1. 常用方法
| static void yield() | 当前线程让出处理器(离开Running状态),使当前线程进入Runnable状态等待 |
| static void sleep(times) |
使当前线程从Running放弃处理器进入Block状态,休眠times毫秒,再返回到Runnable。 如果其他线程打断当前线程的Block(sleep),就会发生InterruptedException。 |
| int getPriority() | 获取线程的优先级 |
| void setPriority(int newPriority) |
修改线程的优先级 优先级越高的线程,不一定先执行,但该线程获取到时间片的机会,会更多一些 |
| void join() | 等待该线程终止 |
| void join(long millis) | 等待参数指定的毫秒数 |
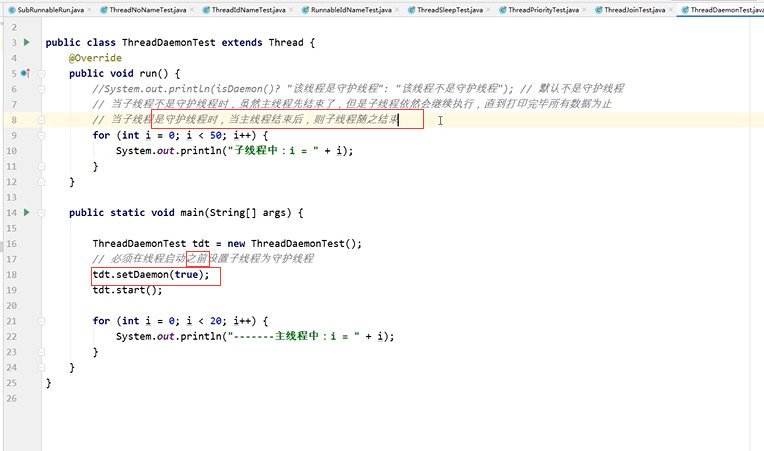
| boolean isDaemon() | 用于判断是否为守护线程 |
| void setDeamon(boolean on) | 用于设置线程为守护线程 |
2.代码实例
<1>ThreadSleepTest.java



<2> ThreadPriorityTest.java



<3> ThreadDaemonTest.java
3. 案例题目
编程创建两个线程,线程一:打印 1 - 100 之间的所有奇数,线程二: 打印 1 - 100 之间的所有偶数。
在main方法,启动上述两个线程,同时执行。主线程:等待两个线程终止。
方式一(实现继承的方式)
1 public class SubThread1 extends Thread { 2 @Override 3 public void run() { 4 // 打印1 ~ 100之间的所有奇数 5 for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i += 2) { 6 System.out.println("子线程一中: i = " + i); 7 } 8 } 9 } 10 11 12 13 public class SubThread2 extends Thread { 14 @Override 15 public void run() { 16 // 打印1 ~ 100之间的所有偶数 17 for (int i = 2; i <= 100; i += 2) { 18 System.out.println("------子线程二中: i = " + i); 19 } 20 } 21 } 22 23 24 public class SubThreadTest { 25 26 public static void main(String[] args) { 27 28 SubThread1 st1 = new SubThread1(); 29 SubThread2 st2 = new SubThread2(); 30 31 st1.start(); 32 st2.start(); 33 34 System.out.println("主线程开始等待..."); 35 try { 36 st1.join(); 37 st2.join(); 38 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 39 e.printStackTrace(); 40 } 41 System.out.println("主线程等待结束!"); 42 } 43 }
方式二(实现接口的方式)
1 class SubRunnable1 implements Runnable { 2 @Override 3 public void run(){ 4 // 打印1 ~ 100之间的所有奇数 5 for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i += 2) { 6 System.out.println("子线程一中: i = " + i); 7 } 8 } 9 } 10 11 class SubRunnable2 implements Runnable { 12 @Override 13 public void run() { 14 // 打印1 ~ 100之间的所有偶数 15 for (int i = 2; i <= 100; i += 2) { 16 System.out.println("------子线程二中: i = " + i); 17 } 18 } 19 } 20 21 class SubRunnableTest { 22 23 main(){ 24 SubRunnable1 sr1 = new SubRunnable1(); 25 SubRunnable2 sr2 = new SubRunnable2(); 26 27 Thread t1 = new Thread(sr1); 28 Thread t2 = new Thread(sr2); 29 30 t1.start(); 31 t2.start(); 32 33 print("主线程开始等待..."); 34 try{ 35 t1.join(); 36 t2.join(); 37 }catch (InterruptedException e) { 38 e.printStackTrace(); 39 } 40 print("主线程等待结束!"); 41 42 } 43 }