; } long long GetMax(){ //旋转卡壳求凸多边形的直径 long long maxx=0; //双指针 + 叉乘比较(面积) if(top==1) return dis(a[sta[0]],a[sta[1]]); //仅有两个点 sta[++top]=sta[0]; int j=2; //把第一个点放到最后 for(int i=0;i<top;i++){ //枚举边 while(cross(a[sta[i]],a[sta[j]],a[sta[i+1]]) >cross(a[sta[i]],a[sta[j+1]],a[sta[i+1]])) j=(j+1)%top; maxx=max(maxx,max(dis(a[sta[i]],a[sta[j]]),dis(a[sta[i+1]],a[sta[j]]))); } return maxx; //凸多边形的直径 } int main(){ cin>>n; for(int i=0;i<n;i++) cin>>a[i].x>>a[i].y; init(),graham(); cout<<(ll)GetMax()<<endl; }

#include <cmath> #include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <string> #include <cstring> #include <vector> #include <algorithm> #include <stack> #include <queue> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; typedef unsigned long long ull; /*【p4166】最大土地面积 平面有N个点,选择其中的任意四个点,满足围成的多边形面积最大。*/ //四边形的四个顶点一定在凸包上,在凸包上枚举对角线,旋转卡壳+向量求△面积。 const double PI=acos(-1.0); struct Point{ int x,y; friend Point operator + (Point a,Point b) { Point t; t.x=a.x+b.x;t.y=a.y+b.y; return t; } friend Point operator - (Point a,Point b) { Point t; t.x=a.x-b.x;t.y=a.y-b.y; return t; } friend int operator ^ (Point a,Point b) { return a.x*b.y-a.y*b.x; } friend int operator * (Point a,Point b) { return a.x*b.x+a.y*b.y; } }a[500019],sta[500019]; int top; int cross(Point p0,Point p1,Point p2) //计算向量叉积 { return (p1.x-p0.x)*(p2.y-p0.y)-(p1.y-p0.y)*(p2.x-p0.x); } double dis(Point p1,Point p2) //计算点p1p2的距离 { return sqrt((double)(p2.x-p1.x)*(p2.x-p1.x)+(p2.y-p1.y)*(p2.y-p1.y)); } bool cmp(Point p1,Point p2){ //进行极角排序 int tmp=cross(a[1],p1,p2); if(tmp>0) return true; else if(tmp==0&&dis(a[1],p1)<dis(a[1],p2)) return true; else return false; //↑↑若角度相同,则距离小的在前面 } void init(int n){ //输入,并把最左下方的点放在a[1],进行极角排序。 Point p0; scanf("%d%d",&a[1].x,&a[1].y); p0.x=a[1].x; p0.y=a[1].y; int k=0; for(int i=2;i<=n;i++){ scanf("%d%d",&a[i].x,&a[i].y); if( (p0.y>a[i].y) || ((p0.y==a[i].y)&&(p0.x>a[i].x)) ) p0.x=a[i].x,p0.y=a[i].y,k=i; //寻找左下角的点 } a[k]=a[1],a[1]=p0; //把原来0位置的点放到k位置(互换位置) sort(a+2,a+n+1,cmp); //除去0号点,其余n-1个点进行极角排序 } void graham(int n){ //极角排序法求凸包 if(n==1) top=1,sta[1]=a[1]; if(n==2) top=2,sta[1]=a[1],sta[2]=a[2]; if(n>2){ top=2,sta[1]=a[1],sta[2]=a[2]; for(int i=3;i<=n;i++){ while(top>=2&&cross(sta[top-1],sta[top],a[i])<=0) top--; sta[++top]=a[i]; } //每加入新的点,判断要出栈的凹点,并将新点入栈 } } double Rotating_caliper(){ double ans=0; sta[top+1]=a[1]; //先复制一个到末尾 for(int i=1;i<=top;i++){ int a=i%top+1,b=(i+2)%top+1; //两个指针(四边形的另外两个点) for(int j=i+2;j<=top;j++){ //枚举对角线,旋转卡壳找最大三角形面积 while(a%top+1!=j&&(((sta[a]-sta[i])^(sta[j]-sta[i]))) <(((sta[a+1]-sta[i])^(sta[j]-sta[i])))) (a%=top)+=1; while(b%top+1!=j&&(((sta[j]-sta[i])^(sta[b]-sta[i]))) <(((sta[j]-sta[i])^(sta[b+1]-sta[i])))) (b%=top)+=1; //i、j是四边形对角线,a、b是上下的两个点,找到使三角形面积max的a、b ans=max(ans,fabs(((sta[a]-sta[i])^(sta[j]-sta[i])) +((sta[j]-sta[i])^(sta[b]-sta[i])))); } //面积 } return ans; //最大四边形面积 } int main(){ int n; scanf("%d",&n); init(n),graham(n); //输入点+求凸包 printf("%.3lf ",Rotating_caliper()/2); return 0; }

