后台写接口,由于要提供接口文档给前台使用,所有研究了一下swagger,看到网上有篇文章写得不错,就直接拿过来了。
swagger用于定义API文档。
好处:
- 前后端分离开发
- API文档非常明确
- 测试的时候不需要再使用URL输入浏览器的方式来访问Controller
- 传统的输入URL的测试方式对于post请求的传参比较麻烦(当然,可以使用postman这样的浏览器插件)
- spring-boot与swagger的集比较成简单
1、项目结构
和上一节一样,没有改变。
2、pom.xml
引入了两个jar。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
<dependency> <groupId>io.springfox</groupId> <artifactId>springfox-swagger2</artifactId> <version>2.2.2</version></dependency><dependency> <groupId>io.springfox</groupId> <artifactId>springfox-swagger-ui</artifactId> <version>2.2.2</version></dependency> |
3、Application.java
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
package com.xxx.firstboot;import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;import springfox.documentation.swagger2.annotations.EnableSwagger2;@SpringBootApplication //same as @Configuration+@EnableAutoConfiguration+@ComponentScan@EnableSwagger2 //启动swagger注解public class Application { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args); }} |
说明:
引入了一个注解@EnableSwagger24、UserController.java
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
|
package com.xxx.firstboot.web;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestHeader;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;import com.xxx.firstboot.domain.User;import com.xxx.firstboot.service.UserService;import io.swagger.annotations.Api;import io.swagger.annotations.ApiImplicitParam;import io.swagger.annotations.ApiImplicitParams;import io.swagger.annotations.ApiOperation;import io.swagger.annotations.ApiResponse;import io.swagger.annotations.ApiResponses;@RestController@RequestMapping("/user")@Api("userController相关api")public class UserController { @Autowired private UserService userService; // @Autowired// private MyRedisTemplate myRedisTemplate; @ApiOperation("获取用户信息") @ApiImplicitParams({ @ApiImplicitParam(paramType="header",name="username",dataType="String",required=true,value="用户的姓名",defaultValue="zhaojigang"), @ApiImplicitParam(paramType="query",name="password",dataType="String",required=true,value="用户的密码",defaultValue="wangna") }) @ApiResponses({ @ApiResponse(code=400,message="请求参数没填好"), @ApiResponse(code=404,message="请求路径没有或页面跳转路径不对") }) @RequestMapping(value="/getUser",method=RequestMethod.GET) public User getUser(@RequestHeader("username") String username, @RequestParam("password") String password) { return userService.getUser(username,password); } // @RequestMapping("/testJedisCluster")// public User testJedisCluster(@RequestParam("username") String username){// String value = myRedisTemplate.get(MyConstants.USER_FORWARD_CACHE_PREFIX, username);// if(StringUtils.isBlank(value)){// myRedisTemplate.set(MyConstants.USER_FORWARD_CACHE_PREFIX, username, JSON.toJSONString(getUser()));// return null;// }// return JSON.parseObject(value, User.class);// } } |
说明:
- @Api:用在类上,说明该类的作用
- @ApiOperation:用在方法上,说明方法的作用
- @ApiImplicitParams:用在方法上包含一组参数说明
- @ApiImplicitParam:用在@ApiImplicitParams注解中,指定一个请求参数的各个方面
- paramType:参数放在哪个地方
- header-->请求参数的获取:@RequestHeader
- query-->请求参数的获取:@RequestParam
- path(用于restful接口)-->请求参数的获取:@PathVariable
- body(不常用)
- form(不常用)
- name:参数名
- dataType:参数类型
- required:参数是否必须传
- value:参数的意思
- defaultValue:参数的默认值
- paramType:参数放在哪个地方
- @ApiResponses:用于表示一组响应
- @ApiResponse:用在@ApiResponses中,一般用于表达一个错误的响应信息
- code:数字,例如400
- message:信息,例如"请求参数没填好"
- response:抛出异常的类
- @ApiModel:描述一个Model的信息(这种一般用在post创建的时候,使用@RequestBody这样的场景,请求参数无法使用@ApiImplicitParam注解进行描述的时候)
- @ApiModelProperty:描述一个model的属性
以上这些就是最常用的几个注解了。
需要注意的是:
- ApiImplicitParam这个注解不只是注解,还会影响运行期的程序,例子如下:

如果ApiImplicitParam中的phone的paramType是query的话,是无法注入到rest路径中的,而且如果是path的话,是不需要配置ApiImplicitParam的,即使配置了,其中的value="手机号"也不会在swagger-ui展示出来。
具体其他的注解,查看:
https://github.com/swagger-api/swagger-core/wiki/Annotations#apimodel
测试:
启动服务,浏览器输入"http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui.html"
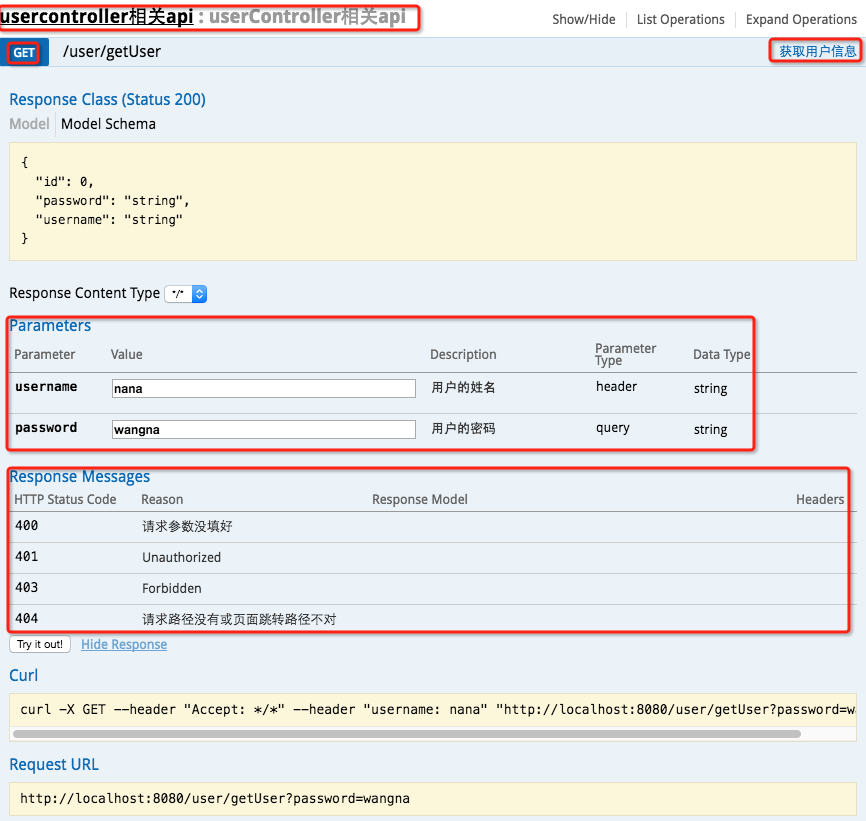
最上边一个红框:@Api
GET红框:method=RequestMethod.GET
右边红框:@ApiOperation
parameter红框:@ApiImplicitParams系列注解
response messages红框:@ApiResponses系列注解
输入参数后,点击"try it out!",查看响应内容:
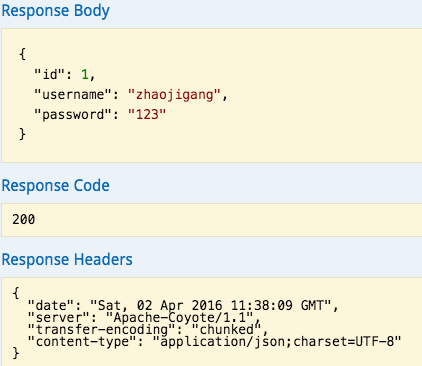
转载----https://www.cnblogs.com/gavin-liu/p/6491545.html