0.编写一个程序,统计当前目录下每个文件类型的文件数,程序实现如图:

代码实现:
1 import os 2 # 使用os.curdir表示当前目录更标准 3 all_files = os.listdir(os.curdir) 4 type_dict = dict() 5 6 for each_file in all_files: 7 if os.path.isdir(each_file): 8 # get()返回指定键的值,如果值不在字典中返回default值. 9 # setdefault()和get()类似, 但如果键不存在于字典中,将会添加键并将值设为default 10 type_dict.setdefault('文件夹',0) 11 type_dict['文件夹'] += 1 12 else: 13 ext = os.path.splitext(each_file)[1] 14 type_dict.setdefault(ext,0) 15 type_dict[ext] += 1 16 17 for each_type in type_dict.keys(): 18 print("该文件夹下共有类型为【%s】的文件%d个" % (each_type,type_dict[each_type]))
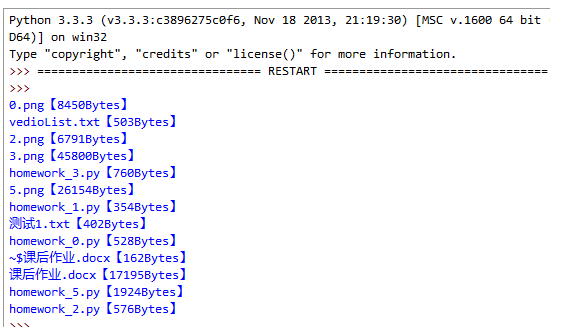
1.编写一个程序,计算当前文件夹下所有文件的大小,程序实现如图:
实现代码:
1 import os 2 all_files = os.listdir(os.curdir) 3 file_dict = dict() 4 5 for each_file in all_files: 6 if os.path.isfile(each_file): 7 file_size = os.path.getsize(each_file) 8 file_dict[each_file] = file_size 9 for each in file_dict.items(): 10 print('%s 【%dBytes】' % (each[0],each[1]))
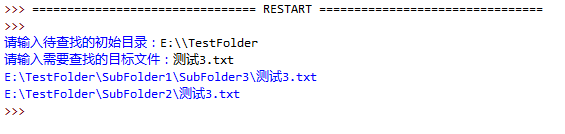
2.编写一个程序,用户输入文件名以及开始搜索的路径,搜索该文件是否存在。如遇到文件夹,则进入文件夹继续搜索,程序实现如图:
实现代码:
1 import os 2 def search_file(file_mulu,aim_file): 3 # 改变目录 4 os.chdir(file_mulu) 5 for each_file in os.listdir(os.curdir): 6 if each_file == aim_file: 7 # 使用OS表达路径更准确# os.getcwd()返回当前目录# os.sep按照系统输出相应的分隔符 8 print(os.getcwd() + os.sep + each_file) 9 if os.path.isdir(each_file): 10 # 递归调用 11 search_file(each_file,aim_file) 12 # 递归调用后返回上一层目录 13 os.chdir(os.pardir) 14 file_mulu = input("请输入待查找的初始目录:") 15 aim_file = input("请输入需要查找的目标文件:") 16 search_file(file_mulu,aim_file)
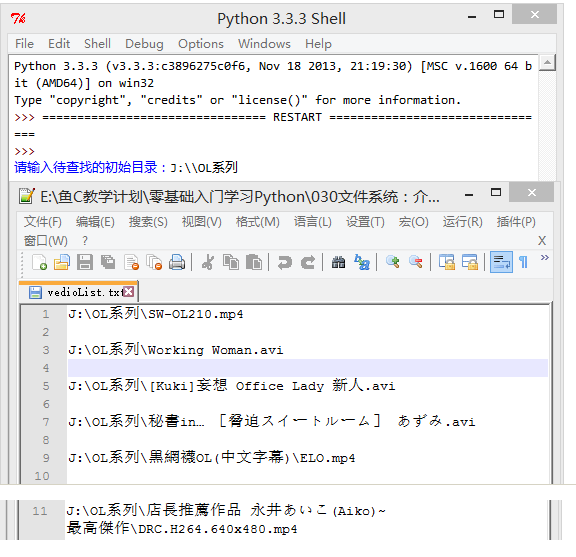
3.编写一个程序,用户输入开始搜索的路径,查找该路径下(包含子文件夹内)所有的视频格式文件(要求查找MP4,RMVB,AVI的格式即可),并把创建一个文件(vedioList.txt)存放所有找到的文件的路径,程序实现如图:
实现代码:
1 import os 2 3 def search_file(file_mulu,file_aim): 4 # 更改工作路径 5 os.chdir(file_mulu) 6 # os.listdir(os.curdir) 列举指定文件的文件名 7 for each_file in os.listdir(os.curdir): 8 # 分离文件名与扩展名,返回(f_name, f_extension)元组从0开始 9 ext = os.path.splitext(each_file)[1] 10 if ext in file_aim: 11 