#include <iostream> #include <string.h> #include <algorithm> #include <stdio.h> #include <math.h> using namespace std; const int N=50000; const double eps=1e-9; const double INF=1e99; struct Point { double x,y; }; Point P[N],Q[N]; double cross(Point A,Point B,Point C) { return (B.x-A.x)*(C.y-A.y)-(B.y-A.y)*(C.x-A.x); } double dist(Point A,Point B) { return sqrt((A.x-B.x)*(A.x-B.x)+(A.y-B.y)*(A.y-B.y)); } double multi(Point A,Point B,Point C) { return (B.x-A.x)*(C.x-A.x)+(B.y-A.y)*(C.y-A.y); } //顺时针排序 void anticlockwise(Point p[],int n) { for(int i=0;i<n-2;i++) { double tmp=cross(p[i],p[i+1],p[i+2]); if(tmp>eps) return; else if(tmp<-eps) { reverse(p,p+n); return; } } } //计算C点到直线AB的最短距离 double Getdist(Point A,Point B,Point C) { if(dist(A,B)<eps) return dist(B,C); if(multi(A,B,C)<-eps) return dist(A,C); if(multi(B,A,C)<-eps) return dist(B,C); return fabs(cross(A,B,C)/dist(A,B)); } //求一条直线的两端点到另外一条直线的距离,反过来一样,共4种情况 double MinDist(Point A,Point B,Point C,Point D) { return min(min(Getdist(A,B,C),Getdist(A,B,D)),min(Getdist(C,D,A),Getdist(C,D,B))); } double Solve(Point P[],Point Q[],int n,int m) { int yminP=0,ymaxQ=0; for(int i=0;i<n;i++) if(P[i].y<P[yminP].y) yminP=i; for(int i=0;i<m;i++) if(Q[i].y>Q[ymaxQ].y) ymaxQ=i; P[n]=P[0]; Q[m]=Q[0]; double tmp,ans=INF; for(int i=0;i<n;i++) { while(tmp=cross(P[yminP+1],Q[ymaxQ+1],P[yminP])-cross(P[yminP+1],Q[ymaxQ],P[yminP])>eps) ymaxQ=(ymaxQ+1)%m; if(tmp<-eps) ans=min(ans,Getdist(P[yminP],P[yminP+1],Q[ymaxQ])); else ans=min(ans,MinDist(P[yminP],P[yminP+1],Q[ymaxQ],Q[ymaxQ+1])); yminP=(yminP+1)%n; } return ans; } int main() { int n,m; while(cin>>n>>m) { if(n==0&&m==0) break; for(int i=0;i<n;i++) cin>>P[i].x>>P[i].y; for(int i=0;i<m;i++) cin>>Q[i].x>>Q[i].y; anticlockwise(P,n); anticlockwise(Q,m); printf("%.5lf ",min(Solve(P,Q,n,m),Solve(Q,P,m,n))); } return 0; }

#include <cmath> #include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <string> #include <cstring> #include <vector> #include <algorithm> #include <stack> #include <queue> #include <iomanip> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; typedef unsigned long long ull; /*【p3187】最小矩形面积 给定一些点的坐标,求能够覆盖所有点的最小面积的矩形。*/ //矩形的一条边一定在凸包上。枚举此边,用旋转卡壳计算离这条边最远、最左、最右的三个点。 //求最上点,即旋转卡壳求最远距离,用叉积求面积;求最右(左)点,用点积。 //对于当前直线AB和旋转到的点Ci,如果AB*CiCi+1>0,就接着往下旋转。 #define eps 1e-8 struct Point{ //坐标结构体 double x,y; Point() { } //坐标转化为()形式表示 Point(double __x, double __y) : x(__x), y(__y) { } friend bool operator<(Point a,Point b) { return fabs(a.y-b.y)<eps?a.x<b.x:a.y<b.y; } friend double operator *(Point a,Point b) { return a.x*b.y-a.y*b.x; } friend Point operator *(Point a,double b) { return Point(a.x*b,a.y*b); } friend double operator /(Point a,Point b) { return a.x*b.x+a.y*b.y; } friend double dis(Point a) { return sqrt(a.x*a.x+a.y*a.y); } inline Point operator + (const Point &rhs) const { return Point(x+rhs.x,y+rhs.y); } inline Point operator - (const Point &rhs) const { return Point(x-rhs.x,y-rhs.y); } }a[50019],sta[50019],t[5]; int top,n; double ans=1e60; double cross(Point p0,Point p1,Point p2) //计算向量叉积 { return (p1.x-p0.x)*(p2.y-p0.y)-(p1.y-p0.y)*(p2.x-p0.x); } bool cmp(Point p1,Point p2){ double k=(p1-a[0])*(p2-a[0]); if(fabs(k)<eps) return dis(a[0]-p1)-dis(a[0]-p2)<0; return k>0; } void init(){ //把最左下方的点放在a[0],进行极角排序。 Point p0; p0.x=a[0].x; p0.y=a[0].y; int k=0; for(int i=1;i<n;i++){ if( (p0.y>a[i].y) || ((p0.y==a[i].y)&&(p0.x>a[i].x)) ) p0.x=a[i].x,p0.y=a[i].y,k=i; //寻找左下角的点 } a[k]=a[0],a[0]=p0; //把原来0位置的点放到k位置(互换位置) sort(a+1,a+n,cmp); } //除去0号点,其余n-1个点进行极角排序 void graham(){ //极角排序法求凸包 if(n==1) top=0,sta[0]=a[0]; if(n==2) top=1,sta[0]=a[0],sta[1]=a[1]; if(n>2){ top=1,sta[0]=a[0],sta[1]=a[1]; for(int i=2;i<n;i++){ while(top>0&&cross(sta[top-1],sta[top],a[i])<=0) top--; top++; sta[top]=a[i]; } //每加入新的点,判断要出栈的凹点,并将新点入栈 } sta[++top]=sta[0]; } void solve(){ int l=1,r=1,p=1; double L,R,D,H; for(int i=0;i<top;i++){ D=dis(sta[i]-sta[i+1]); while((sta[i+1]-sta[i])*(sta[p+1]-sta[i]) -(sta[i+1]-sta[i])*(sta[p]-sta[i])>-eps) p=(p+1)%top; while((sta[i+1]-sta[i])/(sta[r+1]-sta[i]) -(sta[i+1]-sta[i])/(sta[r]-sta[i])>-eps) r=(r+1)%top; if(i==0) l=r; while((sta[i+1]-sta[i])/(sta[l+1]-sta[i]) -(sta[i+1]-sta[i])/(sta[l]-sta[i])<eps) l=(l+1)%top; L=(sta[i+1]-sta[i])/(sta[l]-sta[i])/D; R=(sta[i+1]-sta[i])/(sta[r]-sta[i])/D; H=(sta[i+1]-sta[i])*(sta[p]-sta[i])/D; if(H<0) H=-H; double tmp=(R-L)*H; if(tmp<ans){ ans=tmp; t[0]=sta[i]+(sta[i+1]-sta[i])*(R/D); t[1]=t[0]+(sta[r]-t[0])*(H/dis(t[0]-sta[r])); t[2]=t[1]-(t[0]-sta[i])*((R-L)/dis(sta[i]-t[0])); t[3]=t[2]-(t[1]-t[0]); } } } int main(){ cin>>n; for(int i=0;i<n;i++) cin>>a[i].x>>a[i].y; init(),graham(),solve(); printf("%.5lf ",ans); int fir=0; for(int i=1;i<=3;i++) if(t[i]<t[fir]) fir=i; for(int i=0;i<=3;i++) printf("%.5lf %.5lf ",fabs(t[(i+fir)%4].x)>1e-12? t[(i+fir)%4].x:0.00000,fabs(t[(i+fir)%4].y)>1e-12?t[(i+fir)%4].y:0.00000); }
——时间划过风的轨迹,那个少年,还在等你