vedio_list.append(os.getcwd()+os.sep+each_file+os.linesep) 12 # os.path.isdir()判断指定路径是否存在且是一个目录 13 if os.path.isdir(each_file): 14 search_file(each_file,file_aim) 15 os.chdir(os.pardir) 16 file_mulu = input("请输入待查找的初始目录:") 17 program_dir = os.getcwd() 18 vedio_list = [] 19 file_aim = ['.mp4','.avi','.rmvb'] 20 21 search_file(file_mulu,file_aim) 22 23 f = open(program_dir + os.sep + 'vedioList.txt',"w") 24 f.writelines(vedio_list) 25 f.close()
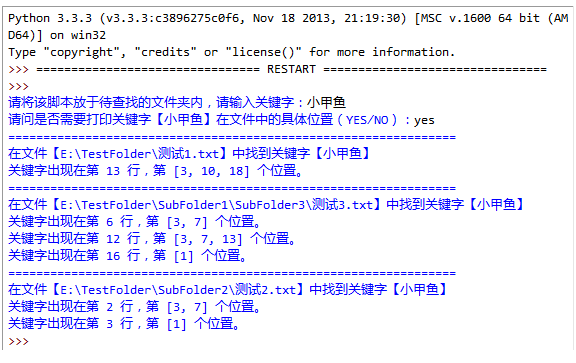
4.编写一个程序,用户输入关键字,查找当前文件夹内(如果当前文件夹内包含文件夹,则进入文件夹继续搜索)所有含有该关键字的文本文件(.txt后缀),要求显示该文件所在的位置以及关键字在文件中的具体位置(第几行第几个字符),程序实现如图:
实现代码:
1 # 没看懂~ 2 import os 3 def print_pos(key_dict): 4 keys = key_dict.keys() 5 # 由于字典是无序的,我们这里对行数进行排序 6 keys = sorted(keys) 7 for each_key in keys: 8 print('关键字出现在第%s行,第%s个位置。' % (each_key , str(key_dict[each_key]))) 9 10 def pos_in_line(line,key): 11 pos = [] 12 begin = line.find(key) 13 while begin != -1: 14 # 在用户角度是从1 开始 15 pos.append(begin+1) 16 # 从下一个位置继续查找 17 begin = line.find(key,begin +1) 18 return pos 19 20 def search_in_file(file_name,key): 21 f = open(file_name) 22 # 记录行数 23 count = 0 24 # 字典,用户存放key所在具体行数对应具体位置 25 key_dict = dict() 26 27 for each_line in f: 28 count +=1 29 if key in each_line: 30 31 pos = pos_in_line(each_line,key) 32 key_dict[count] = pos 33 f.close() 34 return key_dict 35 36 def search_files(key,detail): 37 all_files = os.walk(os.getcwd()) 38 txt_files = [] 39 for i in all_files: 40 for each_file in i[2]: 41 # 根据后缀判断是不是文本文件 42 if os.path.splitext(each_file)[1] == ".txt": 43 each_file = os.path.join(i[0],each_file) 44 txt_files.append(each_file) 45 for each_txt_file in txt_files: 46 key_dict = search_in_file(each_txt_file,key) 47 if key_dict: 48 print("======================================") 49 print("在文件【%s】中找到关键字【%s】" % (each_txt_file.key)) 50 if detail in ['Yes',"YES","yes"]: 51 print_pos(key_dict) 52 key = input("请将该脚本放于待查找的文件夹内,请输入关键字:") 53 detail = input("请问是否需要打印关键字【%s】在文件中的额具体位置(YES/No):" %key) 54 search_files(key,detail)